Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Types of oscillations
Types of oscillations
There are three
main types of oscillations.
(i)Free oscillations
When a body
vibrates with its own natural frequency, it is said to execute free
oscillations. The frequency of oscillations depends on the inertial factor and
spring factor, which is given by,
n=1/2π root(k/m)
Examples
(i)
(I)
Vibrations of tuning fork
(ii)
(ii) Vibrations in a stretched string
(iii)
(iii)
Oscillations of simple pendulum
(iv)
(iv)
Air blown gently across the mouth of a bottle.
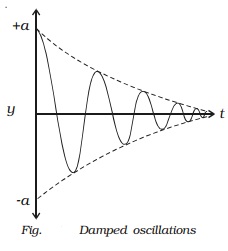
ii. Damped oscillations
Most of the
oscillations in air or in any medium are damped. When an oscillation occurs,
some kind of damping force may arise due to friction or air resistance offered
by the medium. So, a part of the energy is dissipated in overcoming the
resistive force. Consequently, the amplitude of oscillation decreases with time
and finally becomes zero. Such oscillations are called damped oscillations
(Fig.).
Examples :
i)
The
oscillations of a pendulum
ii)
Electromagnetic
damping in galvanometer (oscillations of a coil in galvanometer)
iii)
Electromagnetic
oscillations in tank circuit
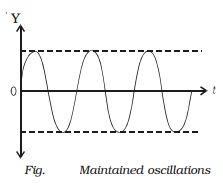
(iii ) Maintained oscillations
The amplitude of
an oscillating system can be made constant by feeding some energy to the
system. If an energy is fed to the system to compensate the energy it has lost,
the amplitude will be a constant. Such oscillations are called maintained
oscillations (Fig.).
Example :
A swing to which
energy is fed continuously to maintain amplitude of oscillation.
(iv ) Forced oscillations
When a vibrating body is maintained in the
state of vibration by a periodic force of frequency (n) other than its natural
frequency of the body, the vibrations are called forced vibrations. The
external force is driver and body is driven.
The body is
forced to vibrate with an external periodic force. The amplitude of forced
vibration is determined by the difference between the frequencies of the driver
and the driven. The larger the frequency difference, smaller will be the
amplitude of the forced oscillations.
Examples :
(i)
Sound
boards of stringed instruments execute forced vibration,
(ii)
Press
the stem of vibrating tuning fork, against tabla. The tabla suffers forced
vibration.
(v ) Resonance
In the case of
forced vibration, if the frequency difference is small,
the amplitude will be large (Fig.). Ultimately
when the two frequencies are same, amplitude becomes maximum.This is a special case of forced vibration..
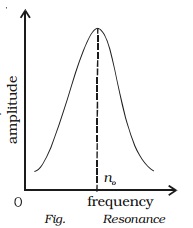
If
the frequency of the external periodic force is equal to the natural frequency
of oscillation of the system, then the amplitude of oscillation will be large
and this is known as resonanc.
Advantages
(i)
Using resonance,
frequency of a given tuning fork is determined with a sonometer.
(ii)
In radio and
television, using tank circuit, required frequency can be obtained.
Disadvantages
(i) Resonance can cause disaster in an earthquake,
if the natural frequency of the building matches the frequency of the periodic
oscillations present in the Earth. The building begins to oscillate with large
amplitude thus leading to a collapse.
(ii)
A singer maintaining a
note at a resonant frequency of a glass, can cause it to shatter into pieces
Related Topics