Equation, Diagram, Procedure, Calculation, Example - Estimation of carbon and hydrogen | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Estimation of carbon and hydrogen
Estimation of elements
After detecting the various elements present in a given organic compound by qualitative analysis it is necessary to determine their composition by weight. The estimation of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur halogens are discussed here. No dependable method is however available for determination oxygen and hence its amount is always determined by difference.
Estimation of carbon and hydrogen:
Both carbon and hydrogen are estimated by the same method. A known weight of the organic substance is burnt in excess of ox-ygen and the carbon and hydrogen present in it are oxidized to carbon dioxide and wa-ter, respectively.
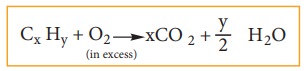
The weight of carbon dioxide and water thus formed are determined and the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the organic substance is calculated.
The apparatus employed for the purpose consists of three units (i) oxygen supply (2) combustion tube (3) absorption apparatus. (Refer Page 153 Fig. 11.2)
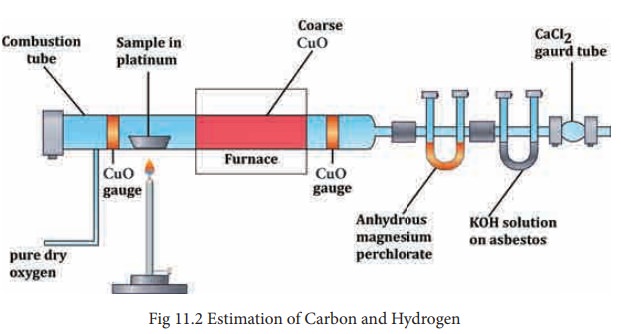
(1) Oxygen supply: To remove the moisture from oxygen it is allowed to bubble through sulphuric acid and then passed through a U-tube containing sodalime to remove CO2. The oxygen gas free from moisture and carbondioxide enters the combustion tube.
(2) Combustion tube: A hard glass tube open at both ends is used for the combustion of the organic substance. It contains (i) an oxidized copper gauze to prevent the backward diffusion of the products of combustion (ii) a porcelain boat containing a known weight of the organic substance (iii) coarse copper oxide on either side and (iv) an oxidized copper gauze placed towards the end of the combustion tube. The combustion tube is heated by a gas burner.
(3) Absorption Apparatus The combustion products containing moisture and carbon-dioxide are then passed through the absorption apparatus which consists of (1) a weighed U-tube packed with pumice soaked in Conc. H2SO4to absorb water (ii) a set of bulbs containing a strong solution of KOH to absorb CO2and finally (iii) a guard tube filled with anhydrous CaCl2 to prevent the entry of moisture from atmosphere.
Procedure:
The combustion tube is heated strongly to dry its content. It is then cooled slightly and connected to the absorption apparatus. The other end of the combustion tube is open for a while and the boat containing weighed organic substance is introduced. The tube is again heated strongly till the substance in the boat is burnt away. This takes about 2 hours. Finally, a strong current of oxygen is passed through the combustion tube to sweap away any traces of carbon dioxide or moisture which may be left in it. The U-tube and the potash bulbs are then detached and the increase in weight of each of them is determined.
Calculation:
Weight of the organic substance taken = w g
Increase in weight of H2O = x g
Increase in weight of CO2 = y g
18 g of H2O contain 2g of hydrogen
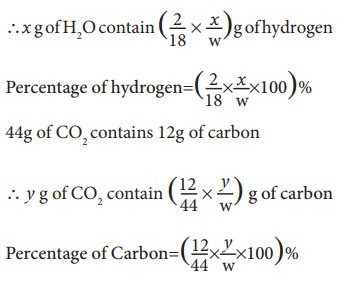
Note:
1. If the organic substance under investigation also contain N, it will produce oxides of nitrogen on combustion. A spiral of copper is introduced at the combustion tube, to reduce the oxides of nitrogen to nitrogen which escapes unabsorbed.
2. If the compound contains halogen as well, a spiral of silver is also introduced in the combustion tube. It converts halogen into silver halide.
3. In case if the substance also contains sulphur, the copper oxide in the combustion tube is replaced by lead chromate. The SO2formed during combustion is thus converted to lead sulphate and prevented from passing into the absorption unit.
Worked out example: 1
0.26g of an organic compound gave 0.039 g of water and 0.245 g of carbon dioxide on combustion. Calculate the percentage of C & H
Weight of organic compound = 0.26g
Weight of water = 0.039g
Weight of CO2 = 0.245g
Percentage of hydrogen
18 g of water contain 2 g of hydrogen
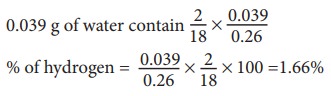
Percentage of carbon
44 g of CO2 contain 12 g of C

Related Topics