Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic Disorders
Management of Patients With Viral Hepatitis
Management of Patients With Viral
Hepatic Disorders
VIRAL HEPATITIS
Viral hepatitis is a systemic, viral infection in which necrosis and inflammation of liver cells produce a characteristic cluster of clin-ical, biochemical, and cellular changes. To date, five definitive types
of viral hepatitis have been identified: hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis
A and E are similar in mode of transmission (fecal–oral route), whereas
hepatitis B, C, and D share many characteristics. Terms associated with viral
hepatitis are listed in Chart 39-5. The increasing incidence of viral hepatitis
is a public health concern. The disease is important because it is easy to
transmit, has high morbidity, and causes prolonged loss of time from school or
employment.

It is
estimated that 60% to 90% of cases of viral hepatitis go un-reported. The
occurrence of subclinical cases, failure to recognize mild cases, and
misdiagnosis are thought to contribute to the under-reporting. Although
approximately 40% of all persons in the United States have antibodies against
hepatitis A virus, many can-not recall an earlier episode or the occurrence of
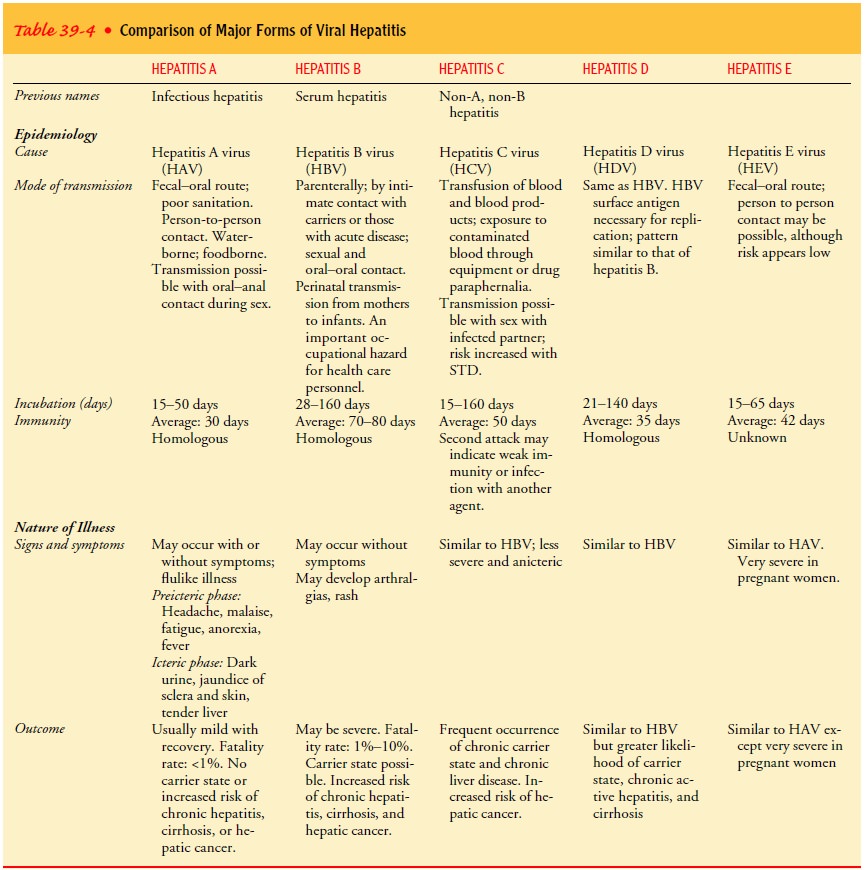
the symptoms of hepatitis (O’Grady et al., 2000). Table 39-4 compares the major
forms of viral hepatitis.
Related Topics