Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Nomenclature of organic compounds
Nomenclature
of organic compounds:
The
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is the world
authority on chemical nomenclature and terminology, naming of new elements in
the periodic table standardized methods for measurement; atomic weights, and
many other critically-evaluated data. According to IUPAC recommendations to
name any organic compound, it is considered as a derivative of its parent
saturated hydrocarbon. The IUPAC name of an organic compound consists of three
parts.
prefix + root word + suffix
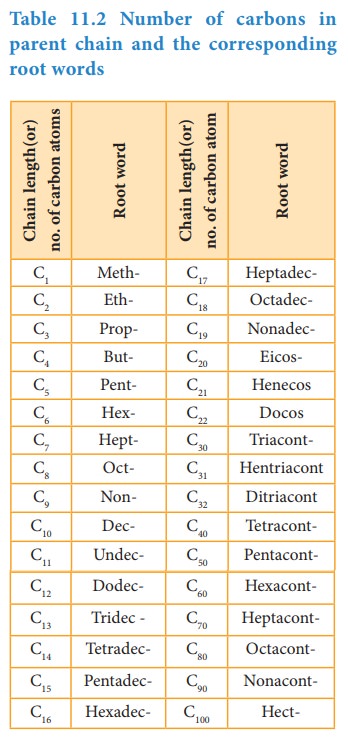
Root
word denotes the number of carbon atoms in the longest continiuous chain in
molecules. Prefix denotes the group(s) attached to the main chain which is
placed before the root. Suffix denotes the funtional group and is paced after
the root word.
Table 11.2 Number of carbons in parent chain and the corresponding root words
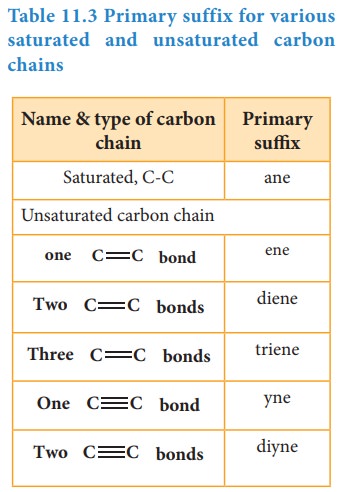
Suffix: There are two types of suffix. They are primary suffix and secondary
suffix
Primary suffix: It denotes the saturation/ unsaturation of organic compounds. It
is added immediately after the root word. Primary suffix for various saturated
and unsaturated carbon chains are as follows:
Table 11.3 Primary
suffix for various saturated and unsaturated carbon chains
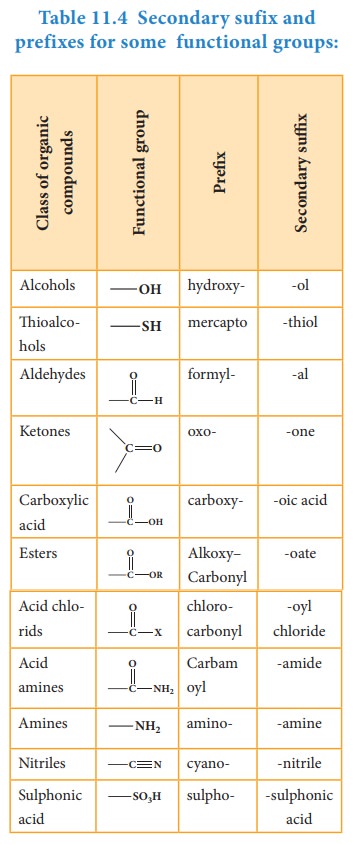
Secondary suffix: It is used to denote the nature of functional group present
in the organic compound. It is added to the primary suffix by removig its
terminal ‘e’. Secondary suffix names for some functional groups is listed below
in table 11.4
Table 11.4 Secondary sufix and prefixes for some functional groups:
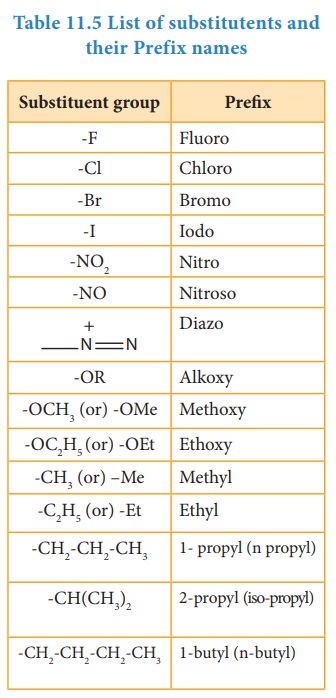
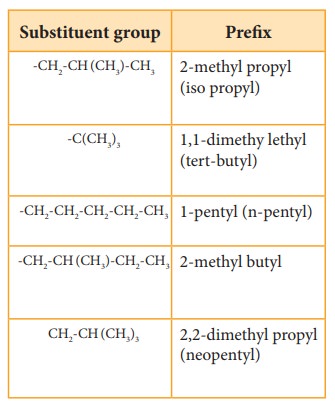
Prefix: Substituents that are attached to
the parent carbon chain are denoted
by adding prefix names before the root word. The prefix names for some common
substituents are listed below. If the functional groups are not part of the
parent chain, they are considered as substituents. In such cases its prefix
name is added before the root word. Prefix names for some functional groups
mentioned along with their secondary prefix are listed in table 11.4
Table 11.5 List of
substitutents and their Prefix names
IUPAC rules for nomenclature of organic compounds
The
following steps should be followed for naming an organic compound as per IUPAC
nomenclature.
