Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 2 : Plant Kingdom
General Characteristic features of Algae
General Characteristic features
The algae show a great diversity in size, shape and
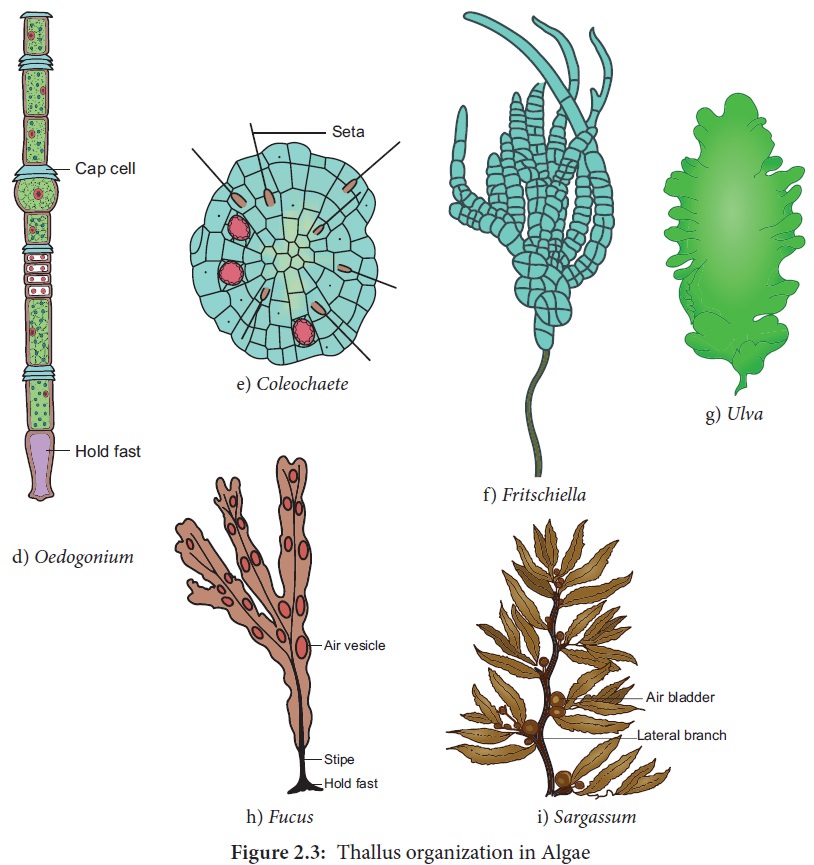
structure. A wide range of thallus organisation is found in algae. Unicellular
motile (Chlamydomonas), unicellular
non-motile (Chlorella), Colonial
motile (Volvox), Colonial non motile
(Hydrodictyon), siphonous (Vaucheria), unbranched filamentous (Spirogyra), branched filamentous (Cladophora), discoid (Coleochaete) heterotrichous ( Fritschiella), Foliaceous (Ulva) to Giant Kelps (Laminaria and Macrocystis). The thallus organization in algae is given in Figure 2.3.
Algae are Eukaryotes except blue green algae. The
plant body does not show differentiation into tissue systems. The cell wall of
algae is made up of cellulose and hemicellulose. Siliceous walls are present in
diatoms. In Chara the thallus is
encrusted with calcium carbonate. Some algae possess algin, polysulphate esters
of polysaccharides which are the
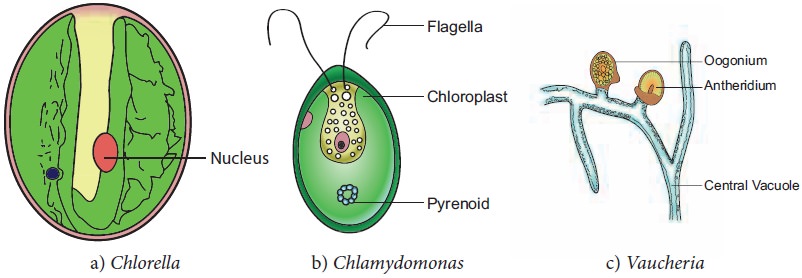
The cell has a membrane bound nucleus and cell organelles like
chloroplast, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi bodies etc., Pyrenoids
are present. They are proteinaceous bodies found in chromatophores and assist
in the synthesis and storage of starch. The pigmentation, reserve food material
and flagellation differ among the algal groups.
Algae reproduces by vegetative, asexual and sexual
methods (Figure 2.4). Vegetative reproduction includes fission (In unicellular
forms the cell divides mitotically to produce two daughter cells Example: Chlamydomonas); Fragmentation (fragments
of parent thallus grow into new individual Example: Ulothrix ) Budding (A lateral bud is formed in some members like Protosiphon and helps in reproduction) Bulbils, (a wedge shaped modified
branch develop in Sphacelaria)
Akinetes (Thick walled spores meant for perennation and germinates with the
advent of favourable condition Example: Pithophora).
Tubers (Structures found on the rhizoids and the lower nodes of Chara which store food materials).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Asexual reproduction
takesplace by the production of zoospores( Ulothrix,
Oedogonium) aplanospore(thin walled non motile spores Example: Vaucheria);
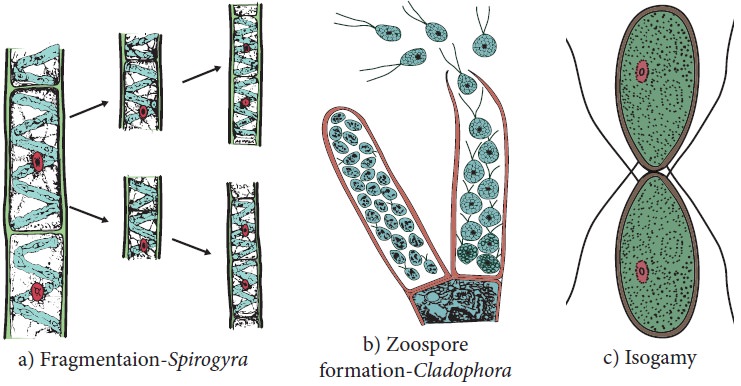
Autospores
(spores which look similar to parent cell Example: Chlorella ); Hypnospore (thick walled aplanospore – Example: Chlamydomonas nivalis); Tetraspores (Diploid thallus of Polysiphonia produce haploid spores
after meiosis).
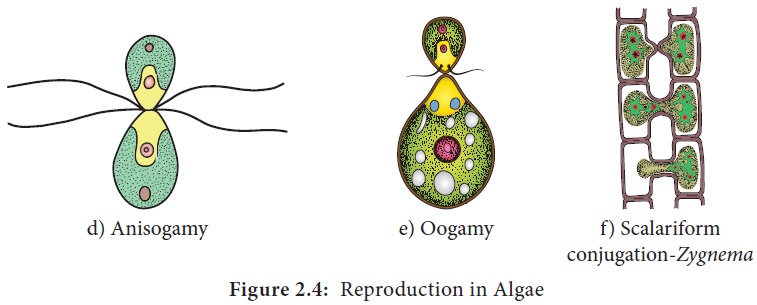
Sexual reproduction in algae are of three types 1.
Isogamy (Fusion of morphologically and Physiologically similar gametes Example:
Ulothrix) 2. Anisogamy (Fusion of
either morphologically or physiologically dissimilar gametes Example: Pandorina) 3. Oogamy (Fusion of both
morphologically and physiologically dissimilar gametes.
Example: Sargassum).
The life cycle shows distinct alternation of generation.
Related Topics