Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 2 : Plant Kingdom
Types of Stele - Pteridophytes
Types of Stele
The term stele refers to the central cylinder of
vascular tissues consisting of xylem, phloem, pericycle and sometimes medullary
rays with pith (Figure 2.37).
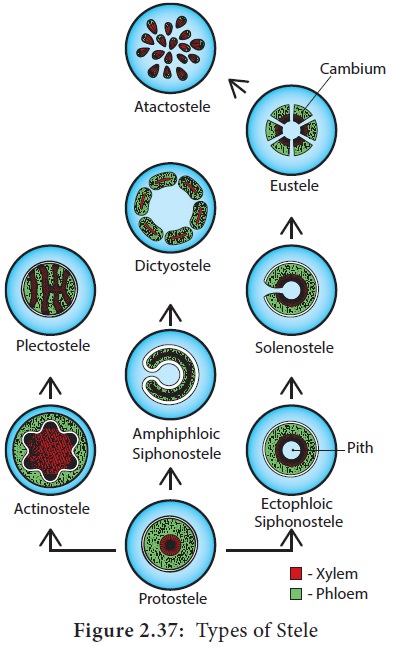
There are two types of steles
1.
Protostele
2.
Siphonostele
1. Protostele:
In protostele phloem surrounds xylem. The type
includes Haplostele, Actinostele, Plectostele, and Mixed protostele.
(i) Haplostele: Xylem surrounded by phloem is known as haplostele.
Example: Selaginella.
(ii) Actinostele: Star shaped xylem core is surrounded by phloem is known
as actinostele. Example: Lycopodium serratum.
(iii) Plectostele: Xylem plates alternates with phloem plates. Example: Lycopodium clavatum.
(iv) Mixed prototostele: Xylem groups uniformly scattered in the phloem. Example: Lycopodium cernuum.
2. Siphonostele:
In siphonostele xylem is surrounded by phloem with
pith at the centre. It includes Ectophloic siphonostele, Amphiphloic siphonostele,
Solenostele,
(i)
Ectophloic
siphonostele: The phloem is
restricted only on the external side of the xylem. Pith is in centre. Example: Osmunda.
(ii)
Amphiphloic
siphonostele: The phloem
is present on both the sides of xylem. The pith is in the centre. Example: Marsilea.
(iii) Solenostele: The stele is perforated at a place or places corresponding the
origin of the leaf trace.
(a)
Ectophloic solenostele – Pith is in the centre and the xylem is surrounded
by phloem Example Osmunda.
(b)
Amphiphloic
solenostele – Pith is in
the centre and the phloem is present on both sides of the xylem. Example: Adiantum pedatum.
(c)
Dictyostele
– The
stele is separated into several
vascular strands and each one is called meristele. Example: Adiantum capillus-veneris.
(iv) Eustele: The stele is split into
distinct collateral vascular bundles
around the pith. Example: Dicot stem.
(v) Atactostele: The stele is split into
distinct collateral vascular bundles and are scattered in the ground tissue
Example: Monocot stem.
(vi) Polycyclicstele: The vascular tissues are present in the form of two or more
concentric cylinders. Example: Pteridium.
Related Topics