Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Female Reproductive Disorders
Candidiasis - Vulvovaginal Infections
CANDIDIASIS
Vulvovaginal candidiasis is a fungal or yeast infection caused by strains of Candida (Table 47-1). Candida albicans accounts for most cases, but other strains, such as Candida glabrata, may also be implicated. Many women with a healthy vaginal ecosystem harbor Candida but are asymptomatic. Certain conditions favor the change from an asymptomatic state to colonization with symptoms. For example, use of antibiotics decreases bacteria, thereby altering the natural protective organisms usually present in the vagina. Clinical infection may occur during pregnancy, with a systemic condition such as diabetes mellitus or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, or in a patient taking corticosteroids or oral contraceptives.
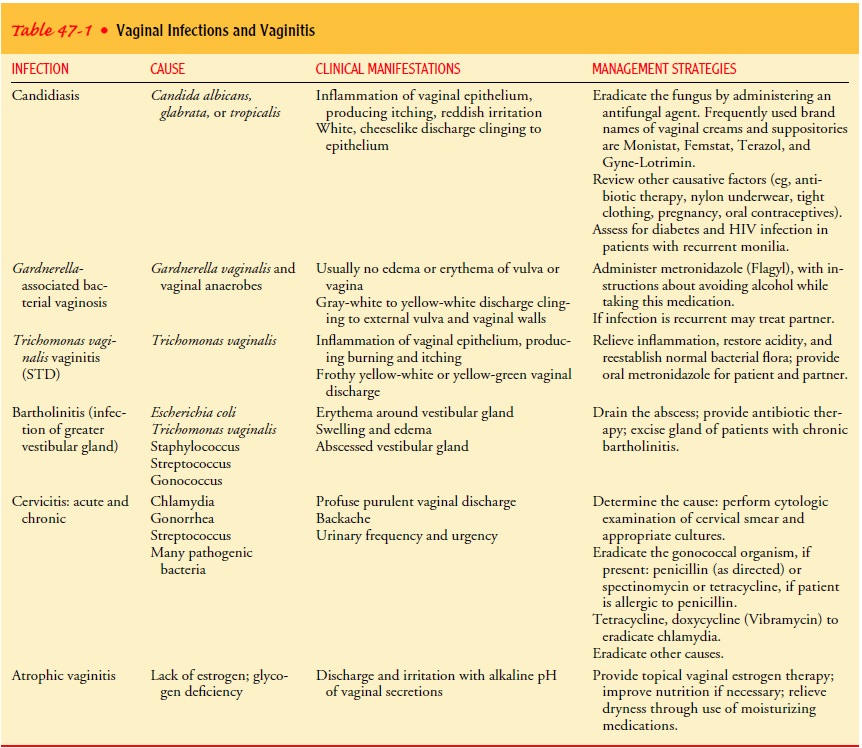
Clinical Manifestations
Clinical
manifestations include a vaginal discharge that causes pruritus (itching) and
subsequent irritation. The discharge may be watery or thick but has a white,
cottage cheese-like appearance. Symptoms are usually more severe just before
menstruation and are usually less responsive to treatment during pregnancy.
Diag-nosis is made by microscopic identification of spores and hyphae on a glass slide prepared from a
discharge specimen mixed with potassium hydroxide. With candidiasis, the pH is
4.5 or less.
Medical Management
The
goal of management is to eliminate symptoms. Treatments include antifungal
agents such as miconazole (Monistat), nystatin (Mycostatin), clotrimazole
(Gyne-Lotrimin), and terconazole (Terazol) cream. These agents are inserted
into the vagina with an applicator at bedtime and may be applied to the vulvar area
for pruritus. There are 1-night, 3-night, or 7-night treatment courses
available. Oral medication is also available (fluconazole [Diflu-can]).
Fluconazole is given in a one-pill dose; relief should be noted within 3 days.
Vaginal
creams are available without a prescription; however, patients are cautioned to
use these creams only if they are certain that they have a yeast or monilial
infection. Many patients use these remedies for problems other than yeast
infections. If the pa-tient is uncertain about the cause of her symptoms or has
not ob-tained relief after using these creams, she is instructed to seek health
care promptly. Yeast infections can sometimes become re-current and may be
related to cell-mediated immunity or to an allergic response. Women with
recurrent yeast infections benefit from a comprehensive gynecologic workup.
Related Topics