Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Metallurgy of Lead: Ores, Properties, Extraction, Purification, Uses
Metallurgy of Lead
Ores
1. Galena
PbS
2. Cerrusite
PbCO3
3. Anglesite PbSO4
4. Lead
ochre PbO
Extraction: Lead is mainly extracted from the sulphide ore galena. Galena contains lead sulphide and small quantities of silver.
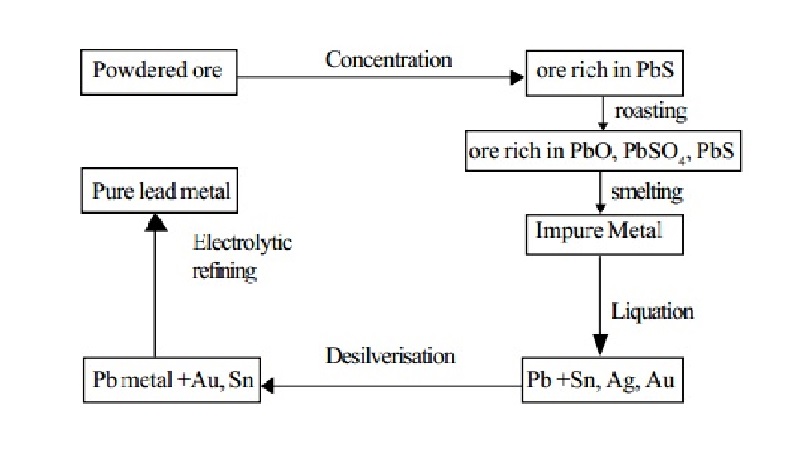
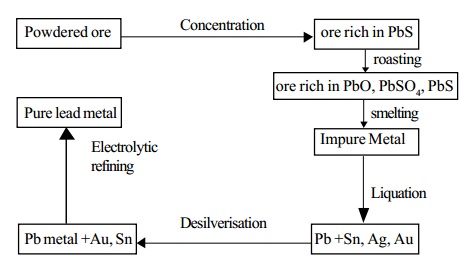
1. Concentration: The ore is concentrated by froth floatation process.
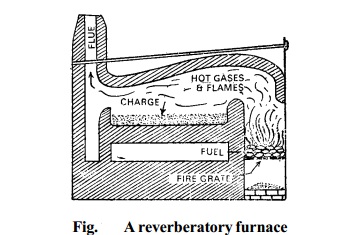
2. Smelting in a Reverberatory furnace: The concentrated ore is roasted in a reverberatory furnace at a moderate temperature.
The temperature of furnace is controlled
by regulating the air supply. During roasting, galena is partly oxidized to lead monoxide and partly to lead sulphate.
2PbS + 3O2 ® 2 PbO +
2SO2
PbS + 2O2 ® PbSO4
More of galena is then added. The temperature is raised and simultaneously the air supply is reduced. Lead sulphide reacts with the two oxidised products giving lead.
PbS+2PbO ® 3Pb+SO2
PbS+PbSO4 ® 2Pb+2SO2
Thus in this process roasting and smelting are carried
out in the same furnace,
at two different temperatures.
About 90% of lead is obtained as metal, the rest passes
into slag. Lead is
recovered from the slag by heating with lime and
powdered coke.
Purification of Lead
Lead extracted by the above method contains impurities such as silver, copper, tin, bismuth, gold and iron. It is refined by the following processes.
a. Liquation
The impure metal is heated on a sloping hearth. Lead melts and flows down the slope. The infusible impurities remain on the hearth.
b. Desilverisation
Silver is removed by either Pattinson's process or
Park's process.
c. Electrolytic refining
Very pure lead is obtained by this process.
Anode - Impure lead
Cathode - Very pure lead
Electrolyte - Lead fluosilicate + Hydrofluosilicic Acid
(PbSiF6) (H2SiF6)
The metallic impurities which are more electropositive
than lead, such as iron and tin, go into the solution while the rest of the
impurities are thrown down as anode mud.
Physical
properties
1.
Lead is a bluish
grey metal with a bright luster.
2.
It is soft and can
be cut with a knife and drawn into a wire and rolled into a sheet.
3.
It is not a good
conductor of heat and electricity. It marks paper.
Chemical properties
1. Action of air
i.
It is unaffected by
dry air but in moist air a layer of lead carbonate or lead hydroxide is deposited on its surface which protects it
from further action of air.
ii.
When heated in air
or oxygen, lead is oxidized to litharge (PbO) and red
lead (Pb3O4)
2Pb
+ O2 ® 2PbO 3Pb + 2O2 ®
Pb3O4
2. Action of water
Lead is not attacked by pure water in the absence of air,
but water containing dissolved air has
a solvent action on it due to the formation of lead hydroxide (a poisonous
substance). This phenomenon is called Plumbo solvency.
2Pb + O2 + 2H2O ® 2Pb(OH)2
3. Action of acids
i) Dilute H2SO4 and HCl
have no action on lead.
ii) Hot Conc. H2SO4 liberates
SO2 but the reaction is retarded by the formation
of an insoluble layer of lead sulphate.
Pb + 2H2SO4® PbSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
iii) Concentrated HCl evolves hydrogen and also forms
Chloroplumbic acid
Pb + 2HCl ® PbCl2 +H2
PbCl2 + 2HCl --- > < --- H2PbCl4 (chloroplumbic acid)
Uses: Lead is
used
i.
For making lead
pipes,
ii.
For making
telegraph and telephone wires,
iii.
In making bullets
and lead accumulators,
iv.
In lead chambers,
for the manufacture of sulphuric acid,
v.
For making alloys
like solder, pewter and type metal,
vi.
For preparing
tetraethyl lead (Pb(C2H5)4) which is
used as an additive to petrol to prevent
knocking
Problem
An element A belongs to 14th group and occupies period number 6. A reacts with conc. HCl. to give B an acid. A is used to prepare C which is used as an antiknock in automobiles. Identify the element A and the compounds B and C Write the reactions.
Solution
1. As per the position in the periodic table, the
element A is lead. 2. Lead with
Conc. HCl gives B
Pb + 4 HCl ® H2PbCl4 + H2
∴ Compound B is chloroplumbic acid.
3. Compound C is tetraethyl lead.
Related Topics