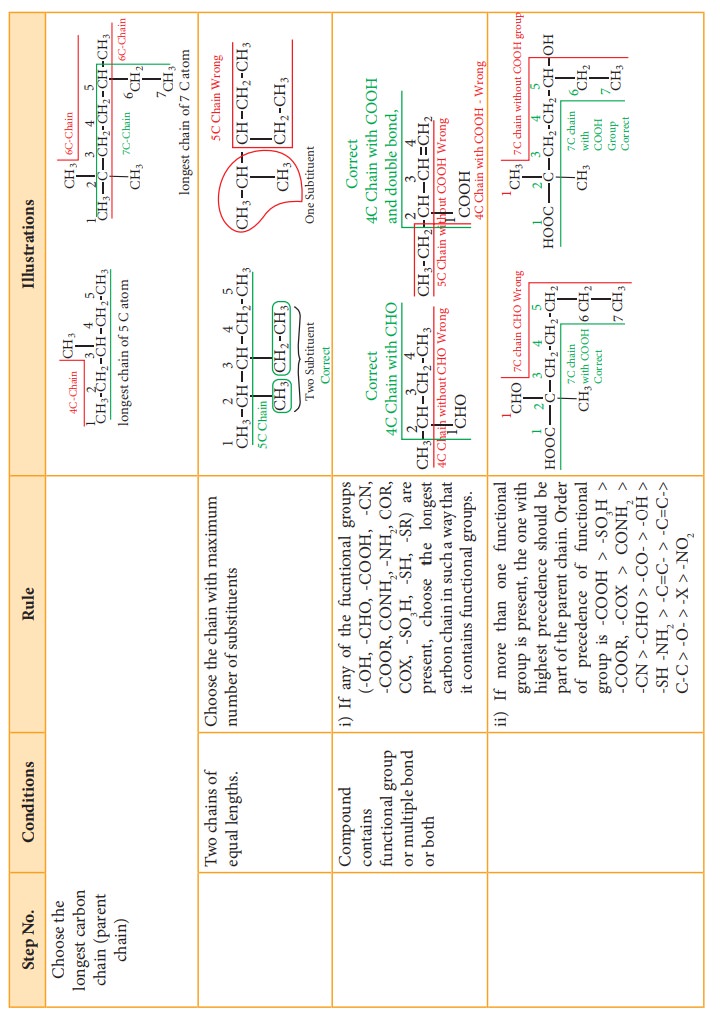
1.
Choose the longest carbon chain. (Root word). Consider all the other groups
attached to this chain as substitutents.
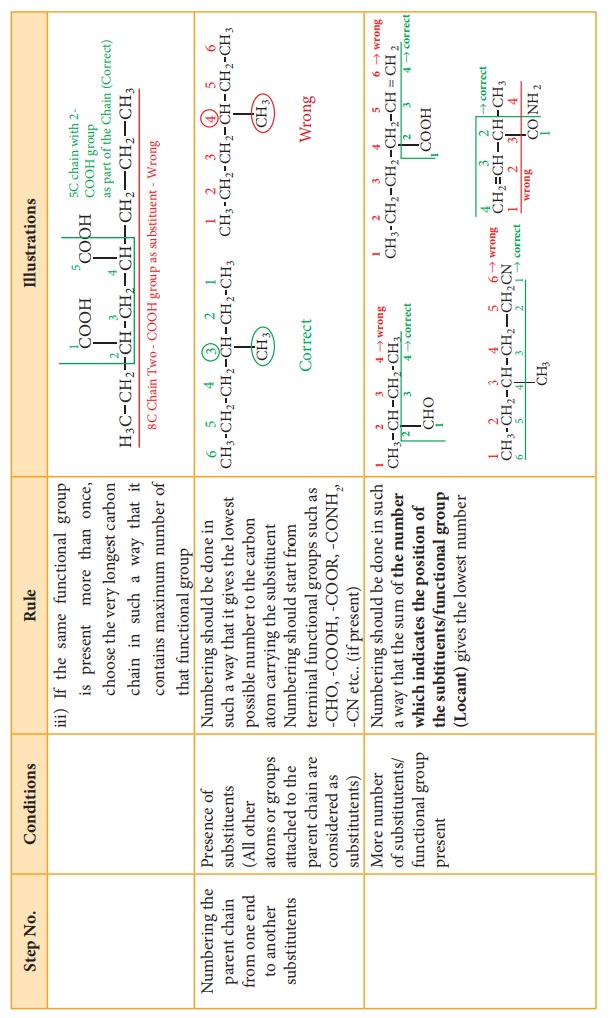
2.
