Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Polarity of Covalent Bonds
Polarity of Covalent
Bonds
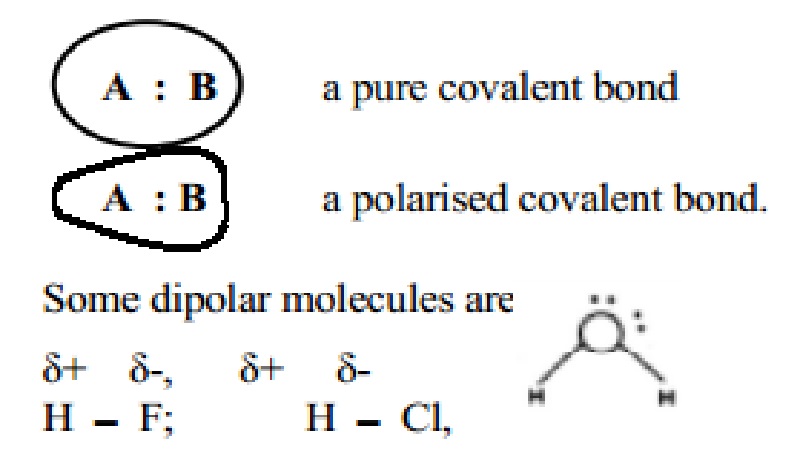
The existence of a purely ionic or covalent bond represents an ideal
situation. In the covalently bonded molecules like H2, Cl2,
F2 (homonuclear diatomics), the bond is a pure covalent bond. In
case of heteronuclear molecules like, HF, HCl, CO, NO etc, the shared electron
pair gets displaced more towards the atom possessing higher electronegativity
value than the other one. In HF, the shared electron pair is displaced more
towards fluorine because the electronegativity of Fluorine is far greater than
that of Hydrogen. This results in partial ionic character induced in the
covalent bond and is represented as:
(Delta +) H - F
(Delta -)
However, no specific charges are being found on H or F and the molecule
as a whole is neutral. Thus the extent of ionic character in a covalent bond
will depend on the relative attraction of electrons of the bonded atoms which
depends on the electro negativity differences between the two atoms
constituting the covalent bond.
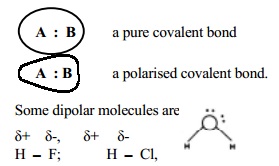
Polarisation of a covalent bond causes fractional charge (Delta + or
Delta - ) on the atoms which are separated by the bond
distance. This causes a dipolar molecule formation.
As a result of polarisation, the molecule
possessed a dipole moment. In a triatomic molecule like water two covalent
bonds exist between the oxygen atom and the two H atoms. Oxygen with higher
electronegativity attracts the shared pair of electrons to itself and thus
oxygen becomes the negative end of the dipole while the two hydrogen atoms form
the positive end. Thus the two covalent bonds in the water molecule possess
partial ionic character.
H(+) - Cl (-)
Generally larger the electronegativity difference between the atoms
consisting the bond, greater will be the ionic character. For H atom
electronegativity is 2.1 and for Cl atom it is 3.0. Thus H-Cl covalent bond is
polarised and it has more ionic character.
Consider the molecule like hydrogen cyanide HCN,
the bond between hydrogen atoms and the cyanide anion is of covalent type. CN-
ion has more capacity to pull the shared pair of electrons in the H-CN bond
that, partially H+ CN- are created. Thus in water medium
this compound is ionised into H+ and CN- ions.
H-C == N -- > H(+) - CN(-)
Related Topics