Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Earth?s magnetic field and magnetic elements
Magnetism
The word magnetism is derived
from iron ore magnetite (Fe3O4), which was found in the
island of magnesia in Greece. It is believed that the Chinese had known the
property of the magnet even in 2000 B.C. and they used magnetic compass needle
for navigation in 1100 AD. But it was Gilbert who laid the foundation for
magnetism and had suggested that Earth itself behaves as a giant bar magnet.
The field at the surface of the Earth is approximately 10-4 T and
the field extends upto a height of nearly five times the radius of the Earth.
Earth?s magnetic field and
magnetic elements
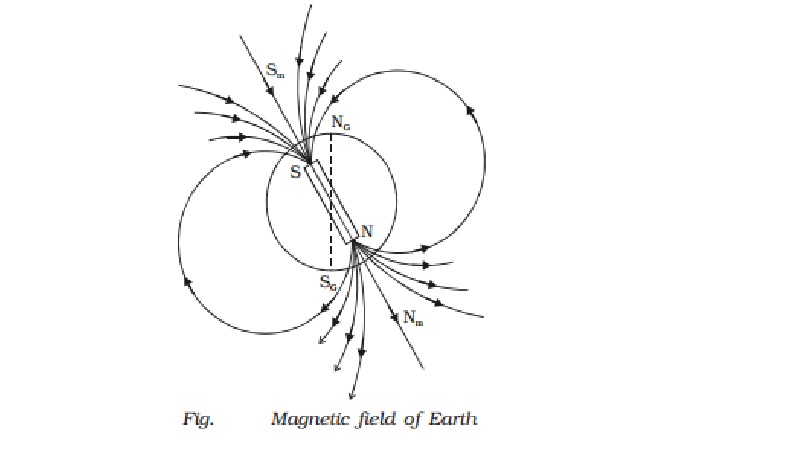
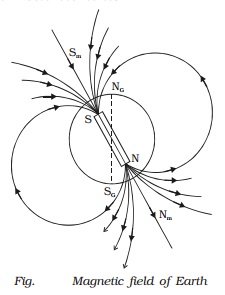
A freely suspended magnetic
needle at a point on Earth comes to rest approximately along the geographical
north - south direction. This shows that the Earth behaves like a huge magnetic
dipole with its magnetic poles near its geographical poles. Since the north
pole of the magnetic needle approximately points towards geographic north (NG)
it is appropriate to call the magnetic pole near NG as the magnetic
south pole of Earth Sm. Also, the pole near SG is the
magnetic north pole of the Earth (Nm). (Fig.)
The Earth?s magnetic field at any
point on the Earth can be completely defined in terms of certain quantities
called magnetic elements of the Earth, namely
(i) Declination or the magnetic
variation θ.
(ii) Dip or inclination δ and
(iii)The horizontal component of the Earth?s magnetic
field Bh
Causes of the Earth?s magnetism
The exact cause
of the Earth?s magnetism is not known even today. However, some important
factors which may be the cause of Earth?s magnetism are:
(i) Magnetic masses in the Earth.
(ii) Electric currents in the Earth.
(iii)Electric currents in the upper regions of the
atmosphere.
(iv)
Radiations from the Sun.
(v)
Action of moon etc.
However, it is
believed that the Earth?s magnetic field is due to the molten charged metallic
fluid inside the Earth?s surface with a core of radius about 3500 km compared
to the Earth?s radius of 6400 km.
Bar magnet
The iron ore
magnetite which attracts small pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel etc. is a natural
magnet. The natural magnets have irregular shape and they are weak. A piece of
iron or steel acquires magnetic properties when it is rubbed with a magnet.
Such magnets made out of iron or steel are artificial magnets. Artificial magnets
can have desired shape and desired strength. If the artificial magnet is in the
form of a rectangular or cylindrical bar, it is called a bar magnet.
Basic properties of magnets
(i)When the magnet is dipped in iron filings, they cling
to the ends of the magnet. The attraction is maximum at the two ends of the
magnet. These ends are called poles of the magnet.
(ii) When a magnet is freely
suspended, it always points along north-south direction. The pole pointing
towards geographic north is called north pole N and the pole which points towards geographic south is called
south pole S.
(iii) Magnetic poles always exist in
pairs. (i.e) isolated magnetic pole does not exist.
The magnetic length of a magnet
is always less than its geometric length, because the poles are situated a
little inwards from the free ends of the magnet. (But for the purpose of
calculation the geometric length is
always taken as magnetic length.)
(v)
Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
North pole of a magnet when brought near north pole of another magnet, we can
observe repulsion, but when the north pole of one magnet is brought near south
pole of another magnet, we observe attraction.
(vi)The force of attraction or repulsion between two
magnetic poles is given by Coulomb?s inverse square law.
Note : In recent days, the
concept of magnetic poles has been completely changed. The origin of magnetism
is traced only due to the flow of current. But anyhow, we have retained the
conventional idea of magnetic poles in this chapter. Pole strength is denoted
by m and its unit is ampere metre.
Related Topics