Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 4 : Hydrogen
Physical and Chemical properties of Hydrogen Peroxide
Physical properties:
Pure hydrogen peroxide is almost a colorless liquid (pale blue), less volatile and more viscous than water.
A 30 % solution of hydrogen peroxide is marketed as ‘100-volume’ hydrogen peroxide indicating that at S.T.P., 100 ml of oxygen is liberated by 1 ml of this solution on heating.
Chemical properties:
Hydrogen peroxide is highly unstable and the aqueous solution spontaneously disproportionates to give oxygen and water. The reaction is, however, slow but is explosive when catalyzed by metal. If it is stored in glass container, it dissolves the alkali metals from the glass, which catalyzes the disproportionation reaction. For this reason, H2O2 solutions are stored in plastic bottles.
H2O2 → H2O + ½O2
Hydrogen peroxide can act both as an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. Oxidation is usually performed in acidic medium while the reduction reactions are performed in basic medium
In acidic conditions:
H2O2 + 2 H+ +2 e- → 2 H2O (E0 = + 1.77 V)
For example
2FeSO4+H2SO4 + H2O2 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 2H2O
In basic conditions:
HO2- + OH- oO2 + H2O + 2 e-
(E0 = + 0.08 V)
For Example,
2KMnO4 (aq) + 3 H2O2 (aq)
↓
2MnO2 + 2 KOH + 2 H2O +3O2 (g)
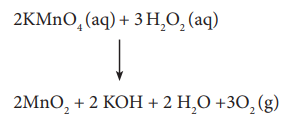
Related Topics