Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antihypertensive Agents
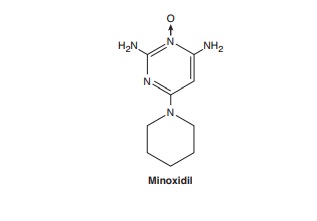
Minoxidil
MINOXIDIL
Minoxidil
is a very efficacious orally active vasodilator. The effect results from the
opening of potassium channels in smooth muscle membranes by minoxidil sulfate,
the active metabolite. Increased potassium permeability stabilizes the membrane
at its resting potential and makes contraction less likely. Like hydrala-zine,
minoxidil dilates arterioles but not veins. Because of its greater potential
antihypertensive effect, minoxidil should replace hydralazine when maximal
doses of the latter are not effective or in patients with renal failure and
severe hyperten-sion, who do not respond well to hydralazine.
Pharmacokinetics & Dosage
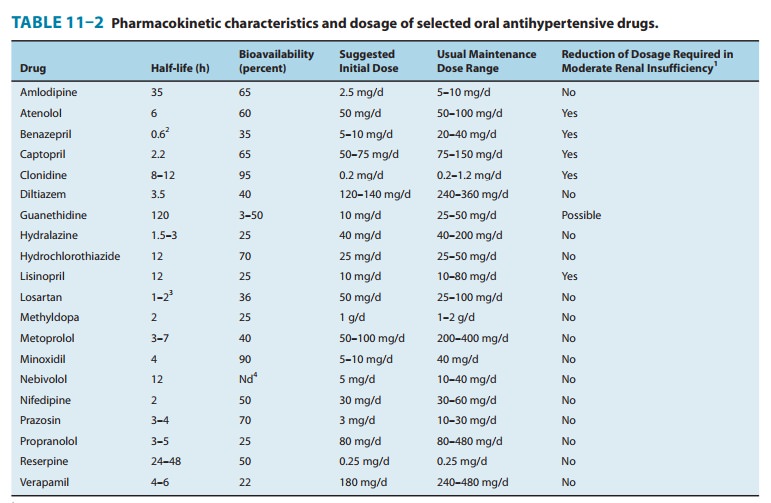
Pharmacokinetic
parameters of minoxidil are listed in Table 11–2. Even more than with
hydralazine, the use of minoxidil is associ-ated with reflex sympathetic
stimulation and sodium and fluid retention. Minoxidil must be used in
combination with a β
blocker and a loop diuretic.
Toxicity
Tachycardia,
palpitations, angina, and edema are observed when doses of β blockers and
diuretics are inadequate. Headache, sweat-ing, and hypertrichosis, which is
particularly bothersome in women, are relatively common. Minoxidil illustrates
how one person’s toxicity may become another person’s therapy. Topical
minoxidil (as Rogaine) is used as a stimulant to hair growth for correction of
baldness.
Related Topics