Chapter: Embedded Systems
Introduction to Embedded Systems
INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Definition
and Classification
An
embedded system is a system that has software embedded into computer-hardware, which
makes a system dedicated for an application (s)or specific part of an
application or product or part of a larger system.
An
embedded system is one that has dedicated purpose software embedded in computer
hardware.
It is a
dedicated computer based system for an application(s) or product. It maybe an
independent system or apart of large system. Its software usually embeds into a
ROM (Read Only Memory) or flash.
―It is
any device that includes a programmable computer but is not itself intended to
be a general purpose computer.‖ –Wayne Wolf, Ref: 61
―Systems
are the electronic systems that contain a microprocessor or a microcontroller,
but we do not think of them as computers– the computer is hidden or embedded
inthe system.‖ – Todd
D.
Morton,Ref: 38
Main Embedded System Components
1. Embeds
hardware to give computer like functionalities
2. Embeds
main application software generally into flash or ROM and the application
software performs concurrently the number of tasks.
3. Embeds a
real time operating system (RTOS), which supervises the application software
tasks running on the hardware and organizes the accesses to system resources
according to priorities and timing constraints of tasks in the system.
PROCESSOR IN EMBEDDED SYSTEM
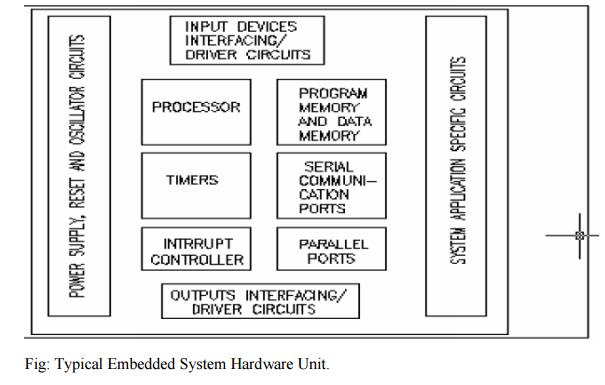
Fig:
Typical Embedded System Hardware Unit.
Program
Flow and data path Control Unit (CU) —includes a fetch unit for fetching
instructions from the memory
Execution
Unit (EU) —includes circuits for arithmetic and logical unit
(ALU),
and for instructions for a program control task, say, data transfer
instructions, halt, interrupt, or jump to another set of instructions or call
to another routine or sleep or reset
1a. General purpose microprocessor
For
example, Intel 80x86, Sparc, or Motorola 68HCxxx
1b. Embedded general purpose processor
Fast
context switching features, use of on-chip Compilers, for example, Intel®
XScale™
Applications
Personal Internet Client Architecture-based PDAs, cell phones and other
wireless devices,
2.Application Specific Instruction-Set Processor
(ASIP)
(a)Microcontroller
— Intel, Motorola, Hitachi, TI, Philips and ARM, for example, an Intel® MCS51,
Philips®51XA, 51MX, or Motorola — 68HC11, 68HC12, 68HC16
(b) DSP
or Typically a Texas Instruments- C28xSeries, C54xx or C64xx or Analog Devices
SHARC or Tiger SHARC, Motorola 5600xx
(c) Media
processor TI DSP TMS320DM310 or TrimediaPhillips Media Processor 1x00series for
Processing Streaming and Data Networks and Image, Video and Speech: PNX 1300,
PNX 1500(2002)
(d) IO
processor or
(e) Network
processor or
(f) A domain
specific processor
3. GPP or
ASIP core (s)
GPP or
ASIP integrated into either an Application Specific Integrated Circuit
(ASIC),
or a Very Large Scale Integrated Circuit
(VLSI) circuit or a FPGA core integrated with processor unit(s) in a VLSI
(ASIC) chip
4.
Application Specific System Processor (ASSP)
Typically
a set top box processor or mpeg video-processor or network application
processor or mobile application processor
5. Single purpose processor or Application Specific
Instruction processor
• Floating
point Coprocessor
• CCD Pixel
coprocessor and image codec in digital camera
• Graphic
processor
• Speech
processor
• Adaptive
filtering processor Encryption engine
• Decryption
engine
• Communication
protocol stack processor
• Java
accelerator Examples Java Accelerator Nazonin
Communications Java codes run 15 to60 Times fast, Video Accelerator for
fast Video Processing
6. Multi core processors or multiprocessor system
using GPPs
Examples
• Multiprocessor
system for Real time performance in a video-conference system,
• Embedded
firewall cum router, High-end cell phone.
Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems
(i) Power Source
1. System
own supply with separate supply rails for IOs, clock, basic processor and
memory and analog units
2. Supply
from a system to which the embedded system interfaces, for example in a network
card,
3. Charge
pump concept used in a system of little power needs, for examples, in the mouse
or contact-less smart card.
Power Dissipation Management
1. Clever
real-time programming by Wait and Stop instructions
2. Clever
reduction of the clock rate during specific set of instructions
3. Optimizing
the codes and
4. Clever
enabling and disabling of use of caches or cache blocks
(ii) Clock Oscillator Circuit and Clocking Units
1. Appropriate
clock oscillator circuit
2. Real Time
Clock( System Clock)and Timers driving hardware and software
(iii) Reset Circuit
1. Reset on
Power-up
2. External
and Internal Reset circuit
3. Reset on
Timeout of Watchdog timer
(iv)Memory
a. Functions Assigned to the ROM or EPROM or Flash
1. Storing
'Application' program from where the processor fetches the instruction codes
2. Storing
codes for system booting, initializing, Initial input data and Strings.
3. Storing
Codes for RTOS.
4. Storing
Pointers (addresses) of various service routines.
b. Functions Assigned to the Internal, External and Buffer
RAM
1. Storing
the variables during program run,
2. Storing
the stacks,
3. Storing
input or output buffers for example, for speech or image .
c. Functions Assigned to the EEPROM or Flash
Storing
non-volatile results of processing
d. Functions Assigned to the Caches
1. Storing
copies of the instructions, data and branch-transfer instructions in advance
from external memories
2. Storing
temporarily the results in write back caches during fast processing
(v) Interrupts Handler
Interrupt
Handling element for the external port interrupts, IO interrupts, timer and RTC
interrupts, software interrupts and Exceptions
(vi)Linking Embedded System Hardware
• Linking
and interfacing circuit for the Buses by using the appropriate multiplexers,
and decoders, demultiplexers Interface
the various system units
3. IO Communication Unit
a. Communication Driver(s):Network
Ethernet or serial driverto communicate with host embedded system Expansion Facility …
Serial Bus(es): For example, UART(512 kbaud/s),
1-wire CAN (33 kbps),
Industrial
I2C (100kbps), SM I2C Bus(100 kbps), SPI (100 kbps), Faulttolerant CAN (110
kbps), Serial Port(230 kbps), MicroWire (300 kbps), SCSI parallel (40 Mbps),
Fast SCSI
(8M to 80
Mbps) , Ultra SCSI-3 (8Mto 160 Mbps), FireWire/IEEE 1394(400 Mbps, 72 meter),
High SpeedUSB 2.0 (480 Mbps, 25 meter)
Parallel Bus(es): PCI,
PCI-X
b. Media IO Control Element
c. Keypad or Keyboard IO Interface
d. LCD Display System Interface
e. ADC – Single or Multi
channel
f. DAC
g. GPIB
Interface Element
h. Pulse
Dialling Element
i. Modem
j.
Bluetooth, 802.11, IrDA,
Software for Embedding in a System
ROM
image, Programming Languages and Program models
1. ROM
Image
• Final
stage software also called ROM image
(Just as
an image is a unique sequence and arrangement of pixels, embedded software is
also a unique placement and arrangement at each ROM address of bytes for instructions
and data.)
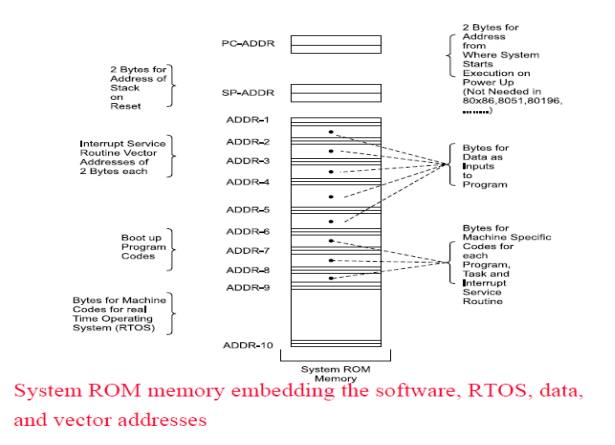
Final machine software
Ø Bytes at
each address defined for creating the ROM image.
