Definition, Types, Causes, Risk factors and Symptoms, Diagnosis, management - Hydrocele | 12th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Medical Surgical and Applied Nursing Management Psychology of Human Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Medical Surgical and Applied Nursing Management Psychology of Human Diseases
Hydrocele
Hydrocele
The testes, or testicles, are the two male reproductive glands
that produce sperm and the male hormone testosterone. They are located in the
scrotum, which is a pouch located behind the penis. Hydroceles can occur on
either side of the scrotum or, in rarer cases, on both sides.
Definition
Hydrocele is a collection of excessive fluid in the tunica vaginal
sac.
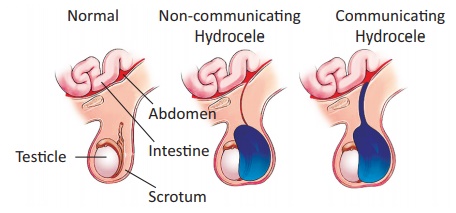
Types
•
Vaginal Hydrocele occurs when hydrocele sac in patient only
in the scrotum.
•
Infantile Hydrocele The sac from the scrotum in patient upto
the deep ingunial rings
•
True congenital Hydrocele The scrotal sac communicates with
peritoneal cavity.
•
Hydrocele of canal of Nuck: It presents as a smelling in the inguinal
region in female.
Risk factors
Injury or inflammation of the scrotum
Causes
•
Excessive production of fluid within the sac
•
Defective absorption of fluid
•
Defective lymphatic drainage of scrotal structures as in case of
elephantiasis
•
by connection with a hernia of the peritoneal cavity in the
congenital variety, which presents as hydrocele of the cord
Symptoms
•
Soft, Cystic, Not reducible, Scrotal swelling
•
Scrotal pain
•
Redness of the scrotum
•
Heaviness
•
Fullness
•
Fluid accumulation with translumination
•
Dragging sensation
•
Fever
•
Chills
•
Nausea
•
Vomiting
Diagnosis
•
History.
•
Physical examination
•
Ultrasound.
•
Blood and urine tests to check for underlying infection.
Management
•
Lord/s Plication is indicated in small hydrocoeles. The
sac is opened and the cut edge of the sac is plicated to tunica albuginea.
•
Partical excision and eversion of the sac: Jaboula’s operation
•
Aspiration-is a temporary method.
Nursing management
•
Teach about the hydrocele bandage
•
Teach coping techniques
Complications
•
Infection
•
Inguinal hernia.
•
Haematocoele
•
Pyocoele
Related Topics