Numbering of the longest carbon chain
3.
Naming of the substituents (prefixes or suffixes)
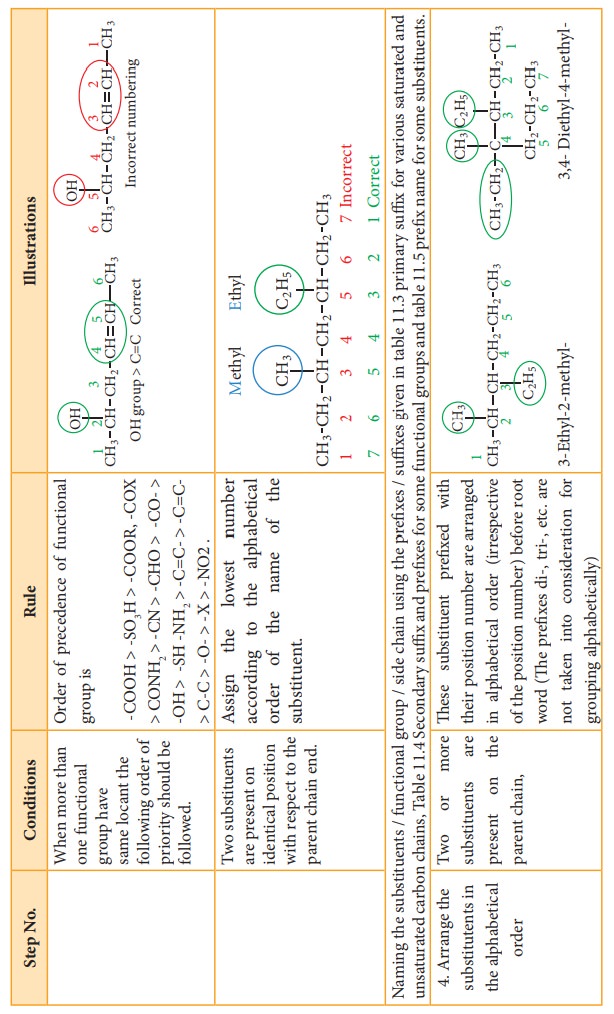
4.
Arrange the substitutents in the alphabetical order
5.
Write the name of the compound as below
"prefix
+ root word + primary suffix + secondary suffix"
The following are guide lines for writing IUPAC of the organic compound.
1.
The IUPAC names are always written as single word, with notable exception of
organic salts, acids and acid derivatives.
2.
Commas are used between two adjacent number or letter symbols, and hypens are
used to separate numbers and letter symbol in names Eg: 2,2-Dimethyl-3-hexene N,N-Dimethyl
methanamide
3.
Structural prefix such as, meso-, cis-, trans-, are italicised and joined to
the name by a hypen. These prefixes are omitted in alphabetising compound names
or in capitalising names at the beginning of a sentence.Eg:trans-2-Butene
4.
Structural prefixes such as di, tri, tetra are treated as a part of the basic
name and therefore are neither italicised nor separated by a hypen. These
prefixes are not taken into account in alphabetising compound names eg: 4- Ethyl -2,2-dimethyl hexane.
5.
