Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : TQM Tools & Techniques
Six Sigma
SIX SIGMA
Prerequisite Discussion
Six Sigma is a set of techniques and
tools for process improvement. It was developed by Motorola in 1986, coinciding
with the Japanese asset price bubble which is reflected in its terminology.
Six Sigma seeks to improve the
quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects
(errors) and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes. It
uses a set of quality management methods, including statistical methods, and
creates a special infrastructure of people within the organization
("Champions", "Black Belts", "Green Belts",
"Yellow Belts", etc.) who are experts in these methods.
WHAT IS SIX SIGMA?
┬Ę
Six sigma stands for six standard
deviation from mean (sigma is the Greek letter used to represent
standard deviation in statistics).
┬Ę
Six sigma, similar to Zero Defect (ZD), is a
philosophical benchmark or standard of excellence proposed by Philip Crosby.
┬Ę
Six sigma methodology provides the techniques and
tools to improve the capability and reduce the defects in any process.
┬Ę
It was started by Motorola in 1987, in its
manufacturing division.
┬Ę
Six sigma strives for perfection. It allows for
only 3.4 defects per million opportunities (or 99.999666 percent
accuracy). Here a defect can be anything from a faulty party to an incorrect
customer bill.
┬Ę
Six sigma improves the process performance,
decrease variation and maintains consistent quality of the
process output. This leads to defect reduction and improvements in profits, product
quality and customer satisfaction.
┬Ę
Six sigma incorporates the basic principles and
techniques used in business, statistics and engineering.
The objective of six sigma
principle is to achieve zero defects products/process. It allows 3.4 defects
per million opportunities.
WHY DO WE NEED SIX SIGMA?
(Three sigma quality is not enough. Why?)
We know that, the three sigma
quality, i.e., the natural variability (x ┬▒ 3s) is equal
to tolerance (= upper specification limit ŌĆō lower
specification limit). It means, in normal distribution curve, only 0.27% of the
output would be expected to fall outside the specifications limits.
![]()
The real meaning of 3s concept: A medium aircraft consists of
10,000 different parts. At 3s quality,
27 of those parts in an assembled aircraft would be defective. So three sigma
quality level cannot be accepted as good enough quality level. So we have to
increase the sigma level (i.e.,
reducing the number of
defectives). In fact, even four sigma quality also not sufficient for the
aircraft case. ThatŌĆÖs why six sigma quality level is
preferred than 3Žā and 4Žā quality levels.
CONCEPT
Six Sigma ŌĆō A vision of quality which equates with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities for each product or service transaction. Strives for perfection.
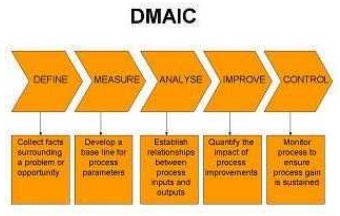
DMAIC methodology provides a structured framework for solving business problems by assuring correct and effective process execution.
This methodology has 6 phases in which, in the case of Six Sigma, teams take total employee involvement approaches to complete the cycle of process management and use self-diagnosis skills to fulfill the goals of each phase.
DMAIC
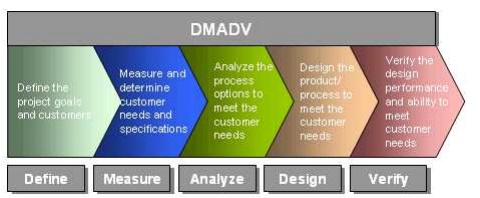
DMADV
DMAIC ŌĆō It is
used for improving existing processes/products.
DMADV ŌĆō It is
applied to a new processes/products.
Example: (Need for Six Sigma)
ŌĆó Aircraft consist 10000 different parts.
ŌĆó At 3 sigma level27 parts will be defective.
ŌĆó It cannot afford to fail 27 parts in million at 3 sigma level.
ŌĆó Similarly 1). Failure in surgery. 2). Testing of nuclear plant.
ŌĆó Therefore increased to six sigma level. (reduce the number of defects)
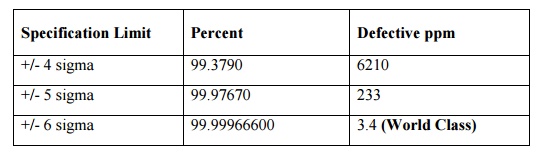
Significance:
Each Six Sigma project carried out within an organization follows a defined sequence of steps and has quantified value targets, for example: reduce process cycle time, reduce pollution, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and increase profits.
Companies
which have adopted six sigma:
┬Ę
Motorola
┬Ę
Sony
┬Ę
IBM
┬Ę
Honda
┬Ę
Texas Instruments
┬Ę
Hitachi
┬Ę
Polaroid
┬Ę
Canon
Glossary
:
DMAIC ŌĆō It is
used for improving existing processes/products.
DMADV ŌĆō It is
applied to a new processes/products.
Related Topics