Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antiprotozoal Drugs
Metronidazole & Tinidazole
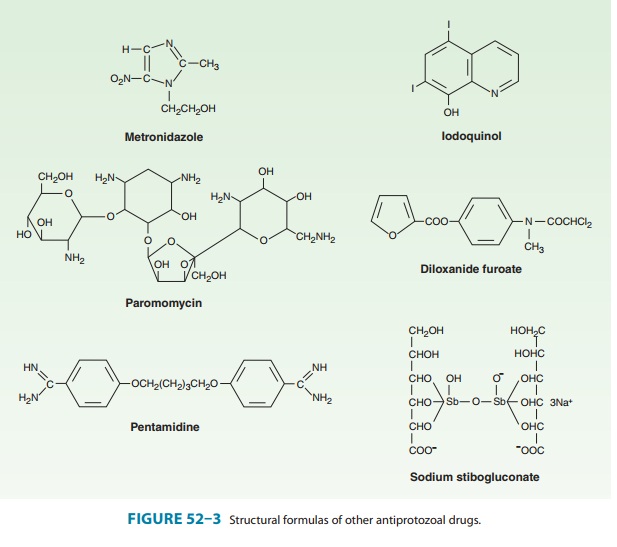
METRONIDAZOLE & TINIDAZOLE
Metronidazole, a
nitroimidazole (Figure 52–3), is the drug of choice in the treatment of extraluminal
amebiasis. It kills tropho-zoites but not cysts of E histolytica and effectively eradicates
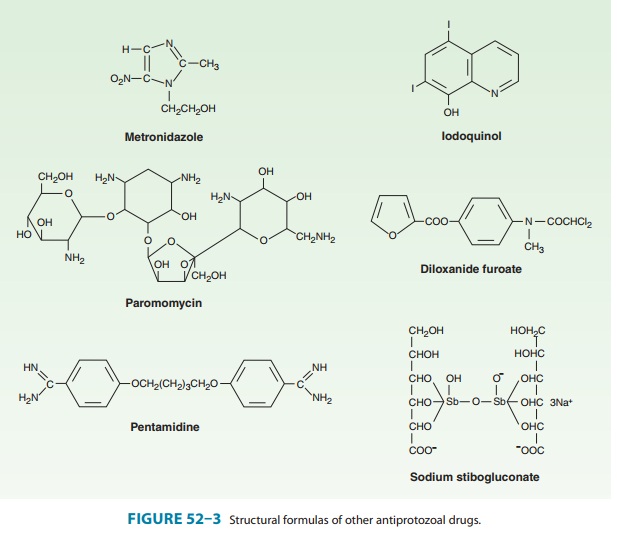
Tinidazole, a related nitroimidazole
available in the USA since 2004, appears to have similar activity and a better
toxicity profile than metronidazole. It offers simpler dosing regimens and can
be substituted for the indications listed below.
Pharmacokinetics & Mechanism
of Action
Oral metronidazole and
tinidazole are readily absorbed and permeate all tissues by simple diffusion.
Intracellular concentrations rapidly approach extracellular levels. Peak plasma
concentrations are reached in 1–3 hours. Protein binding of both drugs is low
(10–20%); the half-life of unchanged drug is 7.5 hours for metronidazole and
12–14 hours for tinidazole. Metronidazole and its metabolites are excreted
mainly in the urine. Plasma clearance of metronidazole is decreased in patients
with impaired liver function.
The
nitro group of metronidazole is chemically reduced in anaerobic bacteria and
sensitive protozoans. Reactive reduction products appear to be responsible for
antimicrobial activity. The mechanism of tinidazole is assumed to be the same.
Clinical Uses
A. Amebiasis
Metronidazole or
tinidazole is the drug of choice in the treatment of all tissue infections with
E histolytica. Neither drug is
reliably effective against luminal parasites and so must be used with a luminal
amebicide to ensure eradication of the infection.
B. Giardiasis
Metronidazole
is the treatment of choice for giardiasis. The dosage for giardiasis is much
lower—and the drug thus better tolerated— than that for amebiasis. Efficacy
after a single treatment is about 90%. Tinidazole is at least equally effective.
C. Trichomoniasis
Metronidazole is the treatment of choice. A single dose of 2 g is effective. Metronidazole-resistant organisms can lead to treatment failures. Tinidazole may be effective against some of these resistant organisms.
Adverse Effects & Cautions
Nausea, headache, dry
mouth, or a metallic taste in the mouth occurs commonly. Infrequent adverse
effects include vomiting, diarrhea, insomnia, weakness, dizziness, thrush,
rash, dysuria, dark urine, vertigo, paresthesias, and neutropenia. Taking the
drug with meals lessens gastrointestinal irritation. Pancreatitis and severe
central nervous system toxicity (ataxia, encephalopathy, seizures) are rare.
Metronidazole has a disulfiram-like effect, so that nausea and vomiting can
occur if alcohol is ingested during therapy. The drug should be used with
caution in patients with central nervous system disease. Intravenous infusions
have rarely caused seizures or peripheral neuropathy. The dosage should be adjusted
for patients with severe liver or renal disease. Tinidazole has a similar
adverse-effect profile, although it appears to be some-what better tolerated
than metronidazole.
Metronidazole
has been reported to potentiate the anticoagu-lant effect of coumarin-type
anticoagulants. Phenytoin and phe-nobarbital may accelerate elimination of the
drug, whereas cimetidine may decrease plasma clearance. Lithium toxicity may
occur when the drug is used with metronidazole.
Metronidazole
and its metabolites are mutagenic in bacteria. Chronic administration of large
doses led to tumorigenicity in mice. Data on teratogenicity are inconsistent.
Metronidazole is thus best avoided in pregnant or nursing women, although
con-genital abnormalities have not clearly been associated with use in humans.
Related Topics