Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antihypertensive Agents
Ganglion-Blocking Agents
GANGLION-BLOCKING AGENTS
Historically,
drugs that block activation of postganglionic auto-nomic neurons by
acetylcholine were among the first agents used in the treatment of
hypertension. Most such drugs are no longer available clinically because of
intolerable toxicities related to their primary action .
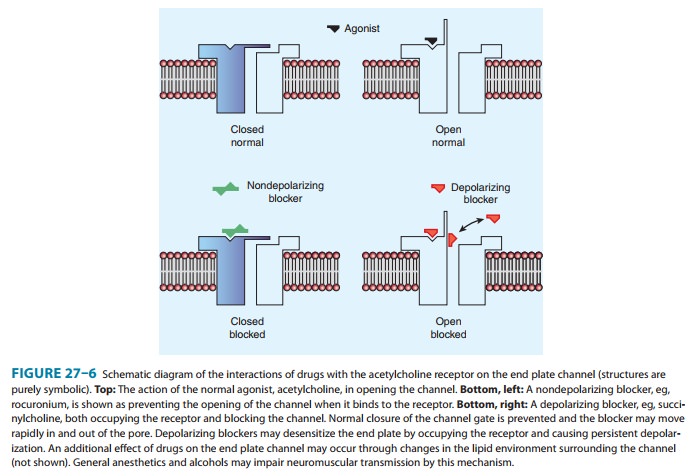
Ganglion
blockers competitively block nicotinic cholinoceptors on postganglionic neurons
in both sympathetic and parasympatheticganglia. In addition, these drugs may
directly block the nicotinic acetylcholine channel, in the same fashion as
neuromuscular nico-tinic blockers (see Figure 27–6).
The
adverse effects of ganglion blockers are direct extensions of their
pharmacologic effects. These effects include both sym-pathoplegia (excessive
orthostatic hypotension and sexual dys-function) and parasympathoplegia
(constipation, urinary retention, precipitation of glaucoma, blurred vision,
dry mouth, etc). These severe toxicities are the major reason for the
abandonment of ganglion blockers for the therapy of hypertension.
Related Topics