Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Constitutional isomers (Formerly structural isomers) and its types
Constitutional isomers (Formerly structural isomers):
This type of isomers have same molecular formula but differ in their bonding sequence. Structural or constitutional isomerism is further classified into following types.
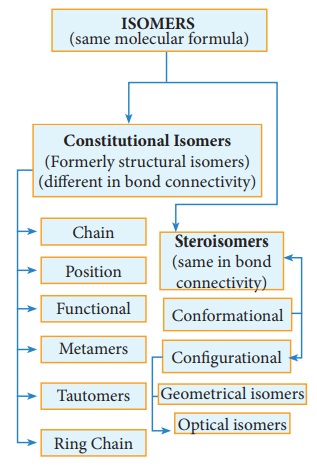
(a) Chain or nuclear or skeletal isomerism:
These isomers differ in the way in which the carbon atoms are bonded to each other in a carbon chain or in other words isomers have similar molecular formula but differ in the nature of the carbon skeleton (ie. Straight or branched)
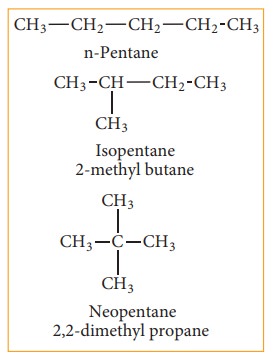
(b) Position isomerism:
If different compounds belonging to same homologous series with the same molecular formula and carbon skeleton, but differ in the position of substituent or functional group or an unsaturated linkage are said to exhibit position isomerism.
Example:
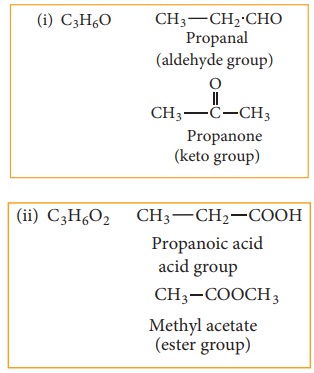
(c) Functional isomerism:
Different compounds having same molecular formula but different functional groups are said to exhibit functional isomerism.
Example:
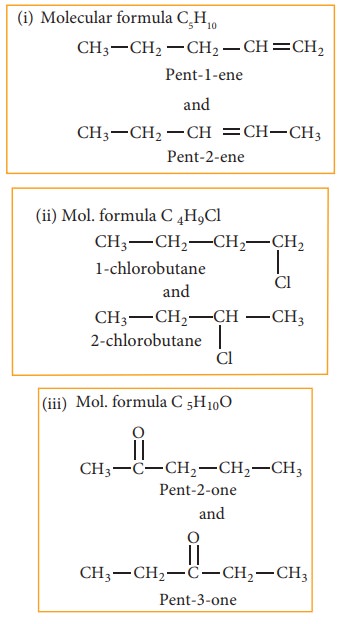
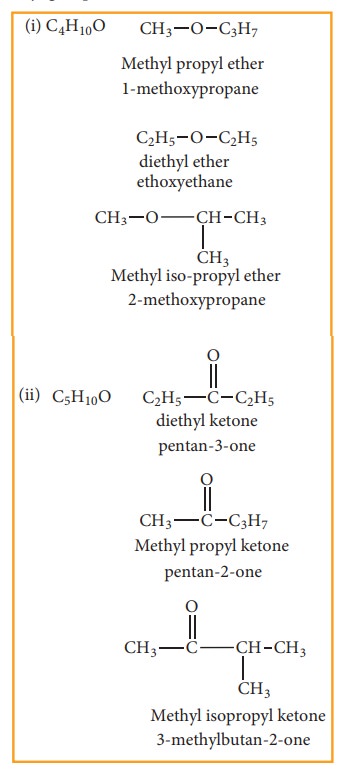
(d) Metamerism:
This type of isomerism is a special kind of structural isomerism arises due to the unequal distribution of carbon atoms on either side of the functional group or different alkyl groups attached to the either side of the same functional group and having same molecular formula. This isomerism is shown by compounds having functional group such as ethers, ketones, esters and secondary amines between two alkyl groups.
(e) Tautomerism:
It is a special type of functional isomerism in which a single compound exists in two readily inter con-vertible structures that differ markedly in the relative position of atleast one atomic nucleus, generally hydrogen. The two dif-ferent structures are known as tautomers. There are several types of tautomerism and the two important types are dyad and triad systems.
(i) Dyad system:
In this system hydrogen atom oscillates between two directly linked polyvalent atoms. Eg:
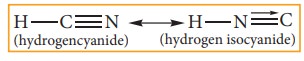
In this example hydrogen atom oscillates between carbon & nitrogen atom
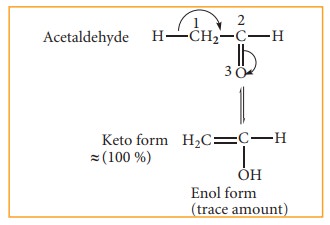
(ii) Triad system: In this system hydrogen atom oscillates between three polyvalent atoms. It involves 1,3 migration of hydrogen atom from one polyvalent atom to other within the mole-cule. The most important type of triad system is keto–enol tautomerism and the two groups of tautomers are ketoform and enol-form. The polyvalent atoms involved are one oxygen and two carbon atoms. Enolisation is a process in which keto-form is converted to enol form. Both tautomeric forms are not equally stable. The less stable form is known as labile form
Example:
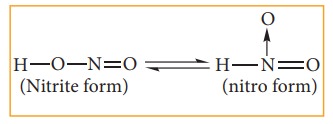
Nitro-aci tautomerism.
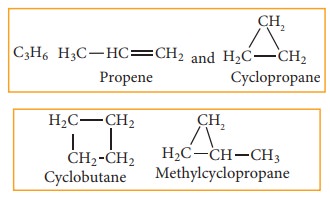
(f) Ring chain isomerism:
In this type of isomerism, compounds having same molecular formula but differ in terms of bonding of carbon atom to form open chain and cyclic structures for eg:
Related Topics