Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Ortho and Para hydrogen: Conversion and Properties
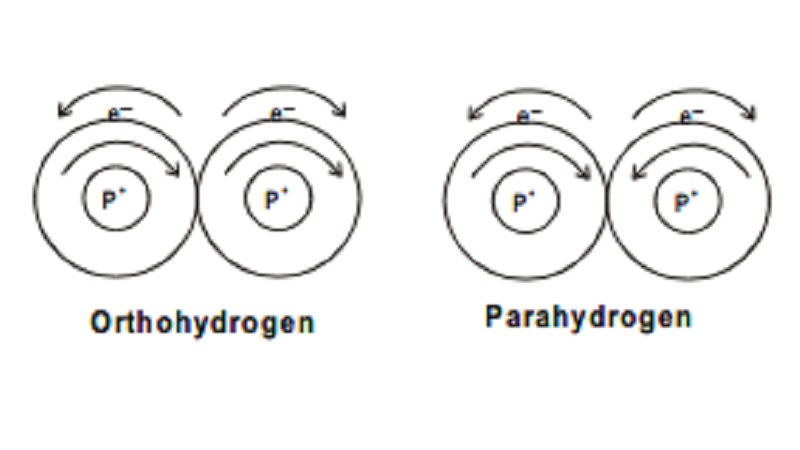
Ortho and Para hydrogen
The nucleus of the hydrogen atom spins about an
axis like a top. When two hydrogen atoms combine, they form molecular hydrogen.
Thus
depending on the direction of the two protons in the nucleus the following two
types of hydrogen molecules are known. Hydrogen molecule in which both the
protons in the nuclei of both H-atoms are known to spin in same direction is
termed as ortho hydrogen. If the protons in the nuclei of both H-atoms spin in
opposite direction, it is termed as parahydrogen.
At room temperature ordinary hydrogen consists of about 75% ortho and
25% para form. As the temperature is lowered, the equilibrium shifts in favour
of para hydrogen. At 25K. There is 99% para and 1% ortho hydrogen. The change
in the proportion of the two forms of hydrogen requires a catalyst such as
platinum or atomic hydrogen or silent electric discharge.
The para form was originally prepared by absorbing ordinary hydrogen in
activated charcoal in a quartz vessel kept at a temperature of 20K. The
charcoal absorbs almost pure para hydrogen. By this method, pure para hydrogen
can be isolated.
Conversion of para into ortho hydrogen
Ortho hydrogen is more stable than para hydrogen. The para form is
transformed into ortho form by the following methods.
1.
By treatment with catalysts like platinum or
iron
2.
By passing an electric discharge
3.
By heating to 800oC or more.
4.
By mixing with paramagnetic molecules like O2,
NO, NO2.
5.
By mixing with nascent hydrogen or atomic
hydrogen.
Properties: Ortho and para hydrogen are similar in chemical properties but differ in some of the physical
properties.
(i)
Melting point of para hydrogen is 13.83K while that of ordinary hydrogen is
13.95 K.
(ii)
Boiling point of para hydrogen 20.26K while that of ordinary hydrogen is
20.39K.
(iii) The vapour pressure of liquid para hydrogen is higher than that of
ordinary liquid hydrogen.
The magnetic moment of para hydrogen is zero
since the spins neutralise each other while in the case of ortho , it is twice
than that of a proton.
Para
hydrogen possesses a lower internal molecular energy than ortho form.
Related Topics