Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antiseizure Drugs
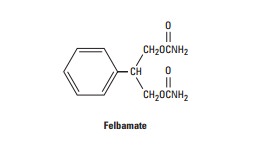
Felbamate
FELBAMATE
Felbamate
has been approved and marketed in the USA and in some European countries.
Although it is effective in some patients with partial seizures, the drug
causes aplastic anemia and severe hepatitis at unexpectedly high rates and has
been relegated to the status of a third-line drug for refractory
cases.Felbamate appears to have multiple mechanisms of action. It produces a
use-dependent block of the NMDA receptor, with selectivity for the NR1-2B
subtype. It also produces a barbitu-rate-like potentiation of GABAA
receptor responses. Felbamate has a half-life of 20 hours (somewhat shorter
when administered with either phenytoin or carbamazepine) and is metabolized by
hydroxylation and conjugation; a significant percentage of the drug is excreted
unchanged in the urine. When added to treat-ment with other antiseizure drugs,
felbamate increases plasma phenytoin and valproic acid levels but decreases
levels of carbamazepine.
In
spite of the seriousness of the adverse effects, thousands of patients
worldwide utilize this medication. Usual dosages are 2000–4000 mg/d in adults,
and effective plasma levels range from 30 mcg/mL to 100 mcg/mL. In addition to
its usefulness in partial seizures, felbamate has proved effective against the
seizures that occur in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Related Topics