Definition, Types, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, management - Diabetes Mellitus | 12th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Medical Surgical and Applied Nursing Management Psychology of Human Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Medical Surgical and Applied Nursing Management Psychology of Human Diseases
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease caused by inherited and /or
acquired deficiency in production of insulin by the pancreas, or by the
increased insulin resistance such a deficiency results in increased
concentrations of glucose in the blood, which in turn damage many of the body's
systems, in particular the blood vessels and nerves.
Definition
The term Diabetic mellitus describes a metabolic disorder of
multiple etiologies characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbance of
carbohydrate fat and protein metabolism resulting from defects of insulin
secretion, insulin action or both.
Types
•
Type 1
•
Type 2
•
Prediabetes
•
Gestational diabetes
Type 1 diabetes/Insulin dependent/ Diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
Type 1 diabetes is also referred to as Juvenile diabetes Mellitus.
It results from destruction of pancreatic β cells which produce insulin leading
to absolute insulin deficiency.
Etiology
•
Viral
•
Autoimmune
•
Environmental factors.
Type 2 diabetes/Non-Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(NIDDM)
Most common form of diabetes. Body produces insulin, but do not
use it properly, glucose doesn’t move into cells, they pile up in the
bloodstream.
Risk factors
•
Genetic
•
Autoimmune
•
Stress
•
Environmental factors
•
Obesity
Prediabetes
Slight elevation of blood glucose levels, regarded as indication
that the person is at risk of progressing to Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
is defined as carbohydrate intolerance during pregnancy.
Risk factors
•
Polycystic ovary syndrome
•
women under age 25
•
Hydraminos
Causes
•
Family history of diabetes
•
Overweight prior to pregnancy
Signs and Symptoms
•
Hyperglycemia - Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia
•
Weight loss
•
Fatigue
•
Blurred vision
•
Poor wound healing
•
Recurrent infection
Diagnosis
Urine analysis
•
Glucose
•
Ketone
•
Microalbuminuria
Blood chemistry
•
Blood glucose estimation, fasting and random blood sugar
•
Oral Glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
•
Check HbA1c (GLYCOSYLATED HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL)
Management
Type 1
•
Maintain and control sugar level
•
Insulin therapy
•
Healthy life style – exercise and diet.
•
Islet transplantation
•
Oral Antidiabetic agents
•
Lipid control
•
DIET
•
Meal plan for Caloric restriction
•
Weight reduction
•
EXERCISE: Regularly scheduled, moderate exercise performed 30 to 60
minutes/day.
•
Islet transplation
Type 2
•
Maintain a healthy lifestyle
•
Oral hypoglycemic agent and injection insulin if needed
•
Dietary management and exercise
Gestational diabetes
•
Insulin
•
Physical activity
•
Diet
•
Plan Increase fiber intake
Nursing management
•
Monitoring blood glucose.
•
Administering antidiabetics/insulin.
•
Foot care.
•
Monitoring for hyper/hypoglycemia.
•
Offering snacks at bedtime if permitted.
•
Lifestyle management
Prevention

Complications of uncontrolled diabetes
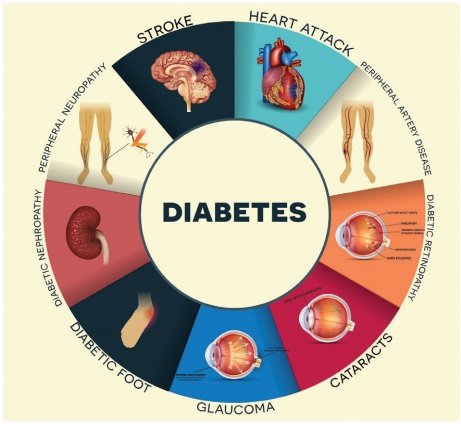
•
Hypoglycemia
•
Macroangiopathy
•
Peripheral Neuropathy
•
Micro angiopathy
•
Autonomic Neuropathy
•
Diabetic Keto acidosis (DKA)
Related Topics