Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Silicones - structure and uses
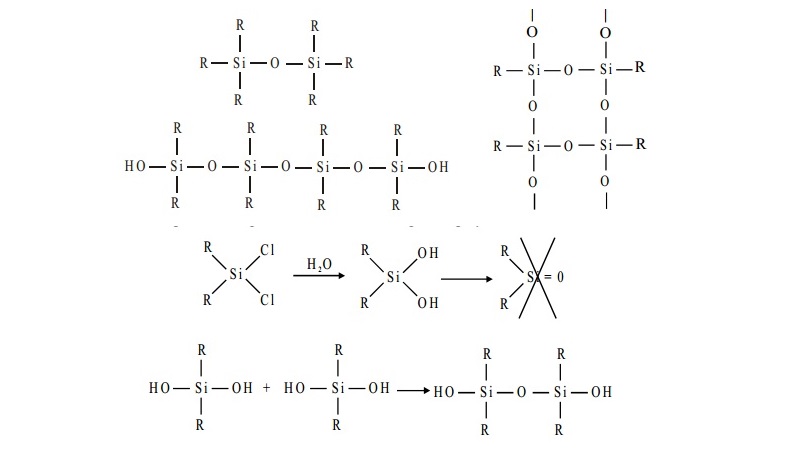
Silicones - structure and uses
The silicones are a group of organosilicon polymers.
They have a wide variety of
commercial uses.
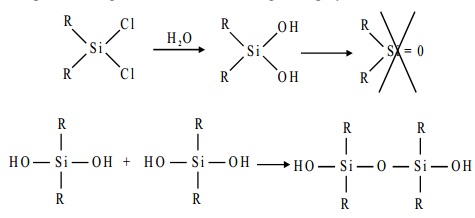
The complete hydrolysis of SiCl4 yields silica SiO2, which has a very stable three-dimensional structure. The fundamental research of
F.S. Kipping on the hydrolysis of
alkyl-substituted chlorosilanes led, not to the expected silicon compound analogous to a ketone, but to long-chain
polymers called silicones.
The starting materials for the manufacture of silicones
are alkyl-substituted chlorosilanes. Thus
the hydrolysis of trialkylmonochlorosilane R3SiCl yields hexa- alkylsiloxane.
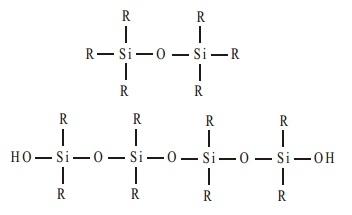
The dialkyldichlorosilane R2SiCl2 on hydrolysis gives rise to straight chain polymers
and, since an active OH group is left at each end of the chain, polymerisation continues and the chain increases
in length.
The hydrolysis of alkyl tricholorosilane RSiCl3 gives a very complex cross- linked polymer.
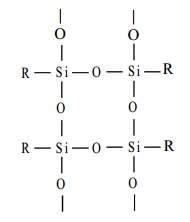
Uses
1.
Silicones act as
excellent insulators for electric motors and other appliances as they can
withstand high temperatures.
2.
Straight chain
polymers of 20 to 500 units are used as silicone fluids. They are water repellent because of the organic side group.
These polymers are used in
waterproofing textiles, as lubricants and as polish.
3.
Silicone rubber
retain their elasticity even at low temperatures and resist chemical attack. They are mixed with paints to make them
damp-resistant.
4.
Silicone resins, a
cross-linked polymer used as non-stick coating for pans and are used in paints and varnish.
5.
Silicone oils are
highly stable and non-volatile even on heating. Hence used for high temperature oil bath, high vacuum pump etc.
Related Topics