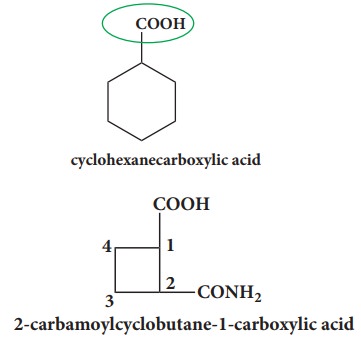
To name alicyclic compounds , the additional rules should be followed as
illustrated in the table 11.x
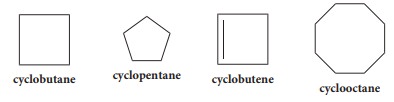
Table 11.6 Rules for naming of alicyclic compounds:
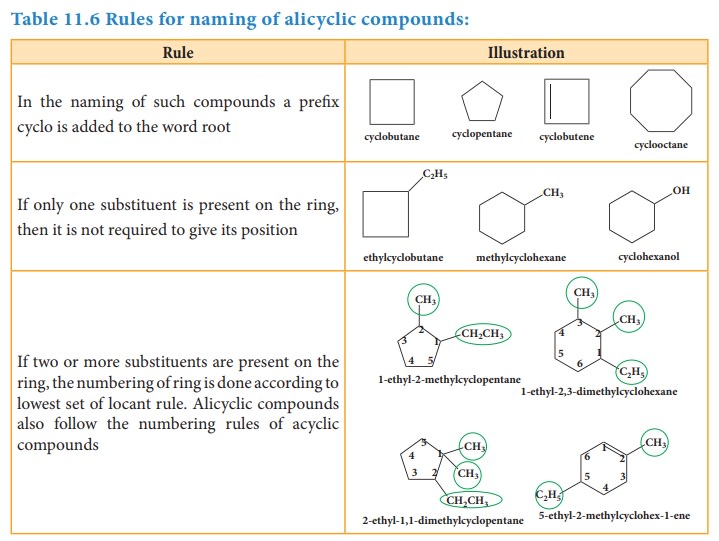
In
the naming of such compounds a prefix cyclo is added to the word root
If
only one substituent is present on the ring, then it is not required to give
its position

If
two or more substituents are present on the ring, the numbering of ring is done
according to lowest set of locant rule. Alicyclic compounds also follow the
numbering rules of acyclic compounds
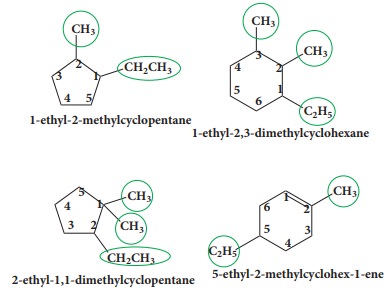
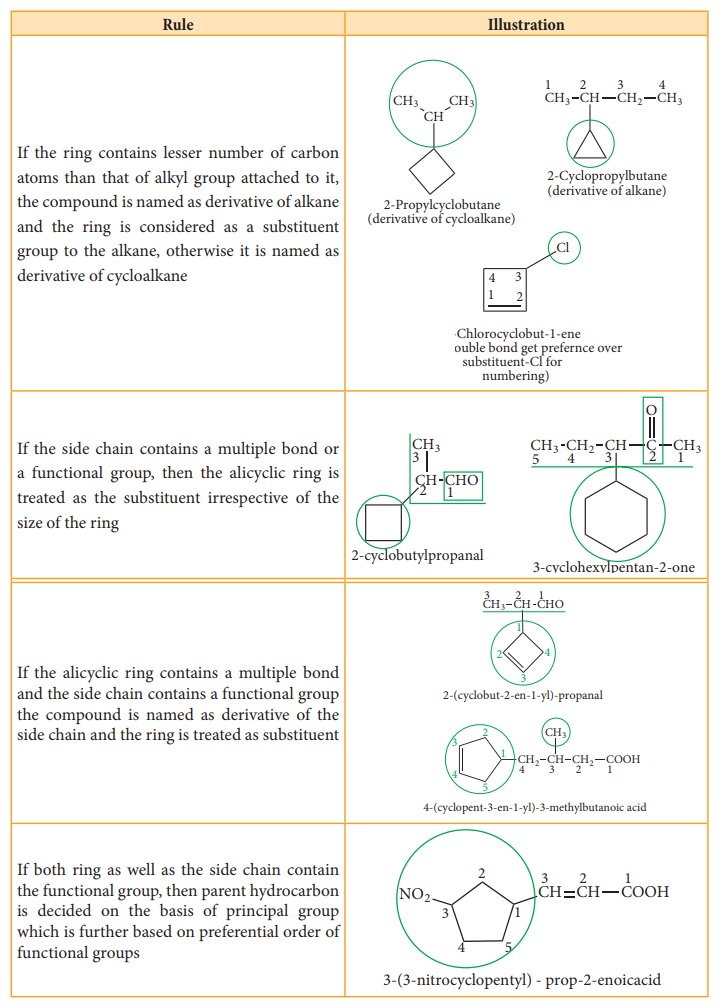
If
the ring contains lesser number of carbon atoms than that of alkyl group
attached to it, the compound is named as derivative of alkane and the ring is
considered as a substituent group to the alkane, otherwise it is named as
derivative of cycloalkane
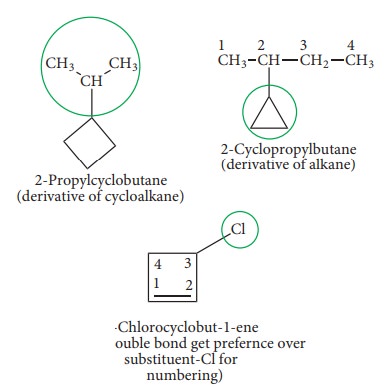
If
the side chain contains a multiple bond or a functional group, then the
alicyclic ring is treated as the substituent irrespective of the size of the
ring
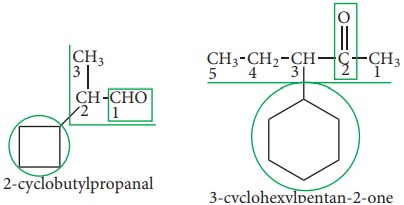
If
the alicyclic ring contains a multiple bond and the side chain contains a
functional group the compound is named as derivative of the side chain and the
ring is treated as substituent
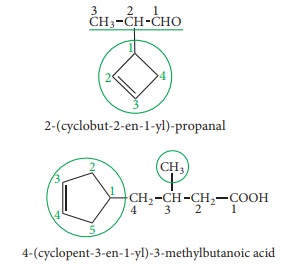
If
both ring as well as the side chain contain the functional group, then parent
hydrocarbon is decided on the basis of principal group which is further based
on preferential order of functional groups
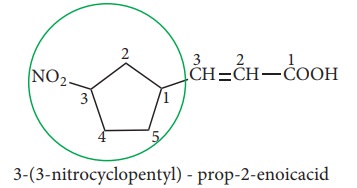