Ø By
changing this image, the same hardware platform work differently and can be
used for entirely different applications or for new upgrades of the same
system.
Ø Distinct
ROM image in a distinctEmbedded System
_
Hardware elements between the distinct systems can be identical but itis the
software that makes
a system unique
and distinct from the other.
Ø Compressed
Codes and Data ROM image may alternatively becompressed software (for example,
the zip format) and data (for example, the pictures in jpg or gif format) along
with the software required for decompression algorithm
Programming Languages
1. Machine
Language Coding Programmer defines the addresses and the corresponding bytes or
bits at each address.
2. Used in
configuring some specific physical device or subsystem like transceiver, the
machine code- based coding is used
3. Assembly
Language Coding Needed for Invoking Processor
Specific
Instructions Requires understanding of the processor and instruction set.
A program
or a small specific partcoded in the assembly language using an Assembler
(software used for developing codes in assembly).
Three
steps when using assembly language
'
Assembler', 'Linker' and
'Locator'
before finally burned at the ROM
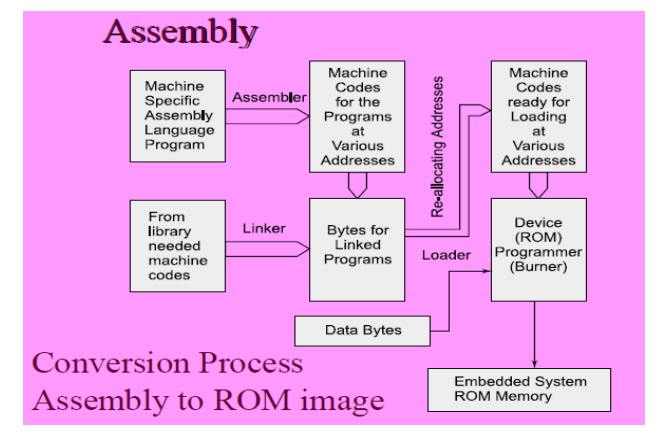
3.
Programming language C or C++ or Visual
C++ or Java
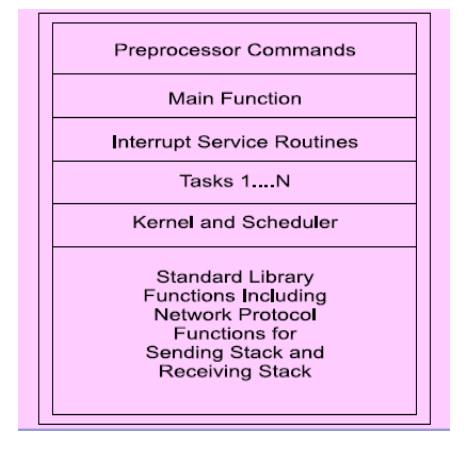
Application
Software - Different Program Layers
Program
various layers–
·
processor commands,
·
main function,
·
task functions and
·
library functions,
·
interrupt service routines
·
and kernel (scheduler), Compiler
·
Generates an object file. Using linker and locator,
the file for ROM image is created for the targeted hardware. C++ and Java are
other languages used for software coding.
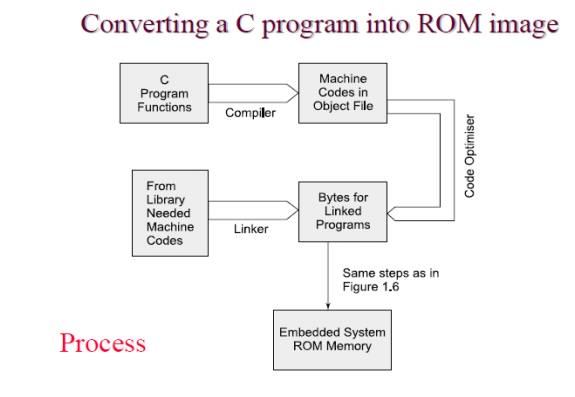
Program
Models
·
Sequential Programming Model
·
Object Oriented Programming Model
·
Control and Data flow graphs or
Synchronous
Data Flow (SDF) Graph or Multi Thread Graph (MTG) Model
·
Finite State Machine for data path
·
Multithreaded Model
·
Concurrent Processing of processes or thread or
tasks
Software for embedding in System- Part 2
Device
drivers, Device manager, OS, RTOS and Software tools
Devices
·
In an embedded system, there are number of physical devices.
