Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 2 : Plant Kingdom
General characteristic features of Gymnosperms
General characteristic features
•
Most of the gymnosperms are evergreen woody trees
or shrubs. Some are lianas (Gnetum)
•
The plant body is sporophyte and is differentiated
into root, stem and leaves.
•
A well developed tap root system is present.
Coralloid Roots of Cycas have
symbiotic association with blue green algae. In Pinus the roots have mycorrhizae.
![]()
![]()
![]()
•
The stem is aerial, erect and branched or
unbranched (Cycas) with leaf scars.
•
In conifers two types of branches namely branches
of limited growth (Dwarf shoot) and Branches of unlimited growth (Long shoot)
is present.
•
Leaves are dimorphic, foliage and scale leaves are
present. Foliage leaves are green, photosynthetic and borne on branches of
limited growth. They show xerophytic features.
•
The xylem consists of tracheids but in Gnetum and Ephedra Vessels are present.
•
Secondary growth is present. The wood may be Manoxylic (Porous, soft, more
parenchyma with wide medullary ray -Cycas)
or Pycnoxylic (compact with narrow
medullary ray-Pinus).
•
They are heterosporous. The plant may be monoecious
(Pinus) or dioecious (Cycas).
•
Microsporangia and Megasporangia are produced on
Microsporophyll and Megasporophyll respectively.
•
Male and female cones are produced.
•
Anemophilous pollination is present.
•
Fertilization is siphonogamous and pollen tube
helps in the transfer of male nuclei.
•
Polyembryony
(presence of many embryo) is Present. The naked ovule
develops into seed. The endosperm is
haploid and develop before fertilization.
•
The life cycle shows alternation of generation. The
sporophytic phase is dominant and gametophytic phase is highly reduced. The
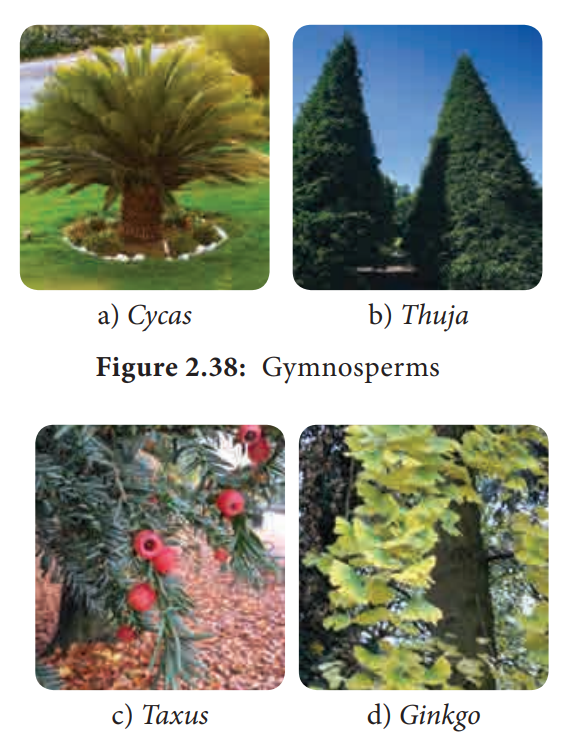
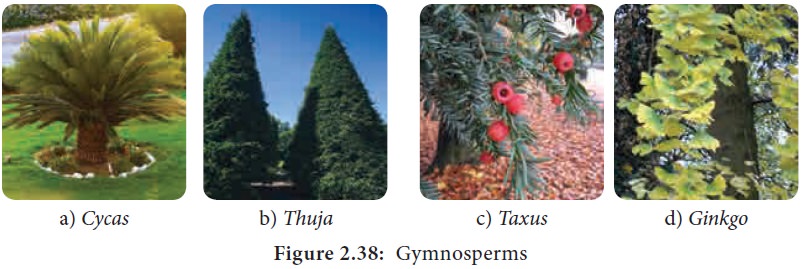
photograph of some of the Gymnosperms is given in Figure 2.38
Related Topics