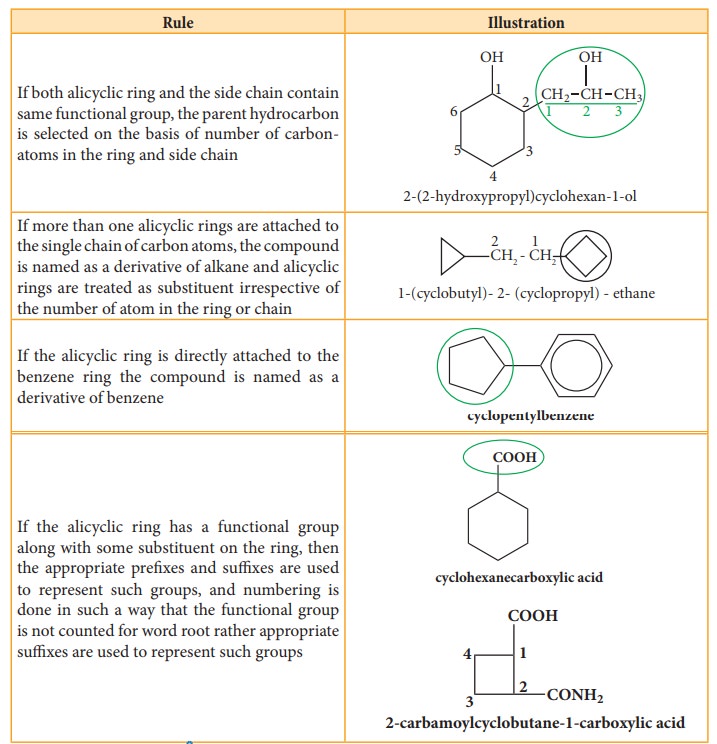
If
both alicyclic ring and the side chain contain same functional group, the
parent hydrocarbon is selected on the basis of number of carbon-atoms in the
ring and side chain
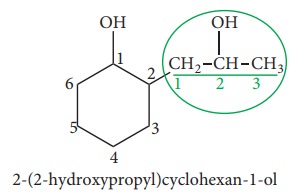
If
more than one alicyclic rings are attached to the single chain of carbon atoms,
the compound is named as a derivative of alkane and alicyclic rings are treated
as substituent irrespective of the number of atom in the ring or chain
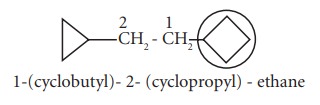
If
the alicyclic ring is directly attached to the benzene ring the compound is
named as a derivative of benzene
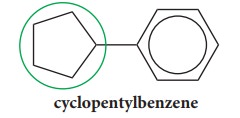
If
the alicyclic ring has a functional group along with some substituent on the
ring, then the appropriate prefixes and suffixes are used to represent such
groups, and numbering is done in such a way that the functional group is not
counted for word root rather appropriate suffixes are used to represent such
groups
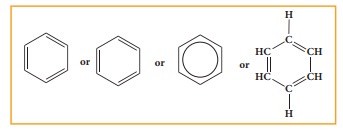
NOMENCLATURE OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS:
An
aromatic compound consists of two parts nucleus and side chain
(A) Nucleus: The benzene ring present
in aromatic compound is called nucleus. It is represented as follows
(B) Side chain: Alkyl or any other aliphatic group attached to the benzene nucleus by replacing one
or more hydrogen atom is called the side chain
If
one hydrogen atom, (or) two hydrogen atoms or three hydrogen atoms are replaced
in the benzene ring by some other groups, they are termed as mono substituted,
di substituted or tri substituted derivative respectively.
