Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
Gypsum: Preparation, Properties, Uses
Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O)
Gypsum beds were formed due to the evaporation of water from the massive prehistoric sea basins. When water evaporates, the minerals present in it become concentrated, and crystallise.

Properties of Gypsum
· Gypsum is a soft mineral, which is moderately soluble in water. The solubility of this mineral in water is affected by temperature. Unlike other salts, gypsum becomes less soluble in water as the temperature increases. This is known as retrograde solubility, which is a distinguishing characteristic of gypsum.
· Gypsum is usually white, colorless, or gray in color. But sometimes, it can also be found in the shades of pink, yellow, brown, and light green, mainly due to the presence of impurities.
· Gypsum crystals are sometimes found to occur in a form that resembles the petals of a flower. This type of formation is referred to as ‘desert rose’, as they mostly occur in arid areas or desert terrains.
· Gypsum is known to have low thermal conductivity, which is the reason why it is used in making drywalls or wallboards. Gypsum is also known as a natural insulator.

· Alabaster is a variety of gypsum, that is highly valued as an ornamental stone. It has been used by the sculptors for centuries. Alabaster is granular and opaque.
· Gypsum has hardness between 1.5 to 2 on Moh’s Hardness Scale. Its specific gravity is 2.3 to 2.4.
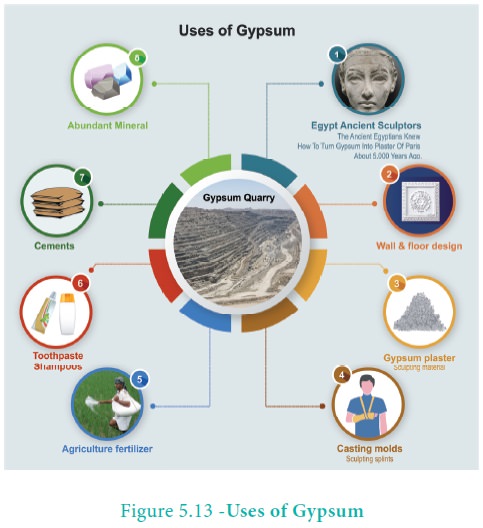
Uses of Gypsum
· The alabaster variety of gypsum was used in ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia by the sculptors. The ancient Egyptians knew how to turn gypsum into plaster of Paris about 5,000 years ago. Today, gypsum has found a wide range of uses and applications in human society, some of which are enlisted below.
· Gypsum is used in making drywalls or plaster boards. Plaster boards are used as the finish for walls and ceilings, and for partitions.
· Another important use of gypsum is the production of plaster of Paris. Gypsum is heated to about 300 degree Fahrenheit to produce plaster of Paris, which is also known as gypsum plaster. It is mainly used as a sculpting material.
· Gypsum is used in making surgical and orthopedic casts, such as surgical splints and casting moulds.
· Gypsum plays an important role in agriculture as a soil additive, conditioner, and fertilizer. It helps loosen up compact or clay soil, and provides calcium and sulphur, which are essential for the healthy growth of a plant. It can also be used for removing sodium from soils having excess salinity.
· Gypsum is used in toothpastes, shampoos, and hair products, mainly due to its binding and thickening properties.
· Gypsum is a component of Portland cement, where it acts as a hardening retarder to control the speed at which concrete sets.
· To sum up, gypsum is one of the most abundant minerals that have endless uses and applications. Mining of gypsum is simple and easy, as the mineral occurs in large thick beds near the Earth’s surface. However, large-scale mining of gypsum involves considerable damage to the environment. Gypsum can also be recycled, but not much importance has been given to recycle this mineral due to its abundance.
Related Topics