·
Physical devices – keypad, LCD display or touch
screen, memory stick(flash memory), wireless networking device, parallel port
and network card In an embedded system, there are number of virtual devices.
o Virtual devices – pipe, file, RAM disk, socket,
A device driver is software for controlling
(configuring), receiving and sending a byte or a stream of bytes from or to a device.
A set of
generic functions, such as create ( ),open ( ), connect ( ), listen ( ), accept
( ), read ( ), write ( ), close ( ), delete ( ) for use by high level
programmers Each generic function calls a specific software (interrupt service
routine), which controls a device function or device input or output
Device
controls and functions by :
1. Calling
an ISR (also called Interrupt Handler Routine) on hardware or software
interrupt
2. Placing
appropriate bits at the control register or word.
3. Setting status
flag(s) in the status register for interrupting, therefore running (driving)
the ISR, Resetting the status flag after interrupt service.
Device
Manager for the devices and drivers
Device
Management software (usually a part of the OS) provide codes for detecting the
presence of devices, for initializing (configuring) these and for testing the
devices that are present.
Also
includes software for allocating and registering port(s) or device codes and
data at memory addresses for the various devices at distinctly different addresses,
including codes for detecting any collision between the allocated addresses, if
any
Multitasking using an operating
·
system (OS) and Real time operating system (RTOS),
Concurrent Processes, tasks or threads
·
A System is composed of twoor more concurrent
processes that execute Operating System
·
Multitasking (multiprocessing or multithreaded)
software Scheduling multiple tasks,
·
Processes, memory, device, ports, network, file
system, timers, event functions, inter processor communication, shared memory, security,
GUIs, ... management
Real Time
Operating System (RTOS)
Embedded
software is most often designed for deterministic performance and task and ISR
latencies in addition to the OS functions
Performing
multiple actions and controlling multiple devices and their ISRs with defined
real time constraints and with deadlines for these Task and ISRs priority
allocations, their preemptive scheduling, OS for providing deterministic
performance during concurrent processing and execution with hard(stringent) or
soft timing requirements with priority allocation and pre-emption. RTOS is
needed when the tasks for the system have real time constraints and deadlines
for finishing the tasks
Important RTOSes
·
OS μCOS-II
·
VxWorks
·
Windows CE
·
OSEK
·
Linux 2.6.24 or RTLinux
·
QNX
So
Development Toolsftware tools
1. Editor,
2. Interpreter,
3. Compiler,
4. Assembler
and Cross Assembler, IDE,
5. Prototyper
Application Software Development Tools
·
Source Code Engineering Tools
·
Stethoscope (tracks the switching from one task to
another as a function of time, stores beats)
·
Trace Scope (traces changes in aparameter(s) as a
function of time)
Simulator
A
Simulator used to simulate the target processor and hardware elements on a host
PC and to run and test the executable module.
Project Manager
To manage
the files that associates with a design stage project and keep several versions
of the source file(s) in an orderly fashion.