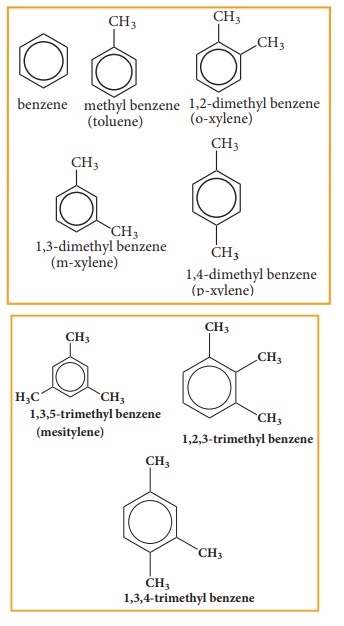
Example
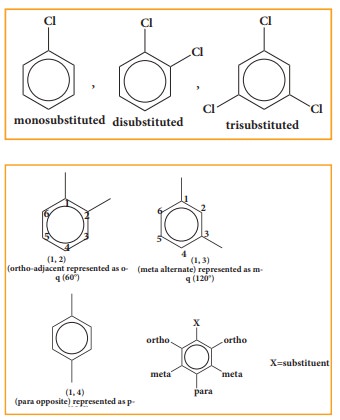
If
more than one hydrogen atom of benzene ring is replaced by some other atom or
group, then their position is mentioned by Arabic numerals 1,2,3 ….. In case of disubstitution, respective position of two groups can also
be mentioned as follows.
ortho
- adjacent; represented as - o
meta
- alternate; represented as - m
Para
- opposite; represented as - p
Aromatic compounds are basically of two types:
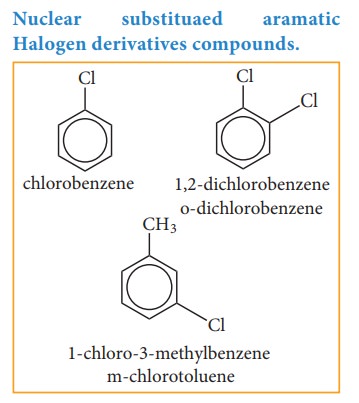
1.
Nuclear substituted aromatic compounds: These are the compounds in which the
functional group is directly attached to the benzene ring. They are named as
derivatives of benzene.
Nuclear substituaed aramatic Halogen derivatives compounds.
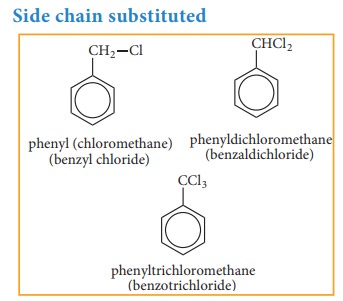
2.
Side chain substituted aromatic compounds: These are the compounds in which the
functional group is present in the side chain of the benzene ring. These are
named as phenyl derivatives of the corresponding aliphatic compounds.
Side chain substituted
Aryl groups
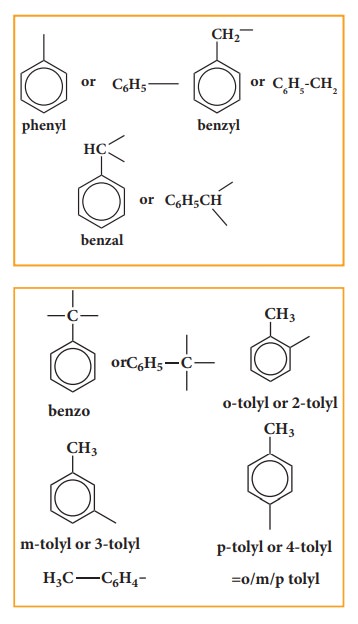
Selection
of parent hydrocarbon out of side chain and benzene ring is based on (more or
less) some rule as for the alicyclic compounds.
