Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : TQM Tools & Techniques
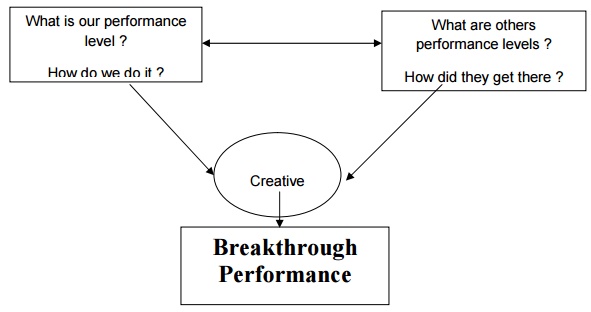
Benchmarking
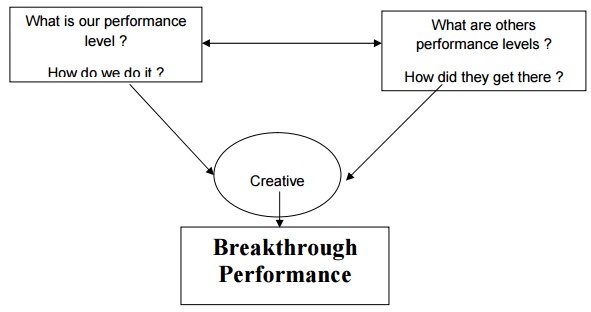
BENCHMARKING
CONCEPT:
├ś Benchmarking
is a systematic method by which organizations can measure themselves against
the best industry practices.
├ś Benchmarking
is a systematic search for the best practices, innovative ideas, and highly
effective operating procedures.
BENCHMARKING CONCEPT
REASONS
TO BENCHMARK :
├ś It is a
tool to achieve business and competitive objectives.
├ś It can
inspire managers (and Organizations) to compete.
├ś It is
time and cost effective.
├ś It
constantly scans the external environment to improve the process.
├ś Potential
and useful technological breakthroughs can be located and adopted early.
PROCESS
OF BENCHMARKING
The
following six steps contain the core techniques of Benchmarking.
1Decide
what to benchmark
├ś Benchmarking
can be applied to any business or production process.
├ś The
strategy is usually expressed in terms of mission and vision statements.
├ś Best to
begin with the mission and critical factors.
├ś Choosing
the scope of the Benchmarking study.
├ś Pareto
analysis ŌĆō what process to investigate.
├ś Cause and
Effect diagram ŌĆō for tracing outputs back.
2Understand current performance
├ś Understand
and document the current process.
├ś Those
working in the process are the most capable of identifying and correcting
problems.
├ś While
documenting, it is important to quantify.
├ś Care
should be taken during accounting information.
3Plan
├ś A
benchmarking team should be chosen.
├ś Organizations
to serve as the benchmark need to be identified.
├ś Time
frame should be agreed upon for each of the benchmarking tasks.
4Types of
benchmarking
┬Ę
Internal
┬Ę
Competitive
┬Ę
Process
5Study
Others
Benchmarking
studies look for two types of information
├ś How best
the processes are practiced
├ś Measurable
results of these practices Three techniques for conducting the research are
├ś Questionnaires
├ś Site
visits
├ś Focus
groups
6Learn
from the data
Answering
a series of questions like
├ś Is there
a gap between the organizationŌĆÖs performance and the
performance of the best-in-class organizations?
├ś What is
the gap? How much is it?
├ś Why is
there a gap? What does the best-in-class do differently that is better?
├ś If
best-in-class practices were adopted, what would be the resulting improvement?
Benchmarking
studies can reveal three different outcomes
├ś Negative
gap
├ś Parity
├ś Positive
gap
7Using the findings
The objective is to close the gap. For this
├ś Findings
must be communicated to the people within the organization
├ś Action
plans must be developed to implement new processes
Groups
that must agree on the change
├ś Process
owners
├ś Upper
management
Steps for
the development and execution of action plans are
1.
Specify tasks
2.
Sequence tasks
3.
Determine resources needs
4.
Establish task schedule
5.
Assign responsibility for each task
6.
Describe expected results
7.
Specify methods for monitoring results
PITFALLS
AND CRITICISMS OF BENCHMARKING :
├ś Idea of
copying others
├ś It is not
a cure or a business philosophy
├ś Some
process have to be benchmarked repeatedly
├ś It is not
a substitute for innovation.
SIGNIFICANCE:
├ś ŌĆó
Benchmarking is a systematic method by which organizations can measure
themselves
├ś against
the best Industry practices
├ś ŌĆó
It promotes superior performance by providing an organized framework
through which
├ś organization
learn how the ŌĆ£ best in classŌĆØ do things.
├ś ŌĆó
It helps for continuous improvement.
├ś ŌĆó
Benchmarking inspire managers (and organization) to compete.
├ś ŌĆó
Through Benchmark process organization can borrow ideas, adopt and refine them
to
├ś gain
competitive advantages.
Application:
Now a days, more than 60% companies in the world uses this
technique for fixing their target for continuous improvement. For them it is an
important tool. But to be effective it must be used properly. It breaks down
(waste money, time and energy and some times morale too) if process owners and
managers feel threatened or do not accept and act on the findings. Finally,
benchmarking is not a substitute for innovation; however, it is a source of
ideas from outsidethe organization.
These 4 questions formed the
basis on which Boeing, Digital equipments company, Motorola and Xerox jointly
developed a benchmarking template.
Related Topics