Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antihypertensive Agents
Inhibitors of Angiotensin
INHIBITORS OF
ANGIOTENSIN
Renin,
angiotensin, and aldosterone play important roles in at least some people with
essential hypertension. Approximately 20% of patients with essential
hypertension have inappropriately low and 20% have inappropriately high plasma
renin activity. Blood pres-sure of patients with high-renin hypertension
responds well to drugs that interfere with the system, supporting a role for
excess renin and angiotensin in this population.
Mechanism & Sites of Action
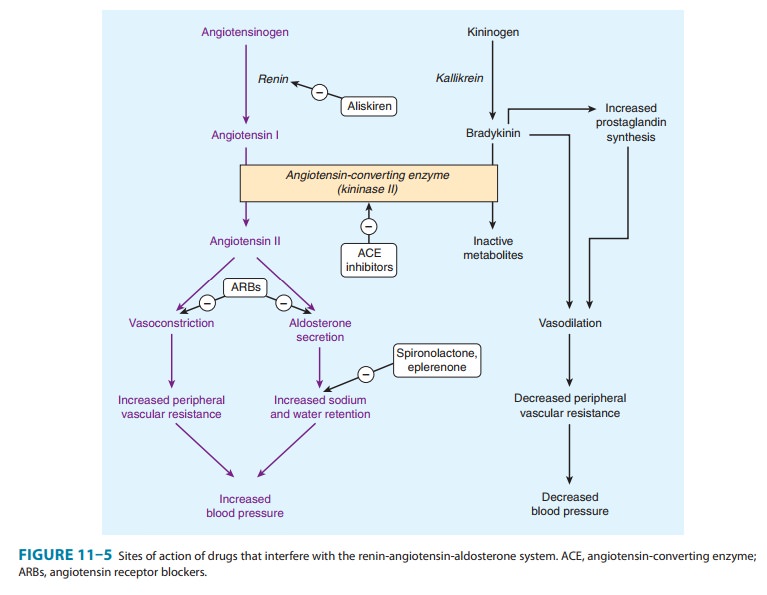
Renin
release from the kidney cortex is stimulated by reduced renal arterial
pressure, sympathetic neural stimulation, and reduced sodium delivery or
increased sodium concentration at the distal renal tubule . Renin acts upon
angio-tensinogen to split off the inactive precursor decapeptide angio-tensin
I. Angiotensin I is then converted, primarily by endothelial ACE, to the
arterial vasoconstrictor octapeptide angiotensin II (Figure 11–5), which is in
turn converted in the adrenal gland to angiotensin III. Angiotensin II has
vasoconstrictor and sodium-retaining activity. Angiotensin II and III both
stimulate aldoster-one release. Angiotensin may contribute to maintaining high
vascular resistance in hypertensive states associated with high plasma renin
activity, such as renal arterial stenosis, some types of intrinsic renal
disease, and malignant hypertension, as well as in essential hypertension after
treatment with sodium restriction, diuretics, or vasodilators. However, even in
low-renin hypertensive states, these drugs can lower blood pressure .
A
parallel system for angiotensin generation exists in several other tissues (eg,
heart) and may be responsible for trophic changes such as cardiac hypertrophy.
The converting enzyme involved in tissue angiotensin II synthesis is also
inhibited by ACE inhibitors.
Three
classes of drugs act specifically on the renin-angiotensin system: ACE
inhibitors; the competitive inhibitors of angiotensin at its receptors,
including losartan and other nonpeptide antago-nists; and aliskiren, an orally
active renin antagonist . A fourth group of drugs, the aldosterone receptor
inhibitors (eg, spironolactone, eplerenone) are discussed with the diuretics.
In addition, β
blockers, as noted earlier, can reduce renin secretion.
Related Topics