Steroisomerism | Organic Chemistry - Optical Isomerism | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Optical Isomerism
Optical Isomerism
Compounds having same physical and chemical property but differ only in the rotation of plane of the polarized light are known as optical isomers and the phenomenon is known as optical isomerism.
Some organic compounds such as glucose have the ability to rotate the plane of the plane polarized light and they are said to be optically active compounds and this property of a compound is called optical activity. The optical isomer, which rotates the plane of the plane polarised light to the right or in clockwise direction is said to be dextrorotary (dexter means right) denoted by the sign (+), whereas the compound which rotates to the left or anticlockwise is said to be leavo rotatory (leavues means left) denoted by sign(-). Dextrorotatory compounds are represented as ‘d’ or by sign (+) and lavorotatory compounds are represented as ‘l’ or by sign (-).
Enantiomerism and optical activity
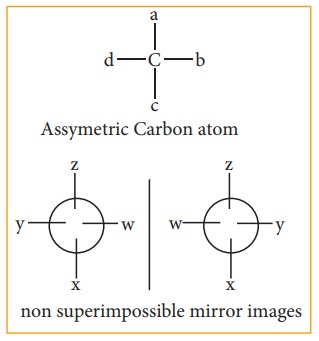
An optically active substance may exist in two or more isomeric forms which have same physical and chemical properties but differ in terms of direction of rotation of plane polarized light, such optical isomers which rotate the plane of polarized light with equal angle but in opposite direction are known as enantiomers and the phenom-enon is known as enantiomerism. Isomers which are non-super impossible mirror im-ages of each other are called enantiomers.
Conditions for enantiomerism or optical isomerism
A carbon atom whose tetra valency is satisfied by four different substituents (atoms or groups) is called asymmetric carbon or chiral carbon. It is indicated by an asterisk as C*. A molecule possessing chiral carbon atom and non-super impossible to its own mirror image is said to be a chiral molecule or asymmetric, and the property is called chirality or dissymmetry.
Related Topics