Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Wire and Cable
Wire and Cable
The medium is the actual path for the
electromagnetic energy of the link or channel of the communication system.
Through the medium, the energy representing the data of the sender can reach
the receiver. This path can take many forms : an electrical conductor such as
wire, vacuum or optical fiber.
Copper is an inexpensive metal that is easily
made into wire, Fortunately, it is also an excellent conductor of electricity.
When separate wires are collected into bundles and are given special protective
jacketing, the term 'cable' is often used.
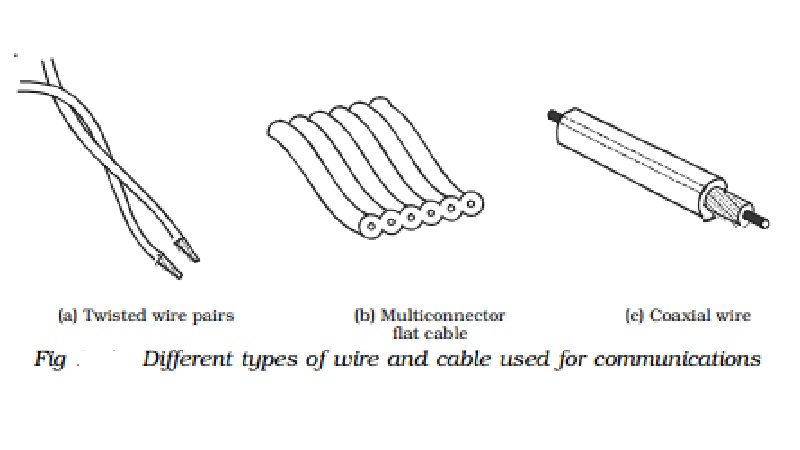
The main types of wire and cable used in data
communications are (a) Twisted pair (b) Multiconductor flat cable and (c)
Coaxial cable and are represented in Fig
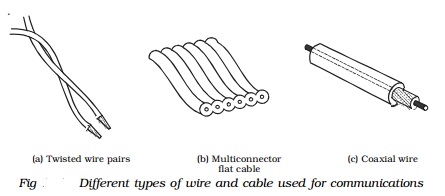
Twisted pair cable is the simplest and lowest
cost cable. It consists of two insulated wire twisted around each other in a
continuous spiral as shown in Fig a. The wire is twisted to minimise the
external noise. Twisted pair is used between telephones and the central office.
It is difficult to use, when many signals must be brought from one place to
another.
The multiconductor flat cable consists of many
parallel wires in a common plastic jacket as shown in Fig. b. A cable of
this type can have any number from 10 to about 50 wires. All the wires are
grouped mechanically and they can be used with a single connector at each end.
Flat cable is more expensive than twisted pair.
For some applications, coaxial cable (coax)
must be used. It consists of a solid-centre conductor surrounded by a plastic
insulator such as teflon. Over the insulator, is a second conductor, a tubular
braid or shield made of fine wires. An outer plastic insulation protects and
insulates the braid. It is fairly expensive to buy and can be difficult to
install, because of its mechanical stiffness and thickness.
Related Topics