Chapter: Case Study in Obstetrics and Gynaecology: Peripartum Care and Obstetric Emergencies
Case Study Reports: Neonatal Care
History
A 19-year-old woman
is in spontaneous labour at 37 weeks
2 days’ gestation. At 4 cm cer-
vical dilatation there
is thick meconium
liquor and a fetal heart
deceleration to 70/min
is heard lasting for 2 min. The woman
is immediately placed
on the continuous cardio-
togograph (CTG), which confirms regular
deep late decelerations.
A decision is made to deliver the baby by immediate Caesarean
section under general anaesthetic. The baby is delivered within
20 min.

Questions
·
How
do you interpret the Apgar and cord blood results?
·
What action would you take in these circumstances?
ANSWER
The Apgar score
is a simple scoring system
to record the
initial assessment of neonates in the
first few minutes
after delivery. For
each variable a score of 0, 1 or 2 may be allocated
(see Table 96.1).
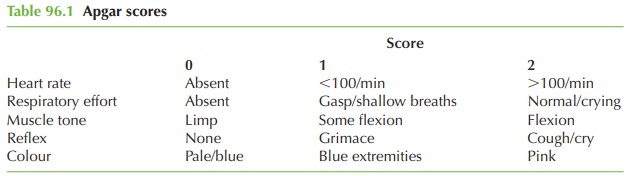
In
this case the baby is clearly showing
no respiratory effort and is bradycardic at birth.
The arterial cord blood shows an acidosis.
Management
Most babies, even with low Apgar scores respond to initial
resuscitation measures:
·
immediately dry the baby with warm towels, replacing any wet towels
with dry ones
·
warm by wrapping in a warm
dry towel and
placing under the
heated rescuscitaire
·
stimulate by rubbing (during drying)
·
if
no immediate respiratory effort is made then proceed
to 5 inflationary breaths with oxygen via a self-limiting pressure bag and appropriately sized
face mask (most
babies will respond and
immediately increase their
heart rate and
begin to make
some respira- tory effort)
·
recheck the respiration and heart rate.
If they have not recovered, clear the airway
with gentle suction (this
baby has been exposed to thick meconium
which may have been
inhaled and be causing a mechanical obstruction)
·
if
the heart rate is above
60/min, continue ventilation with bag and mask until
heart rate increases to above 100/min
·
if
the heart rate
is below 60/min
begin chest compressions, continue bag and
mask ven- tilation and check that the neonatal
resuscitation team has been called.
This baby recovered its heart rate
and respiratory effort
with the first
three measures but continued to display ‘grunting’ respiratory effort, and 3 h later deteriorated and needed
ventilation. A diagnosis of meconium aspiration and pneumonitis was made and anti-
biotics and supportive measures were
initiated with final
extubation after 7 days and
dis- charge home 5 days later.
Related Topics