Chapter: Biochemical Pharmacology : G protein-coupled receptors
GPCR oligomerization
GPCR oligomerization
Another source of variation
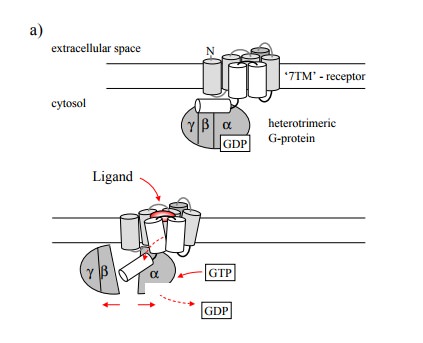
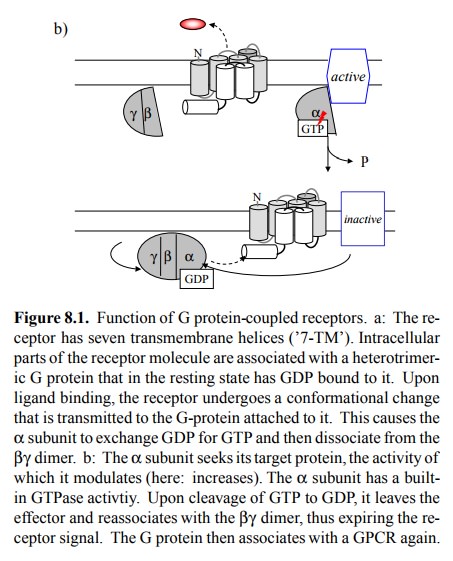
is the oligomeric state of G protein-coupled receptors. In Figure 8.1, the
receptor is depicted as a monomeric molecule, and indeed this was the
prevailing model until fairly recently. However, it is now clear that very many
GPCR are indeed oligomeric. This has several consequences:
• Efficacy and potency of a ligand may be
different for monomeric and oligomeric receptors.
• Dose-effect curves may take different shapes,
due to cooperative ligand binding4.
• Oligomers may be `homomers' but also
`heteromers', which means that they may form from like or from dif ferent
subunits. The existence of heteromers adds an-other dimension to the
variability of receptor types, sim-ilar as with the voltage-gated potassium
channels cov-ered earlier.
• It is possible to develop multivalent drugs
that bind to several binding sites simultaneously. This may result in very high
affinity for the receptor, and it might allow the targeting of certain
heteromeric subtypes, increasing the selectivity of drug action.
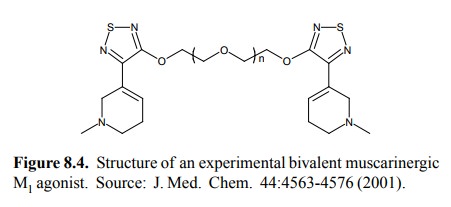
An
example of a bivalent drug that binds to the M1 mus-carinergic
receptor is shown in Figure 8.4. The affinity of this molecule for the receptor
is about 100 times higher than that of the conventional, monomeric agonist
carba-chol. Note that there is a spacer between the two `pharma-cophores',
which will allow the latter to bind to two sepa-rate subunits of the receptor
oligomer. The length of this spacer was systematically varied, and it was found
that a number of three repeating subunits gave both the highest affinity and
the strongest receptor activation. Molecules with shorter spacers still bound
with considerable affinity but failed to stimulate the receptor, possibly
because the sterical constraint imposed by the shorter spacer prevented the
receptor from assuming its active conformation. Since GPCR are all structurally
related, this finding suggests a surprisingly straightforward approach to the
development of agonistic and antagonistic drugs from a single `lead compound'.
Related Topics