Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic Disorders
Diagnostic Evaluation of Patients With Hepatic Disorders
Diagnostic Evaluation
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
More
than 70% of the parenchyma of the liver may be damaged before liver function
test results become abnormal. Function is gen-erally measured in terms of serum
enzyme activity (ie, alkaline phosphatase, lactic dehydrogenase, serum
aminotransferases) and serum concentrations of proteins (albumin and
globulins), biliru-bin, ammonia, clotting factors, and lipids. Several of these
tests may be helpful for assessing patients with liver disease. However, the
na-ture and extent of hepatic dysfunction cannot be determined by these tests
alone, as many other disorders can affect their results.
Serum
aminotransferases (also called transaminases) are sensi-tive indicators of
injury to the liver cells and are useful in detect-ing acute liver disease such
as hepatitis. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (formerly called serum
glutamic-pyruvic transaminase [SGPT]), aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
(formerly called serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase [SGOT]), and gamma
glu-tamyl transferase (GGT) (also called G-glutamyl transpeptidase) are the
most frequently used tests of liver damage. ALT levels in-crease primarily in
liver disorders and may be used to monitor the course of hepatitis or cirrhosis
or the effects of treatments that may be toxic to the liver. AST is present in
tissues that have high metabolic activity; thus, the level may be increased if
there is damage to or death of tissues of organs such as the heart, liver,
skeletal muscle, and kidney. Although not specific to liver disease, levels of
AST may be increased in cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer. Increased GGT
levels are associated with cholestasis but can also be due to alcoholic liver
disease. Although the kidney has the highest level of the enzyme, the liver is
considered the source of normal serum activity. The test determines liver cell
dysfunc-tion and is a sensitive indicator of cholestasis. Its main value in
liver disease is confirming the hepatic origin of an elevated alka-line
phosphatase level. Common liver function tests are listed in Table 39-1.

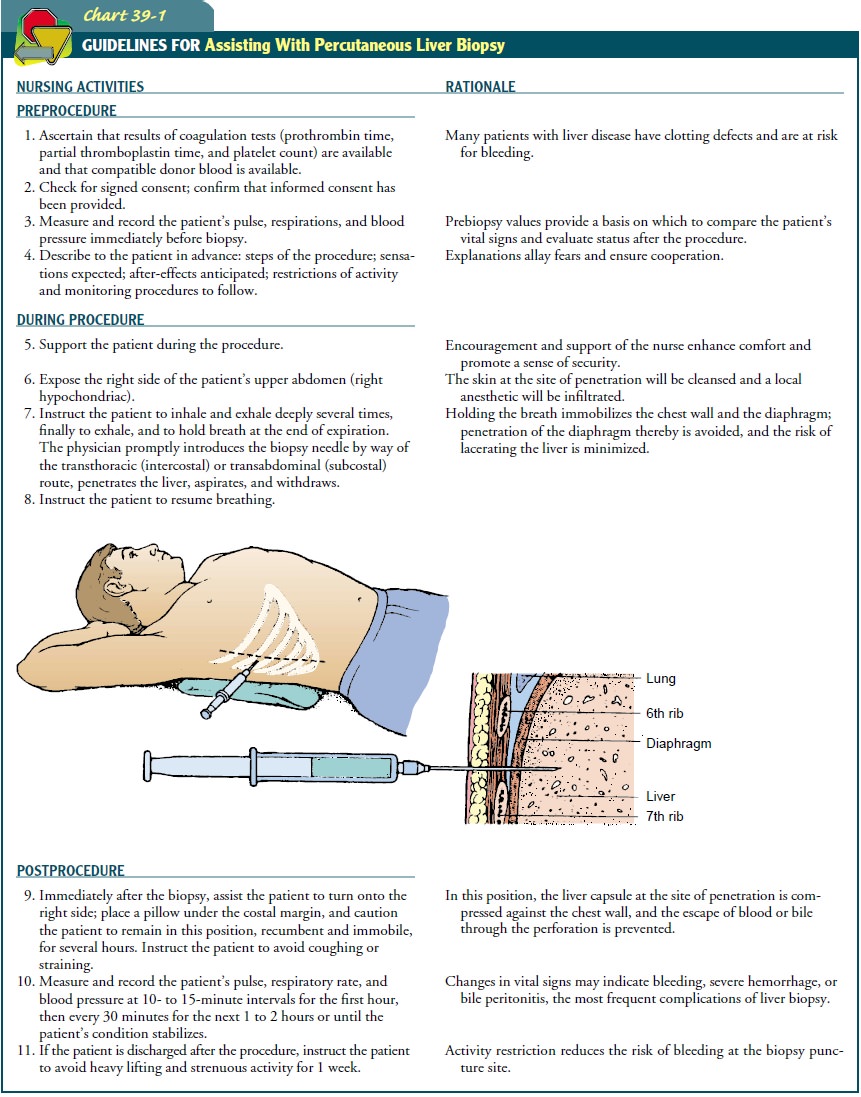
LIVER BIOPSY
Liver
biopsy is the removal of a small amount of liver tissue, usu-ally through
needle aspiration. It permits examination of liver cells. The most common
indication is to evaluate diffuse disorders of the parenchyma and to diagnose
space-occupying lesions. Liver biopsy is especially useful when clinical findings
and laboratory tests are not diagnostic. Bleeding and bile peritonitis after
liver biopsy are the major complications; therefore, coagulation studies are
obtained, their values are noted, and abnormal results are treated before liver
biopsy is performed. Other techniques for liver biopsy are preferred if ascites
or coagulation abnormalities exist. A liver biopsy can be performed
percutaneously under ultrasound guid-ance or transvenously through the right
internal jugular vein to right hepatic vein under fluoroscopic control. Liver
biopsy can also be performed laparoscopically. Nursing responsibilities
re-lated to percutaneous liver biopsy are summarized in Chart 39-1
OTHER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Ultrasonography,
computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to
identify normal structures and abnormalities of the liver and biliary tree. A
radioisotope liver scan may be performed to assess liver size and hepatic blood
flow and obstruction.
Laparoscopy
(insertion of a fiber-optic endoscope through a small abdominal incision) is
used to examine the liver and other pelvic structures. It is also used to
perform guided liver biopsy, to determine the etiology of ascites, and to diagnose
and stage tumors of the liver and other abdominal organs.
Related Topics