Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Reflection of light
Reflection of light
Highly polished metal
surfaces reflect about 80% to 90% of the light incident on them. Mirrors in
everyday use are therefore usually made of depositing silver on the backside of
the glass. The largest reflector in the world is a curved mirror nearly 5
metres across, whose front surface is coated with aluminium. It is the hale
Telescope on the top of Mount Palomar, California, U.S.A. Glass by itself, will
also reflect light, but the percentage is small when compared with the case of
silvered surface. It is about 5% for an air-glass surface.
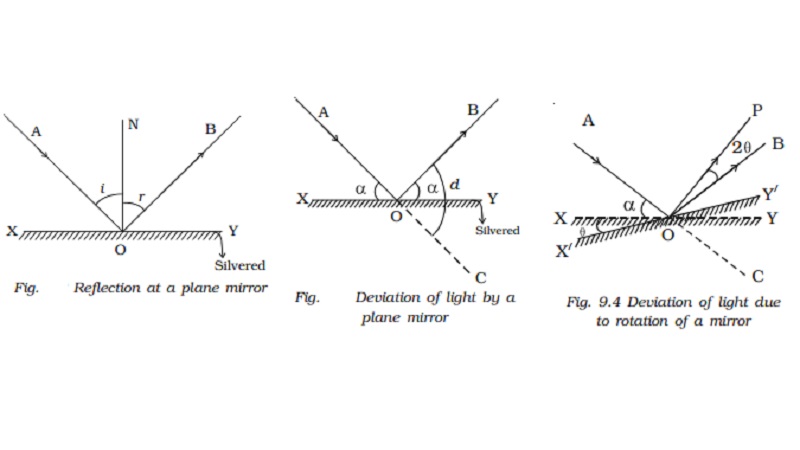
1.Laws of reflection
Consider a ray of
light, AO, incident on a plane mirror XY at O. It is reflected along OB. Let
the normal ON is drawn at the point of incidence. The angle AON between the
incident ray and the normal is called angle of incidence, i (Fig.) the angle BON between the reflected ray and the normal is
called angle of reflection, r.
Experiments show that :
(i) The incident ray,
the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point
of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The angle of
incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. (i.e) i = r.
These are called the
laws of reflection.
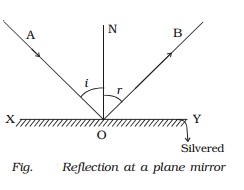
2.Deviation of light by plane
mirror
Consider
a ray of light, AO, incident on a plane mirror XY (Fig.) at O. It is reflected along
OB. The angle AOX made by AO with XY is known as the glancing angle α with the
mirror. Since the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, the
glancing angle
BOY
made by the reflected ray OB with the mirror is also equal to α.
The
light has been deviated from a direction AO to a direction OB. Since angle COY
= angle AOX, it follows that angle of deviation, d = 2α
So,
in general, the angle of deviation of a ray by a plane mirror or a plane
surface is twice the glancing angle.
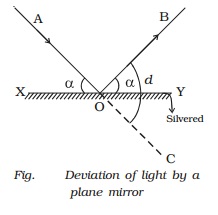
3.Deviation of light due to
rotation of a mirror
Let
us consider a ray of light AO incident on a plane mirror XY at O. It is
reflected along OB. Let α be the glancing angle with XY (Fig.). We know that
the angle of deviation COB = 2α.
Suppose
the mirror is rotated through an angle θ to a position X′Y′.
The
same incident ray AO is now reflected along OP. Here the glancing angle with
X′Y′ is (α + θ). Hence the new angle of deviation COP = 2 (α + θ). The
reflected ray has thus been rotated through an angle BOP when the mirror is
rotated through an angle θ.
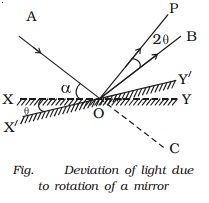
Angle
BOP = Angle COP = Angle COB
Angle
BOP = 2 (α + θ) ? 2α = 2θ
For
the same incident ray, when the mirror is rotated through an angle, the
reflected ray is rotated through twice the angle.
Related Topics