Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : TQM Tools & Techniques
Quality Function Deployment
QUALITY FUNCTION DEPLOYMENT
Prerequisite discussion:
Ultimately the goal of QFD is to translate often subjective quality criteria into objective ones.
That can be quantified and measured and which can then be used to design and manufacture the product.
It is a complimentary method for determining how and where priorities are to be assigned in product development.
Quality Function Deployment was developed by Yoji Akao in Japan in 1966.
QFD TEAM :
There are two types of teams namely
1. Team for designing a new product
2. Team for improving an existing product
BENEFITS OF QFD :
1. Improves Customer satisfaction
├ś Creates focus on customer requirements
├ś Uses competitive information effectively
├ś Prioritizes resources
├ś Identifies items that can be acted upon
2. Reduces Implementation Time
├ś Decreases midstream design changes
├ś Limits post introduction problems
├ś Avoids future development redundancies
3. Promotes Team Work
├ś Based on consensus
├ś Creates communication
├ś Identifies actions
4. Provides Documentation
├ś Documents rationale for design
├ś Adds structure to the information
├ś Adapts to changes (a living document)
HOUSE OF QUALITY:
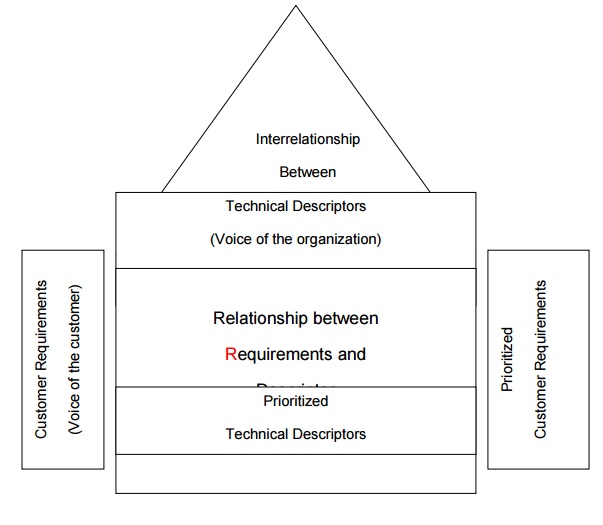
THE STEPS IN BUILDING A HOUSE OF QUALITY ARE :
1. List Customer Requirements (WHATŌĆÖs)
2. List Technical Descriptors (HOWŌĆÖs)
3. Develop a Relationship Matrix Between WHATŌĆÖs and HOWŌĆÖs
4. Develop an Inter-relationship Matrix between HOWŌĆÖs
5. Competitive Assessments
a. Customer Competitive Assessments
b. Technical Competitive Assessments
6. Develop Prioritized Customer Requirements
7. Develop Prioritized Technical Descriptors
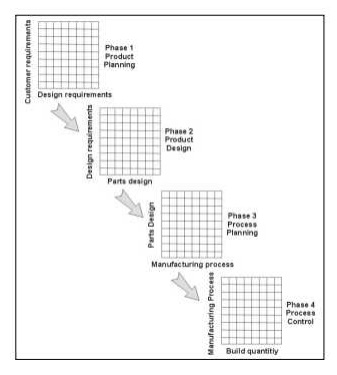
Phase 1, Product Planning: Building the House of Quality. Led by the marketing department,Phase 1, or product planning, is also called The House of Quality.
.
Phase 1 documents customer requirements, warranty data, competitive opportunities, product measurements, competing product measures, and the technical ability of the organization to meet each customer requirement.
Getting good data from the customer in Phase 1 is critical to the success of the entire QFD process. Phase 2, Product Design: This phase 2 is led by the engineering department. Product design requires creativity and innovative team ideas. Product concepts are created during this phase and part specifications are documented. Parts that are determined to be most important to meeting customer needs are then deployed into process planning, or Phase 3.
Phase 3, Process Planning: Process planning comes next and is led by manufacturing engineering. During process planning, manufacturing processes are flowcharted and process parameters (or target values) are documented.
Phase 4, Process Control: And finally, in production planning, performance indicators are created to monitor the production process, maintenance schedules, and skills training for operators. Also, in this phase decisions are made as to which process poses the most risk and controls are put in place to prevent failures.
Significance: QFD "is a method for developing a design quality aimed at satisfying the consumer and then translating the consumer's demand into design targets and major quality assurance points to be used throughout the production phase. ...
QFD is a way to assure the design quality while the product is still in the design stage.
Quality Function Deployment is a planning tool used to fulfill customer expectations.
Quality Function Deployment focuses on customer expectations or requirements, often referred to as voice of the customer.
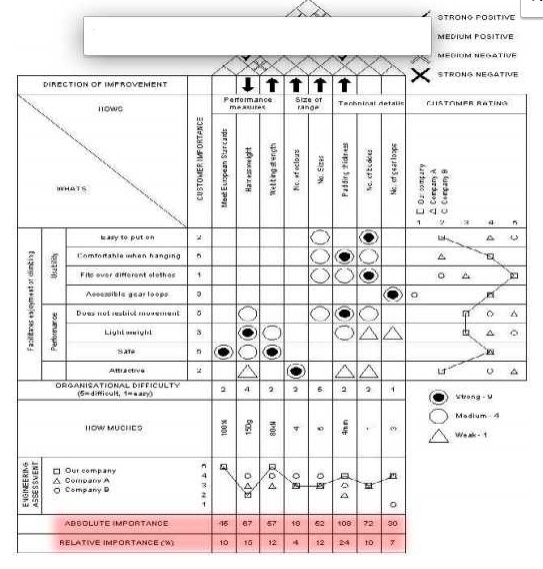
HOUSE OF QUALITY:
The primary planning tool used in QFD is the house of quality. The house of quality converts
the voice of the customer into product design characteristics. QFD uses a series of matrix diagrams, also called ŌĆśquality tablesŌĆÖ, resembles connected houses.
