Chapter: Artificial Intelligence
The RETE matching algorithm
The RETE matching algorithm
One potential problem with expert systems is the number of
comparisons that need to be made between rules and facts in the database.
In some cases, where there are hundreds or even thousands of
rules, running comparisons against each rule can be impractical.
The Rete Algorithm is an efficient method for solving this
problem and is used by a number of expert system tools, including OPS5 and
Eclipse.
The Rete
is a directed, acyclic, rooted graph.
Each path
from the root node to a leaf in the tree represents the left-hand side of a
rule.
Each node
stores details of which facts have been matched by the rules at that point in
the path. As facts are changed, the new facts are propagated through the Rete
from the root node to the leaves, changing the information stored at nodes
appropriately.
This
could mean adding a new fact, or changing information about an old fact, or
deleting an old fact. In this way, the system only needs to test each new fact
against the rules, and only against those rules to which the new fact is
relevant, instead of checking each fact against each rule.
The Rete
algorithm depends on the principle that in general, when using forward chaining
in expert systems, the values of objects change relatively infrequently,
meaning that relatively few changes need to be made to the Rete.
In such
cases, the Rete algorithm can provide a significant improvement in performance
over other methods, although it is less efficient in cases where objects are
continually changing.
The basic
inference cycle of a production system is match, select and execute as
indicated in Fig 8.6. These operations are performed as follows
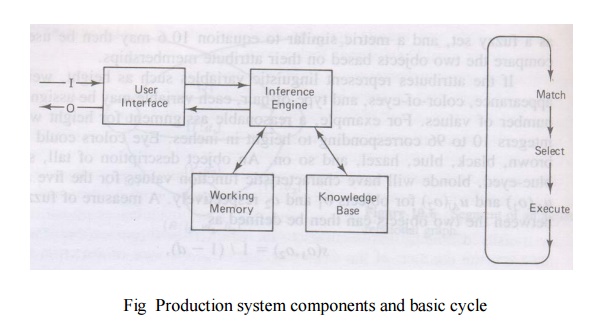
Match
During
the match portion of the cycle, the conditions in the LHS of the rules in the knowledge base are matched
against the contents of working memory to determine which rules have their LHS
conditions satisfied with consistent bindings to working memory terms.
Rules
which are found to be applicable are put in a conflict set
Select
From the
conflict set, one of the rules is selected to execute. The selection strategy may depend on recency of
useage, specificity of the rule or other criteria
Execute
The rule
selected from the conflict set is executed by carrying the action or conclusion part of the rule, the
RHS of the rule. This may involve an I/O operation, adding, removing or
changing clauses in working memory or simply causing a halt
The above
cycle is repeated until no rules are put in the conflict set or until a stopping condition is reached
The main
time saving features of RETE are as follows
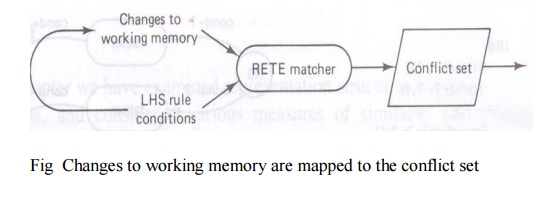
in most
expert systems, the contents of working memory change very little from cycle to
cycle. There is persistence in the data known as temporal redundancy. This
makes exhaustive matching on every cycle unnecessary. Instead, by saving match
information, it is only necessary to compare working memory changes on each
cycle. In RETE, addition to, removal from, and changes to working memory are
translated directly into changes to the conflict set in Fig . Then when a rule
from the conflict set has been selected to fire, it is removed from the set and
the remaining entries are saved for the next cycle. Consequently, repetitive
matching of all rules against working memory is avoided. Furthermore, by
indexing rules with the condition terms appearing in their LHS, only those
rules which could match. Working memory changes need to be examined. This
greatly reduces the number of comparisons required on each cycle
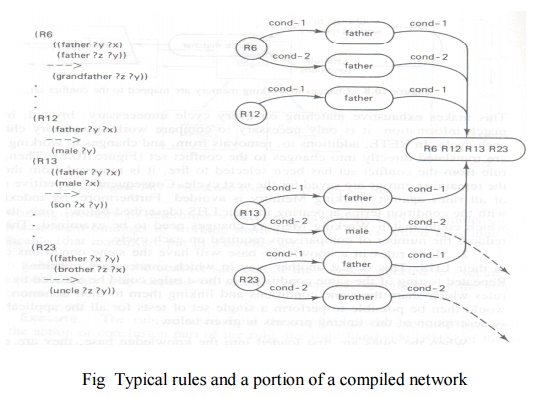
Many
rules in a knowledge base will have the same conditions occurring in their LHS.
This is just another way in which unnecessary matching can arise. Repeating
testing of the same conditions in those rules could be avoided by grouping
rules which share the same conditions and linking them to their common terms.
It would then be possible to perform a single set of tests for all the applicable
rules shown in Fig below
Related Topics