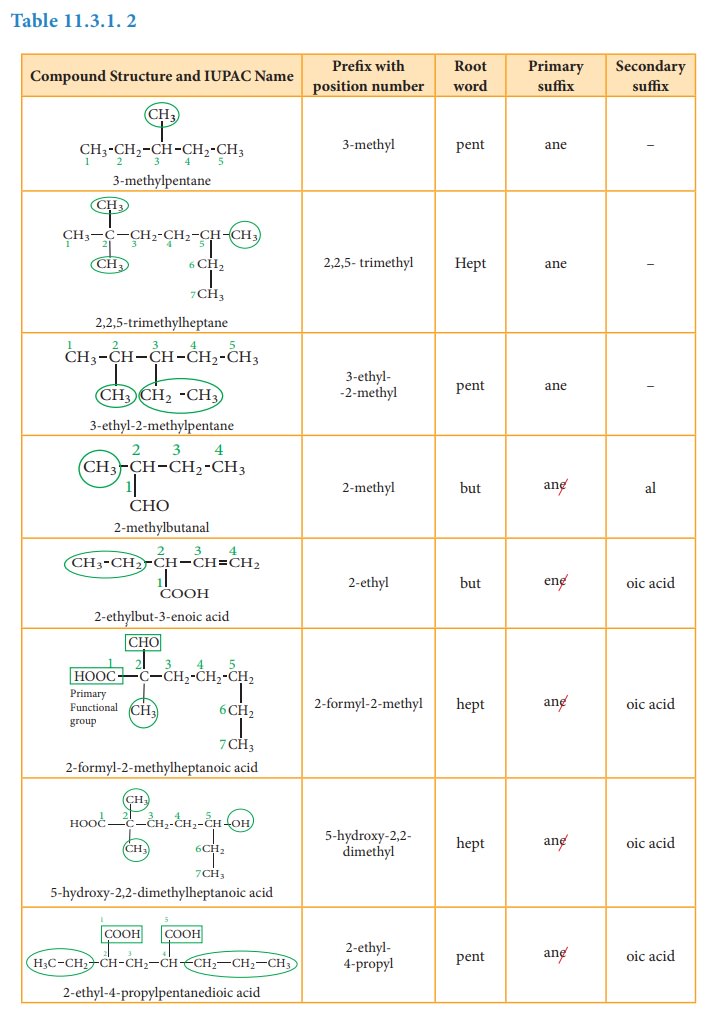
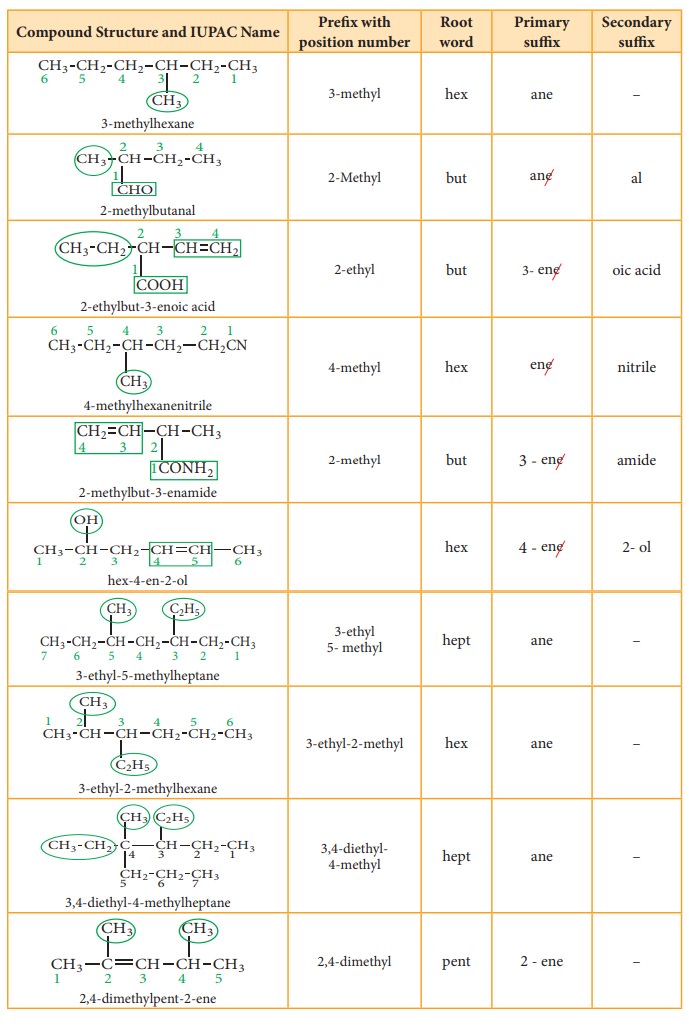