EXAMPLES OFEMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Examples
o Telecom
o Smart Cards,
o Missiles and Satellites,
o Computer Networking,
o Digital Consumer Electronics, and
o Automotive
Applications
o Mobile
phone o Digital
camera o Robots
o Point of sales terminals
o Automatic Chocolate Vending Machine
o Stepper
motor controllers for a robotics system o Washing or cooking system
o Multitasking Toys
o Microcontroller-
based single or multi-displaydigital panel meter for voltage, current,
resistance and frequency
o Keyboard
controller
o Serial
port cards
o CD drive or Hard Disk drive controller
o Peripheral
controllers,, a CRT display controller, a keyboard controller, a DRAM controller,
a DMA controller, a printer controller,
o a laser printer-controller, a LAN controller, a
disk drive controller
o Fax or
photocopy or printer or scanner Machine Remote (controller) of TV o Telephone with memory, display
and other sophisticated features
Motor
controls Systems - for examples, an accurate control of speed and position of
d.c. motor, robot, and CNC machine;, the automotive applications like such as a
close loop engine control, a dynamic ride control, and an anti-lock braking
system monitor
o Electronic data acquisition and supervisory
control system Spectrum analyzer
o Biomedical
systems - for example, an ECG LCD display-cum-recorder, a blood- cell recorder
cum analyzer and a patient monitor system service.
Electronic instruments, such as
industrial process controller
Electronic
smart weight display system, and an industrial moisture recorder cum
controller. Digital storage system for a signal wave form or Electric or Water
Meter Reading
Computer networking systems, - for examples,
router, front-end processor in a server, switch, bridge, hub, and gateway
For Internet appliances, there
are numerous application systems
(i)
Intelligent operation, administration and maintenance
outer (IOAMR) in a distributed network, and
(ii)
Mail Client card to store e-mail and personal
addresses and to smartly connect to a modem or server
Banking systems - for examples, Bank ATM and Credit
card transactions
Signal Tracking Systems - for
examples, an automatic signal tracker and a target tracker.
Communication systems, for
examples, such as for a mobile-communication a SIM card, a numeric pager, a cellular phone, a cable TV terminal, and a FAX
transceiver with or with out a graphic accelerator. Image Filtering, Image
Processing, Pattern Recognizer, Speech Processing and Video Processing.
Entertainment systems - such as
videogame, music system and Video Games
A system
that connects a pocket PC to the automobile driver mobile phone and a wireless
receiver. The system then connects to a remote server for Internet or e-mail or
to remote computer at an ASP (application Service Provider).A personal
information manager using frame buffers in hand- held devices.
Thin
Client to provide the disk-less nodes with the remote boot
capability.[Application of thin- clients is accesses to a data center from a
number of nodes; or in an Internet Laboratory accesses to the Internet leased
line through a remote Server]. Embedded Firewall / Router using
ARM7/multi-processor with two Ethernet interfaces and interfaces support to for
PPP, TCP/IP and UDP protocols.
Sophisticated Applications
·
Mobile Smart Phones and Computing systems
·
Mobile computer
·
Embedded systems for wireless LAN and convergent
technology devices
·
Embedded systems for Video, Interactive video,
broadband IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) Internet and other products, real time
video and speech or multimedia processing systems
·
Embedded Interface and Networking systems using
high speed (400 MHz plus), and ultra high speed (10 Gbps) and large bandwidth:
Routers, LANs, switches and gateways, SANs (Storage Area Networks), WANs (Wide
Area Networks),Security products and High-speed Network security, Gigabit rate
encryption rate products
SYSTEM-ON-CHIP (SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN
TECHNOLOGY
VLSI chip
·
Integration of high-level components
·
Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above
that of the counter, register, multiplier, floating point operation unit and
ALU.
System on chip (SoC) a new
design innovation
SoC is a
system on a VLSI chip that has all needed analog as well as digital circuits,
processors and software, for example, single-chip mobile phone.
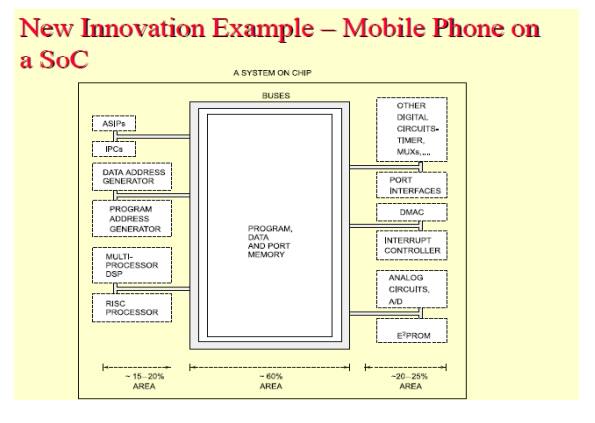
SYSTEM-ON-CHIP
Embeds:
• Multiple
processors,
• memories,
• multiple
standard source solutions (IP Cores),
• Logic and
analog units
Embedding
a Microprocessor
General
Purpose Processor (GPP)microprocessor can be embedded on a VSLI chip.
