Chapter: Ophthalmology: Retina
Retina: Color Vision

Color Vision
Color vision defects may be congenital
(especially in men as they are inherited and X-linked recessive) or acquired,
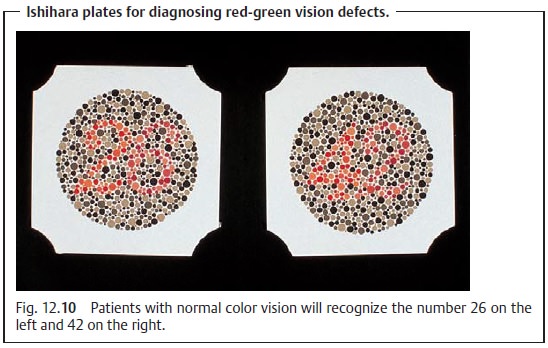
for example in macular dis-orders such as Stargardt’s disease. Qualitative red-green vision defects are evaluated with pseudoisochromatic plates such as the
Ishihara or Stilling-Velhagen plates. They contain numerals or letters composed
of small color dots surrounded by confusion colors (Fig. 12.10) that patients with color vision defects cannot read. The
Farnsworth-Munsell tests (Fig. 12.11) can detect blue-yellow color vision defects.
Pseudoisochromatic plates contain numerals
that patients with color vision defects cannot read. In the Farnsworth-Munsell
test, patients with a color vision defect cannot sort markers with different
hues (according to the colors of the rainbow) in the right order.

The Nagel anomaloscope permits quantitative evaluation of color visiondefects. The test plate consists of a lower yellow
half whose brightness can beadjusted, and an upper half that the patient tries
to match to the lower yellow color by mixing red and green. The anomaly ratio
is calculated from the final adjustment. Green-blind patients will use too much
green, and red-blind patients too much red when mixing the colors.
Related Topics