Chapter: Embedded Systems Design : Memory systems
Disadvantages of memory management
Disadvantages of memory
management
Given that memory management is necessary and beneficial, what are the
trade-offs? The most obvious is the delay it inserts into the memory access
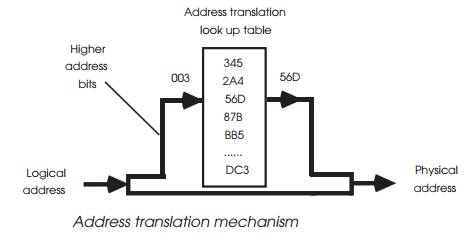
cycle. Before a translation can take place, the logical address from the
processor must appear. The translation usually involves some form of table look
up, where the contents of a segment register or the higher order address bits
are used to locate a descriptor within a memory block. This descriptor provides
the physical address bits and any partitioning information such as read only
etc. These signals are combined with the original lower order address bits to
form the physical memory address. This look up takes time, which must be
inserted into the memory cycle, and usually causes at least one wait state.
This slows the processor and system performance down.
In addition, there can be considerable overheads in manag-ing all the
look up tables and checking access rights etc. These overheads appear on
loading a task, during any memory alloca-tion and when any virtual memory
system needs to swap memory blocks out to disk. The required software support
is usually performed by an operating system. In the latter case, if the system
memory is very small compared with the virtual memory size and application, the
memory management driver will consume a lot of processing and time in simply
moving data to and from the disk. In extreme cases, this overhead starts to
dominate the system which is working hard but achieving very little. The
addition of more memory relieves the need to swap and returns more of the
system throughput to executing the application.
Related Topics