Embedding an ASIP
Processor
with instruction set designed for specific application on a VLSI chip for
example, microcontroller, DSP, IO, media, network or other domain specific
processor Embedding a Microcontroller core
·
68HC11xx,
·
HC12xx,
·
HC16xx8051,
·
80251 PIC 16F84 or
·
16C76, 16F876 and PIC18Microcontroller
·
Enhancements of ARM9/ARM7 ARM
·
Cortex M3 from Philips, Samsung and ST
Microelectronics
Embedding a DSP Core
·
TMS320Cxx, OMAP1Tiger SHARC 5600xx PNX 1300, 15002
·
DSP for mobile phones, for example, OMAP of Texas
Instruments use the effective power dissipation methods of dynamic switching
both of power supply voltage and operating frequency of the CPU core.
·
Filtering, noise cancellation, echo elimination,
compression and encryption
Embedding a Multi-processor or Dual Core using
General Purpose Processors (GPP)
·
Speech signal-compression and coding
·
Signal decoding and decompression
Embedding an Accelerator
Accelerate
the execution of codes, for example, a floating point coprocessor accelerates
the mathematical operations and Java accelerator accelerates the Java code
execution.
Embedding Single purpose processors
·
For Dialling, Modulating, Transmitting.
Demodulating and Receiving.
·
Keypad interface and display interface handling.
·
Touch screen
·
Message display and creation, SMS (Short Message
Service) and MMS
·
Protocol- stack generation.
·
Pixel coprocessor and CODEC in a digital Camera
SoC
·
Embedded processor GPP or ASIP core,
·
Single purpose processing cores or multiple
processor cores,
·
A network bus protocol core,
·
An encryption and decryption functions cores,
·
Cores for FFT and Discrete cosine transforms for
signal processing applications,
·
Memories
Multiple standard source solutions, called IP
(Intellectual Property)cores,
·
Programmable logic device and FPGA (Field
Programmable Gate Array) cores
·
Other logic and analog units.
IPs in SoC
·
IP –a standard source solution for synthesizing a
higher-level component by configuring a core of VLSI circuit or FPGA core
available as an Intellectual Property, called (IP).
·
High Level Components with gate level sophistication
circuit much above level of counters and registers.
IPs
·
Designer or designing company holds the copyright
for the synthesized design of a higher-level component for gate-level
implementation of an IP.
·
One
might have to
pay royalty for every
chip shipped. An
embedded system may
incorporate
several IPs.
An IP may
provide a design for adaptive filtering of a signal.
·
full design for implementing Hypertext Transfer
Protocol (HTTP) or File Transfer Protocol (FTP) to transmit a web page or file
on Internet.
·
USB port controller, Bluetooth, GPS interface,
Wireless 802.11or 802.16interfaces
·
An FPGA consists of a large number of programmable
gates on a VLSI chip. There is a set of gates in each FPGA cell, called 'macro
cell'.
·
Embedded system designed with a view of offering
enhancing functionalities in future, then FPGA core can be used in the
circuits. Each cell has several inputs and outputs. All cells interconnect like
an array (matrix).Each interconnection is programmable through the associated
memory RAM in a FPGA programming tool.
·
A concept is using FPGA (Field Programmable Gate
Arrays) core along with single or multiple processors.
Use of
Xilinx Spartan-3 90 nm based FPGAs with Power PCs(2003 ) Use of FPGAs cum
Processor Cores
· FPGA 125136 Logic Cells along
with the Four IBM PowerPC processors[Exemplary Application: System with a Data
Encryption Engine at 1.5 Gbps]
FPGA
·
An SIMD instruction, Fourier transform and its
inverse, DFT or Laplace transform andits inverse, compression or decompression,
encrypting or deciphering, a specific pattern-recognition (for recognizing a signature
or finger print or DNA sequence).
·
Configure an algorithm into the logic gates of the
FPGA.
Related Topics