Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: RNA-Based Technologies
Allosteric Deoxyribozymes Catalyze Specific Reactions
ALLOSTERIC
DEOXYRIBOZYMES CATALYZE SPECIFIC REACTIONS
Because some RNA has
catalytic properties, researchers investigated whether DNA has catalytic potential.
Although no natural catalytic DNA molecules are known, DNA nonetheless has the
ability to catalyze various reactions in a manner similar to RNA-based
ribozymes. Indeed, in vitro selection was used to create a deoxyribozyme that
can split thymine dimers caused by UV radiation of DNA. Different organisms
have various mechanisms to deal with these dimers. For example, excision repair
removes the damaged strand and replaces it with new DNA. Another mechanism
involves photolyase enzymes, which are activated by light.
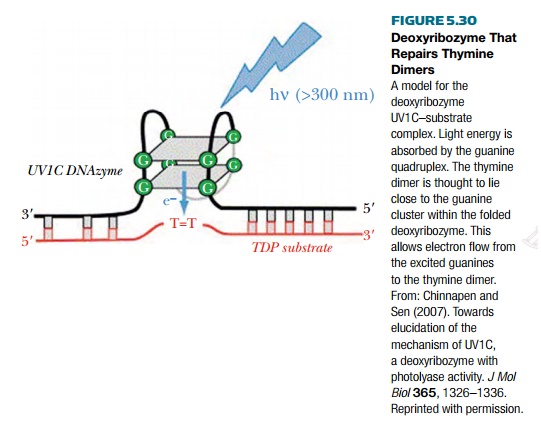
These enzymes recognize and
repair thymine dimers in response to blue light.
In order to identify a DNA
sequence that could accomplish the photolyase reaction, in vitro selection was
carried out on a pool of random DNA oligonucleotide sequences. The random
sequences were first linked to a substrate that consisted of two DNA
oligonucleotides joined via a thymine dimer. If a random oligonucleotide split
the thymine dimer after exposure to blue light, then the overall length of the
DNA construct would be smaller. The smaller species were isolated by gel
electrophoresis. This was successful, and a specific deoxyribozyme (UV1C) that
could catalyze a photolyase reaction was identified (Fig. 5.30).
Related Topics