Chapter: Security in Computing : Security in Networks
Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems
After the perimeter controls,
firewall, and authentication and access controls block certain actions, some
users are admitted to use a computing system. Most of these controls are
preventive: They block known bad things from happening. Many studies (for
example, see [DUR99]) have shown that most computer security incidents are
caused by insiders, people who would not be blocked by a firewall. And insiders require access
with significant privileges to do their daily jobs. The vast majority of harm
from insiders is not malicious; it is honest people making honest mistakes.
Then, too, there are the potential malicious outsiders who have somehow passed
the screens of firewalls and access controls. Prevention, although necessary,
is not a complete computer security control; detection during an incident copes
with harm that cannot be prevented in advance. Halme and Bauer [HAL95] survey the
range of controls to address intrusions.
Intrusion detection systems
complement these preventive controls as the next line of defense. An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a
device, typically another separate computer, that monitors activity to identify
malicious or suspicious events. Kemmerer and Vigna [KEM02] survey the history of
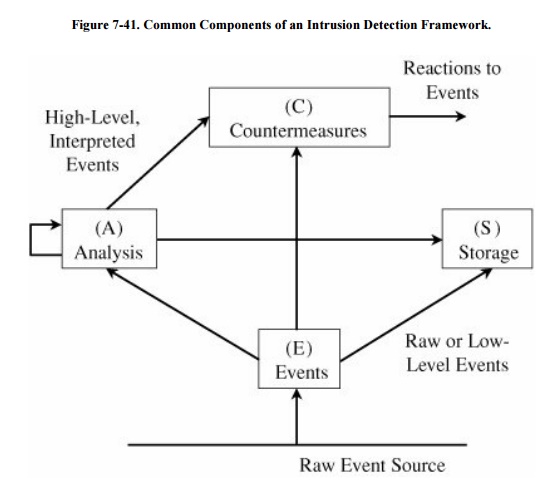
IDSs. An IDS is a sensor, like a smoke detector, that raises an alarm if
specific things occur. A model of an IDS is shown in Figure
7-41. The components in the figure are the
four basic elements of an intrusion detection system, based on the Common
Intrusion Detection Framework of [STA96]. An IDS receives raw inputs from sensors. It saves those
inputs, analyzes them, and takes some controlling action.
IDSs perform a variety of
functions:
o monitoring users and system
activity
o auditing system configuration
for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations
o assessing the integrity of
critical system and data files
o recognizing known attack
patterns in system activity
o identifying abnormal activity
through statistical analysis
o managing audit trails and
highlighting user violation of policy or normal activity
o correcting system
configuration errors
o installing and operating
traps to record information about intruders
No one IDS performs all of these
functions. Let us look more closely at the kinds of IDSs and their use in
providing security.
Related Topics