Basic structure of house of quality:
1. Customer requirements
2. Prioritized customer requirements
3. Technical descriptors
4. Relationship matrix
5. prioritized technical descriptors
6. Competitive assessments
7. Develop a relationship matrix between WHATS AND HOWS
Constructing the house of quality:
Step1: List customer requirements
Step2: List technical descriptors
Step3: Develop a relationship matrix between HOWS
Step4: competitive assessments
Step5: Develop prioritized customer requirements
Step6: Develop prioritized technical descriptors
QUALITY FUNCTION DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
Phase 1: product planning
Step1: list customer requirements Step2: List technical descriptors
Step3: Develop a relationship between WHATS AND HOWS Step4: Develop a interrelationship matrix between HOWS Step5: Do competitive assessments
Step6: Develop prioritized customer requirements Step7: Develop prioritized technical descriptors. Phase 2: part development
Step8: Deploy QFD process down to sub-components level both in terms of requirements and characteristics.
Step9: Deploy the component deployment chart. Relate the critical sub-component control characteristics.
Phase 3: process planning
Step10: Develop the relationship between the critical characteristics and process used to create the characteristics
Step11: Develop the control plan relating critical control to critical processes.
Phase 4: production planning
Step 12: Tabulate operating instructions from process requirements
Step13: develop prototype and do testing
Step14: Launch the final product to the market.
APPLICATION:
QFD is applied in a wide variety of services, consumer products, military needs,[2] and emerging technology products. The technique is also included in the new ISO 9000:2000standard which focuses on customer satisfaction.[3]
While many books and articles on "how to do QFD" are available, there is a relative paucity of example matrices available. QFD matrices become highly proprietary due to the high density of product or service information found therein.
GLOSSARY:
QFD: The voice of the customer translated into the voice of the engineer.
Quality
Function Deployment (QFD)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
is a way of making the 'voice of the customer' heard throughout an
organization. It is a systematic process for capturing customer requirements
and translating these into requirements that must be met throughout the 'supply
chain'. The result is a new set of target values for designers, production
people, and even suppliers to aim at in order to produce the output desired by
customers.
QFD is particularly valuable when
design trade-offs are necessary to achieve the best overall solution, e.g.
because some requirements conflict with others. QFD also enables a great deal
of information to be summarized in the form of one or more charts. These charts
capture customer and product data gleaned from many sources, as well as the
design parameters chosen for the new product. In this way they provide a solid
foundation for further improvement in subsequent design cycles.
QFD is sometimes referred to by
other 'nicknames' - the voice of the customer (from its use as a way of
communicating customer needs), or the House of Quality (from the characteristic
house shape of a QFD chart). History The creation of QFD is generally
attributed to Mitsubishi's Kobe shipyard in Japan. The original approach,
conceived in the late 1960's, was adopted and developed by other Japanese
companies, notably Toyota and its suppliers. In 1986 a study by the Japanese
Union of Scientists and Engineers (JUSE) revealed that 54% of 148 member
companies surveyed were using QFD. The
sectors with the highest
penetration of QFD were transportation (86%), construction (82%), electronics
(63%), and precision machinery (66%). Many of the service companies surveyed
(32%) were also using QFD. Specific design applications in Japan range from
home appliances and clothing to retail outlets and apartment layouts.
Benefits of QFD
The main 'process' benefits of
using QFD are: improved communication and sharing of information within a
cross-functional team charged with developing a new product. This team will
typically include people from a variety of functional groups, such as marketing,
sales, service, distribution, product engineering, process engineering,
procurement, and production the identification of 'holes' in the current
knowledge of the design team the capture and display of a wide variety of
important design information in one place in a compact form support for
understanding, consensus, and decision making, especially when complex
relationships and trade-offs are involved the creation of an informational base
which is valuable for repeated cycles of product improvement
The main 'bottom line' benefits
of using QFD are: greater likelihood of product success in the marketplace, due
to the precise targeting of key customer requirements reduced overall design
cycle time, mainly due to a reduction in time-consuming design changes. This is
a powerful benefit: customer requirements are less likely to have changed since
the beginning of the design project; and more frequent design cycles mean that
products can be improved more rapidly than the competition reduced overall cost
due to reducing design changes, which are not only time consuming but very
costly, especially those which occur at a late stage. reduced product cost by
eliminating redundant features and over-design. When to use QFD QFD is a
powerful tool that leads to significant improvements in product/process
performances. However, it is not a short-term answer to product development
problems.
The method on which QFD is
implemented may have a large impact on benefits derived and companies should
take up QFD only after getting the consent and commitment of the team members.
QFD provides a systematic approach to build a team perspective on what needs to
be done, the best ways to do it, the best order to accomplish the tasks
proposed and the staffing and resources required to enhance customer
satisfaction. It is also a good format for capturing and recording/documenting
decision making. Applied through the Kaizen philosophy under Total Quality
Control, QFD is the most highly developed form of integrated product and
process development in existence. Strengths and weaknesses of QFD
Strengths include:
1. Enhanced
customer satisfaction Listening to the voice of the customer Robust design
2.Shorter time to market Reduced
rework during development Creates team consensus and commitment 3. Reduced
costs

Success with QFD Companies
using QFD for product development have on the average, experienced:
Companies that have successfully
applied QFD include Toyota, Honda, ICI, Black & Decker, Integrated Design
Control Systems and Rover.
QFD ŌĆō House of Quality
Related Topics