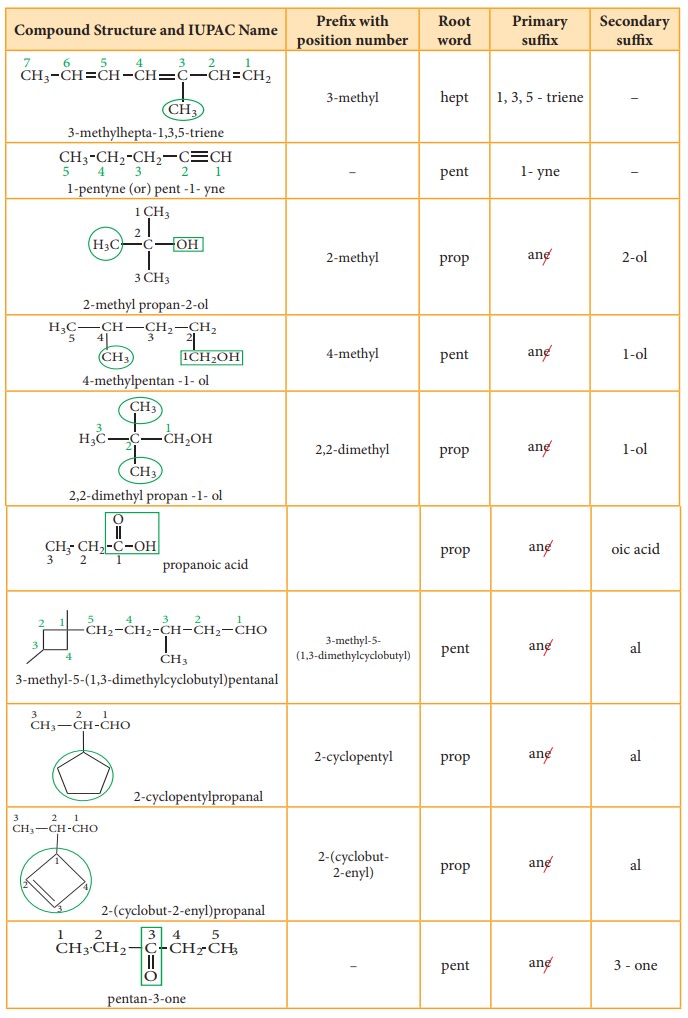
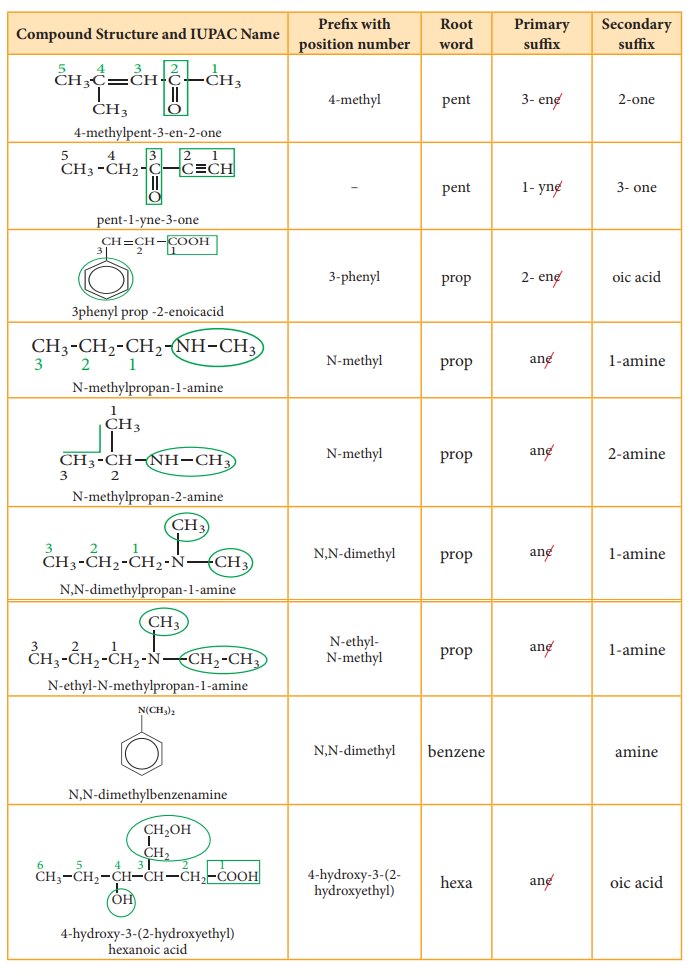
Table 11.3.1. 2
Related Topics