Chapter: The Massage Connection ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY : Cardiovascular System
Blood
Blood
The blood is an example of connective tissue that is liquid. It is the body fluid that supplies oxygen, absorbed from the respiratory system, and nutrients, absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, to the tissue. In the tis-sue, the oxygen and nutrients diffuse out of the blood vessels into the interstitial fluid that bathes the cells and, finally, across the cell membrane into the cell. Similarly, waste products, such as carbon dioxide, dif-fuse out of the cell into the interstitial fluid and then into the blood. The waste products and other products of metabolism are then carried to the lungs, kidneys, skin, and digestive tract for elimination.
Blood helps maintain the body temperature. It transports hormones and other agents that regulate the functioning of individual cells. It also helps regu-late the pH of the body fluids. The composition of blood is important for regulating the volume of water in the body. Blood has a protective function because it contains white blood cells and proteins, such as an-tibodies and interferon, that help fight foreign agents.
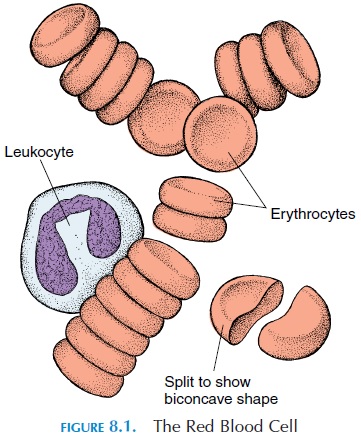
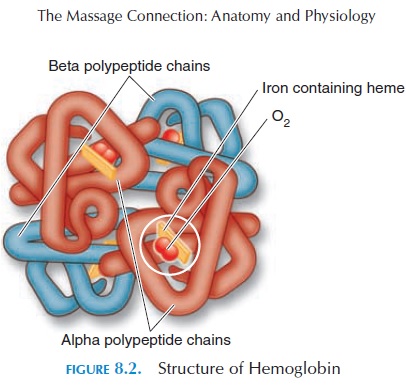
The blood contributes approximately 8% of the body weight. The volume of blood in an adult man is approximately 5–6 liters (5.3–6.3 qt) and, in an adult female, it is about 4–5 liters (4.2–5.3 qt). Blood is more viscous than water. The pH of blood is main-tained between 7.35 and 7.45. The temperature of blood is about 38°C (100.4°F). The color of blood de-pends on hemoglobin content. When the hemoglobin is oxygenated, blood appears red—as in peripheral arteries. If the oxygen content is low, it appears blue—the color of blood in superficial veins.
The blood is made up of two major components— formed elements—the cells and plasma. If a small vol-ume of blood is withdrawn and centrifuged, the heav-ier elements will settle at the bottom of the centrifuge tube. The cells in the blood—the heavier elements— constitute approximately 45% of the volume. The re-maining volume of 55% is plasma—the volume of blood without cells.
The cellular elements of blood are the red bloodcells, white blood cells, and platelets. The red bloodcells make up about 99% of the volume of cells.
Related Topics