Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Management
Diabetes Management
The
main goal of diabetes treatment is to normalize insulin activ-ity and blood
glucose levels to reduce the development of vascular and neuropathic
complications. The importance of tight blood glucose control was demonstrated
by the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), a 10-year prospective
clinical trial conducted from 1983 to 1993. The trial investigated the impact
of intensive glucose control on the development and progression of
complications such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neurop-athy. A cohort of 1,441 people with type 1 diabetes were
ran-domly assigned to conventional treatment (one or two insulin injections per
day) or intensive treatment (three or four insulin injections per day or
insulin pump therapy plus frequent blood glucose monitoring and weekly contacts
with diabetes educators). Results demonstrated that the risk for developing
retinopathy, neuropathy, and early signs of nephropathy (microalbuminuria and
albuminuria) was dramatically reduced. The reduction was attributed to control
of blood glucose levels to normal or near-normal levels. The ADA now recommends
that all patients with diabetes strive for glucose control to reduce their
risks for complications (ADA, Implications of the Diabetes Control and
Complications Trial, 2003).
The major adverse effect of intensive therapy was a threefold in-crease in the incidence of severe hypoglycemia (severe enough to require assistance from another person), coma, or seizure. Because of these adverse effects, intensive therapy must be initiated with caution and must be accompanied by thorough education of the patient and family and by responsible behavior of the patient. Care-ful screening of patients is a key step in initiating intensive therapy.
A
study conducted in the United Kingdom and reported in 1998 supported the
results of the DCCT in type 2 diabetes and demonstrated a decrease in
complications in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving intensive therapy
compared to those receiving conventional therapy (United Kingdom Prospective
Diabetes Study Group [UKPDS], 1998; ADA, Implications of the United Kingdom
Prospective Diabetes Study, 2003).
Therefore,
the therapeutic goal for diabetes management is to achieve normal blood glucose
levels (euglycemia) without hypo-glycemia and without seriously disrupting the
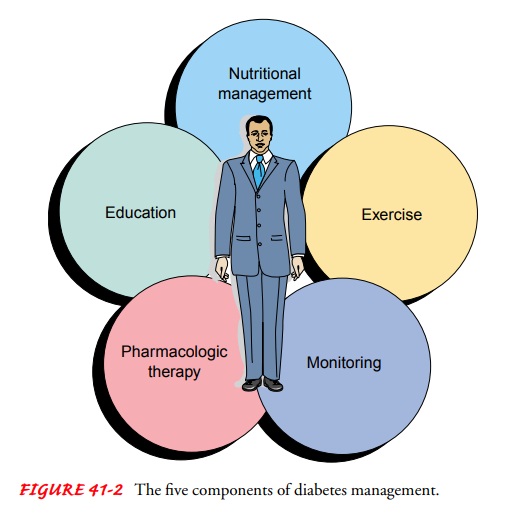
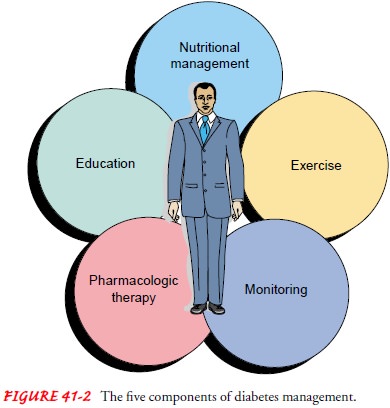
patient’s usual lifestyle and activity. There are five components of diabetes
man-agement (Fig. 41-2):
•
Nutritional management
•
Exercise
•
Monitoring
•
Pharmacologic therapy
•
Education
Treatment
varies because of changes in lifestyle and physical and emotional status as
well as advances in treatment methods. Therefore, diabetes management involves
constant assessment and modification of the treatment plan by health
professionals and daily adjustments in therapy by the patient. Although the
health care team directs the treatment, it is the patient who must manage the
complex therapeutic regimen. For this reason, patient and family education is
an essential component of diabetes treat-ment and is as important as all other
components of the regimen.
Related Topics