Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 6 : Gaseous State
Summary: Gaseous State (Chemistry)
SUMMARY
The state of a gas is defined by a relationship between
the four independent variables pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T) and
number of moles (n). The relationship between these parameters is governed by
different gas laws as summarised below.
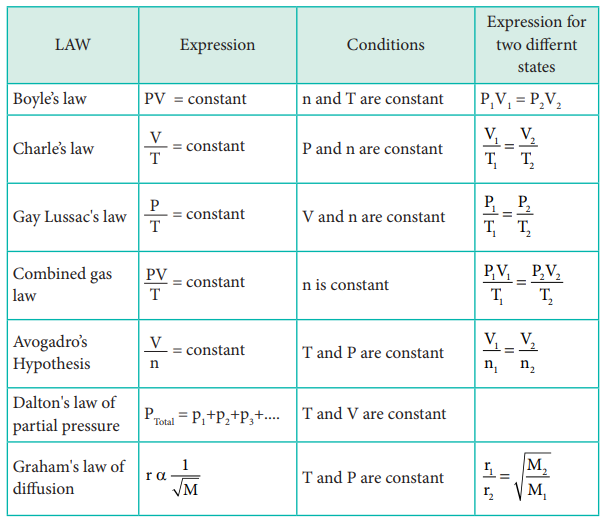
Gases that obey the equation PV=nRT under all conditions
are called ideal gases. But in practice there is no ideal gas. Gases tend to
behave ideally at high temperatures and at low pressures. For real gases, van
der Waals modified the ideal gas equation as
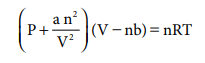
Critical temperature (Tc) of a gas is defined
as the temperature above which it cannot be liquefied at any pressure. Critical
pressure (Pc) of a gas is defined as the minimum pressure required
to liquefy 1 mole of a gas at its critical temperature. Critical volume (Vc)
is defined as the volume occupied by 1 mole of a gas at its critical
temperature and critical pressure. The critical constants are related to Van
der Waals constants as follows
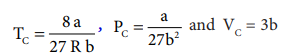
When a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region
of high pressure into a region of low pressure, the temperature of the gas is
reduced rapidly and this is known as Joule-Thomson effect. This effect is used
in the liquefication of gases.
Related Topics