Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
General characteristics of the compounds of the alkaline earth metals
General
characteristics of the compounds of the alkaline earth metals
The dipositive oxidation state (M2+) is the
predominant valence of group 2 elements. The alkaline earth metals form
compounds which are predominantly ionic. However, they are less ionic than the
corresponding compounds of alkali metals. This is due to increased nuclear
charge and smaller size. The general characteristics of some of the compounds
of alkaline earth metals are described below.
(a) Oxides
Generally alkaline earth metals form monoxides and
peroxides.
Monoxides
Monoxides are obtained by heating the metals in oxygen.
BeO and MgO are almost insoluble in water. On the other hand, oxides of other
elements form hydroxides. BeO is amphoteric; MgO is weakly basic while CaO, SrO
and BaO are strongly basic.
BeO oxide is covalent due to the small size of Be2+ion,while
other oxides are ionic in nature.
Peroxides
Except beryllium, all the remaining metals form peroxides.
It is prepared by heating monoxides with oxygen at high temperature.
2 BaO +O2 → 2 BaO2
b) Hydroxides:
All the oxides except BeO are basic in nature and react
with water to form sparingly soluble hydroxides.
MO + H2O →M(OH)2
The solubility, thermal stability and the basic character
of the hydroxides increase down the group. The alkaline earth metal hydroxides
are, however, less basic and less stable than alkali metal hydroxides.
Beryllium hydroxide is amphoteric in nature as it reacts with both acid and
alkali.
Be(OH)2 + 2 NaOH → Na2BeO2 +2H2O
Be(OH)2 + 2HCl → BeCl2 +2H2O
c) Halides:
Alkaline earth metals form halides with general formula MX2.
They can be prepared by heating metals with halogens on heating.
M +X2 → MX2
Beryllium halides are covalent on account of smaller size
of Be+2. Beryllium halides are hygroscopic, fume in moist air and
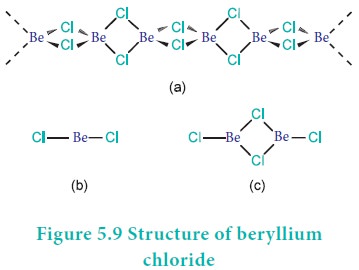
soluble in organic solvents. Beryllium chloride has a chain structure in the
solid state as shown in figure 5.9 (structure-a). In the vapour phase BeCl2
tends to form chloro-bridged dimer (structure-c) which dissociates into the
linear monomer at high temperatures of the order of 1200 K. (structure-b).
Except beryllium halides, all the other halides of
alkaline earth metals are ionic in nature. Chloride and fluorides of the other
metals are ionic solids. These are good conductors of electricity in fused
state and in aqueous solutions. The tendency to form halide hydrates gradually
decreases (for example, MgCl2..8H2O, CaCl2.6H2O,
SrCl2.6H2O and BaCl2.2H2O) down the
group.
Salts of oxo acids
The alkaline earth metals form salts of oxo acids. Some of
these are given below:
Carbonates:
All the carbonates decompose on heating to give carbon
dioxide and the oxide.
MCO3 -- ∆→
MO + CO2
·
The solubility of carbonates in water decreases down the
group.
·
The thermal stability increases down the group with
increasing cationic size.
Sulphates:
The sulphates of the alkaline earth metals are all white
solids and stable to heat. BeSO4, and MgSO4 are readily
soluble in water; the solubility decreases from CaSO4 to BaSO4.
The greater hydration enthalpies of Be2+ and Mg2+ ions
overcome the lattice enthalpy factor and therefore their sulphates are soluble
in water.
Nitrates:
The nitrates are made by dissolution of the carbonates in
dilute nitric acid. Magnesium nitrate crystallises with six molecules of water,
whereas barium nitrate crystallises as the anhydrous salt. This again shows a
decreasing tendency to form hydrates with increasing size. All of them
decompose on heating to give the oxide.
Related Topics