Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: RNA-Based Technologies
RNA SELEX Identifies New Binding Partners for Ribozymes
RNA
SELEX IDENTIFIES NEW BINDING PARTNERS FOR RIBOZYMES
Natural ribozymes normally
act on only one specific substrate. Moreover, natural ribozymes are often
degraded and so do not normally process more than one substrate molecule. An
exception is RNase P, which can catalyze multiple cleavages of different tRNA
molecules. One goal of biotechnology is to increase the number of substrates
for the known ribozymes.
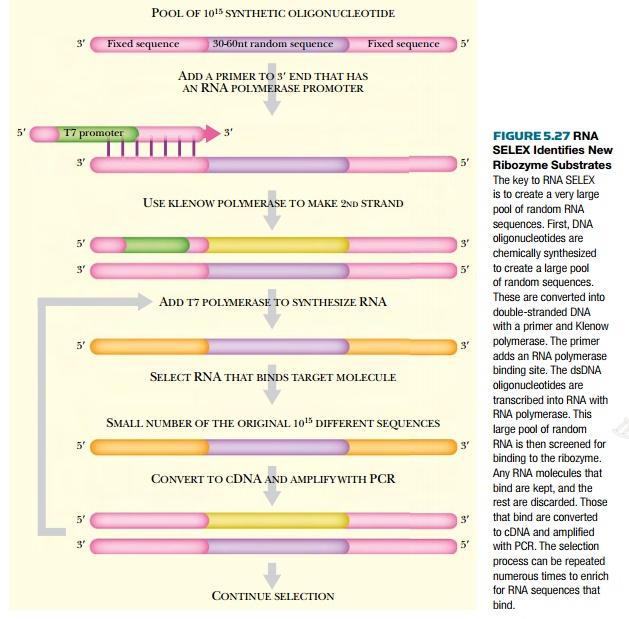
To identify new potential
substrates for existing ribozymes, a procedure called RNA SELEX can be used.
SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment) isolates new
substrates for existing enzymes from a large (1015) population of
random-sequence oligonucleotides (Fig. 5.27). First, the mixture of random
oligonucleotides is chemically synthesized as single-stranded DNA. To make the
RNA, the random oligonucleotides are converted into double-stranded DNA using a
5′ primer and Klenow polymerase. The 5′ primer contains the promoter sequence
for T7 RNA polymerase, which is added to the pool of dsDNA to make multiple
single-stranded RNA copies. The ribozyme of interest is then mixed with this
large pool of ssRNA oligonucleotides, and those RNA molecules that bind to the
ribozyme are isolated. In order to facilitate isolation, the ribozyme can be immobilized
on beads or linked to biotin. The binding sequences can be directly identified,
or they can be pooled and put through repeated cycles of selection, thus
eliminating those that bound nonspecifically. In order to identify the new
binding substrate, the RNA must be released from the ribozyme. It is then
converted into cDNA using a 3′ primer and reverse transcriptase.
Because the actual number of
specific binding molecules is low, these are amplified using PCR before
sequencing.
The use of SELEX extends
beyond ribozymes. It can be applied to drug design and delivery. The process
can be applied to finding DNA binding substrates for different enzymes. In DNA
SELEX, the initial pool of random-sequence oligonucleotides is not converted to
mRNA with RNA polymerase. Instead, the oligonucleotides are used directly in
substrate binding and selection.
Related Topics