Chapter: Television and Video Engineering : Fundamentals of Television
Plumbicon
PLUMBICON
This picture tube has overcome many of the less favorable features of standard vidicon. It has fast response and produces high quality pictures at low light levels. Its smaller size and light weight, together with low-power operating characteristics, makes it an ideal tube for transistorized television cameras. Except for the target, plumbicon is very similar to the standard vidicon. Focus and deflection are both obtained magnetically. Its target operates effectively as a P–I–N semi- conductor diode.
The inner surface of the faceplate is coated with a thin transparent conductive layer of tin
oxide (SnO 2 ). This forms a strong N type (N + ) layer and serves as the signal plate of the target. On the scanning side of this layer is deposited a photoconductive layer of pure lead monoxide (PbO) which is intrinsic or ‘I’ t ype. Finally the pure PbO is doped to form a P type semiconductor on which the scanning beam lands.
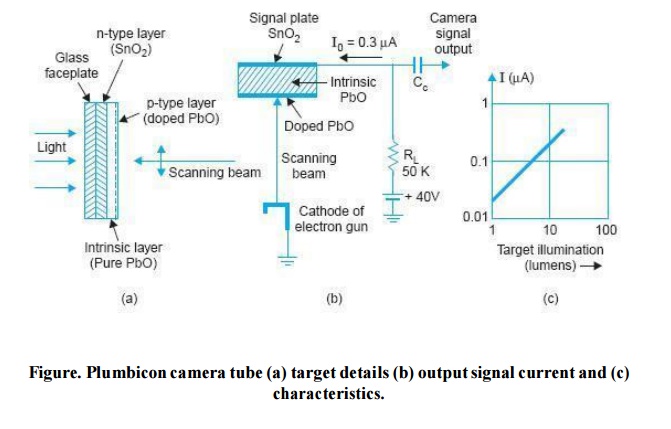
The photoconductive target of the plumbicon functions similar to the photoconductive target in the vidicon, except for the method of discharging each storage element.
In the standard vidicon, each element acts as a leaky capacitor, with the leakage resistance decreasing with increasing light intensity. In the plumbicon, however, each element serves as a capacitor in series with a reverse biased light controlled diode.
In the signal circuit, the conductive film of tin oxide (SnO 2 ), is connected to the target supply of 40 volts through an external load resistance R L to develop the camera output signal voltage.
Light from the scene being televised is focussed through the transparent layer of tin-oxide on the photoconductive lead monoxide. Without light the target prevents any conduction because of absence of any charge carriers and so there is little or no output current. A typical value of dark current is around 4 nA (4 × 10 – 9 Amp).
The incidence of light on the target results in photo excitation of semiconductor junction between the pure PbO and doped layer. The resultant decrease in resistance causes signal current flow which is proportional to the incident light on each photo element. The overall thickness of the target is 10 to 20 μm.
Light Transfer Characteristics
The current output versus target illumination response of a plumbicon is shown in Fig (c).
It is a straight line with a higher slope as compared to the response curve of a vidicon. The higher value of current output, i.e., higher sensitivity, is due to much reduced recombination of photo generated electrons and holes in the intrinsic layer which contains very few discontinuities.
For target voltages higher than about 20 volts, all the generated carriers are swept quickly across the target without much re-combinations and thus the tube operates in a photo saturated mode. The spectral response of the plumbicon is closer to that of the human eye except in the red color region.
Related Topics