Chapter: Biochemical Pharmacology : G protein-coupled receptors
L-DOPA and carbidopa in the therapy of Parkinson's disease
L-DOPA and carbidopa in the
therapy of Parkinson's disease
Like the
transporters for the catecholamines and serotonin, those for their precursor
amino acids are not of very high specificity. This has been exploited in
various ways for pharmacotherapy. A very important example is the use of L-DOPA
as a pre-drug to substitute dopamine to the brain in patients with Parkinson's
disease (Figure 10.18a). Dopamine itself cannot cross the blood brain barrier13.
However, L-DOPA is accepted by an amino acid carrier that normally transports
aromatic amino acids. It can thus enter the brain and there be decarboxylated
to dopamine.
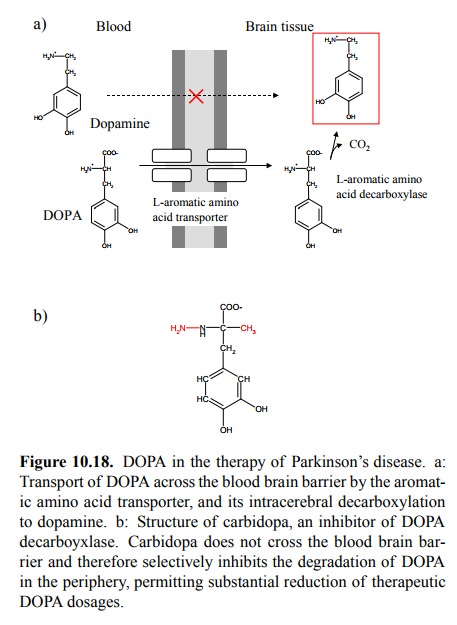
Concurrently with its
permeation into the brain, howev-er, DOPA will also be decarboxylated in the
periphery to dopamine; thus, the overall fraction of DOPA that winds up in the
brain is only about 2%. This means that very high dosages will be required for
the desired clinical effect, and the periphery would be uselessly troubled with
high amounts of dopamine and derived catecholamines. This situation can be
greatly improved by the simultaneous ap-plication of an inhibitor of DOPA
decarboxylase, called carbidopa (Figure 10.18b). Note that this substance will
not cross the blood brain barrier, and therefore not interfere with the
(necessary) decarboxylation in the brain.
Note
that, since dopamine is the precursor of nore-pinephrine and epinephrine,
carbidopa will inhibit the syn-thesis of all three catecholamines. One
therefore might expect it to reduce blood pressure, but it in animal
experi-ments it rather seems to increase it; this has been attributed to the
lack of dopamine in the periphery.
Related Topics