Chapter: Microbiology
Microbiology Taxonomy
TAXONOMY
Biodiversity (Biological diversity), the variability among the galaxy of living organizations, includes the diversity of the species between the species and of ecosystems. It is really difficult to estimate the total number of different types of eubacteria, archaeobacteria and virus, as it is very difficult to isolate and recover the organisms from the environment. Further the natural environment pose varying conditions in different ecosystems rendering huge variation among the species existing in main ecosystem. Not all environments have been investigated fully and therefore
attempts to estimate total number of species of micro organisms become more difficult. In complete understandings of cultural conditions required by certain obligate parasites add to this problem. Mycoplasma are prokaryotes but have obligate associations
with eucaryotic organisms, have remarkable diversity from some infecting insects and some infecting plants. The soil, fresh water and marine ecosystems support a group of diverse organisms on their ecosystem providing luxuriant microbial diversity.
The microorganisms have species that are free living in soil and water, mostly saprophyte in nature, a group that are parasitic on plants and a few others are obligate pathogens of plants, animals and man. Some live in aerobic environment and other living in anaerobic or microaerophilic conditions. Therefore there is a wide diversity.
The advent of DNA techniques like DNA-DNA hybridization, nucleic acid finger printing, RNA sequencing has altered the microbial diversity. The 16S r RNA sequence and DNA fingerprinting techniques have enabled to evaluate the genetic relatednessbetween organisms.
The smallest unit of microbial diversity is a species. Bacteriaare defined as a group of similar strains differentiated fromother similar groups of strains by genotypic, phenotypic and ecologicalcharacters. Bacterial strain is one with approximately 70%
or more DNA-DNA relatedness and with 5% or less in thermalstability. A bacterial species is a genomic species based on DNADNArelatedness and this concept differs from those of other organisms.There is an estimated total species of 40,000 bacteria,1,30,000 viruses, 1,50,000 fungi, 60,000 algae compared to the5000,4,760,6900 and 40,000 known species which constitute4,12,5 and 67% of known species.
The living organisms were grouped as plants, animals andprotista by Haeckel(1866). The protista are primitive organismsincluding microbe. Based on cell anatomy the bacteria were groupas prokaryotes. Whittaker proposed five kingdoms plants, fungianimals, protista and Monera based on cell anatomy and energyyielding systems. Microorganisms are in fungi, protista andmonera. Based on the fact that bacteria are distant from plantsand animals but not that far away from each other Woose and hiscoworkers proposed three domains Archaea,.Bacteria and Eukaryato cover the microorganisms. The domain bacteria include bacteria,cyanobacteria, actinonycetes etc. Archaic includesmethanogens, extremely thermophilic organisms extremely halophilicorganisms and the Eukarya includes molds, yeasts, algae,protozoa etc.
The microorganisms are named following the Linnaeusmethod of binomial nomenclature. The taxonomy denotesclassification, nomenclature and identification of organisms. Thecharacteristics or properties that are common for a few organismsare grouped together in different groups(taxa). Bacteria were traditionally based on morphological, biochemical and physiological characteristics. Serological tests and Genetic tools are valuable in identification.
The general methods of classifying bacteria is by (I) intuitive method(ii) numerical taxonomy iii. Genetic Relatedness method.
While identifying a bacteria morphological, physiological, biochemical general and molecular characteristics of organisms are studied. It may be difficult to classify an organism as different microbiologists may consider different characteristics as important. This is the intuitive method.
Numerical taxonomy gives equal weightage for each character of the strain. The percentage similarly of each strain is determined with the following formula
% S = NS / (NS+ND)
Where NS: Number of characters for each strain which are similar or dissimilar
ND = Number of characters that are different.,
%S, S = Similarly if it is high to each other placed with groups.
In Genetic relatedness classification is based on relatedness(DNA an RNA) between organisms. The percent G+C determines the relatedness. If two bacteria have a different not % G+C then the species are different and not related. DNA homology
(DNA-DNA hybridization) is also determined to assesses the relatedness. The DNA from a bacterium is isolated and the two strands are separated and a single strand is mixed with that obtained from another. If the two bacteria are similar the pairing of strands will occur, otherwise no pairing will occur.



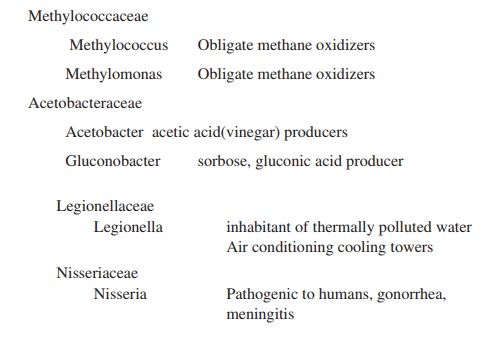

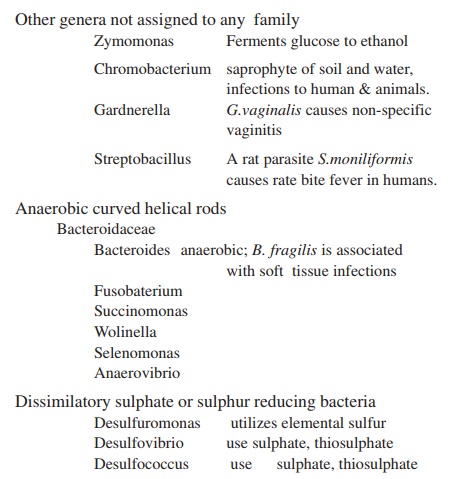





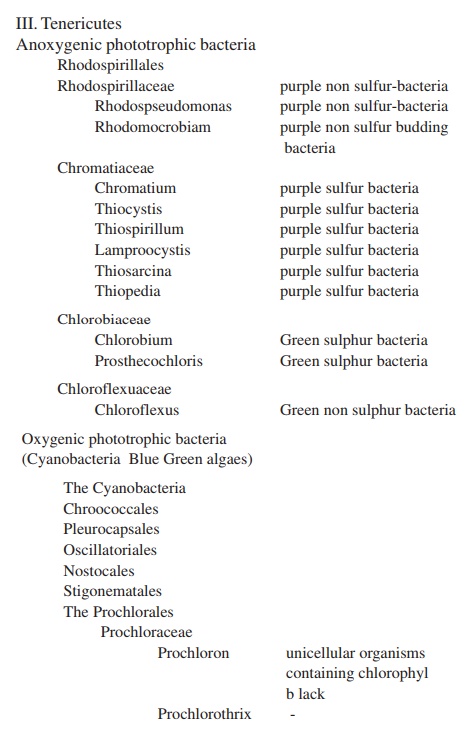



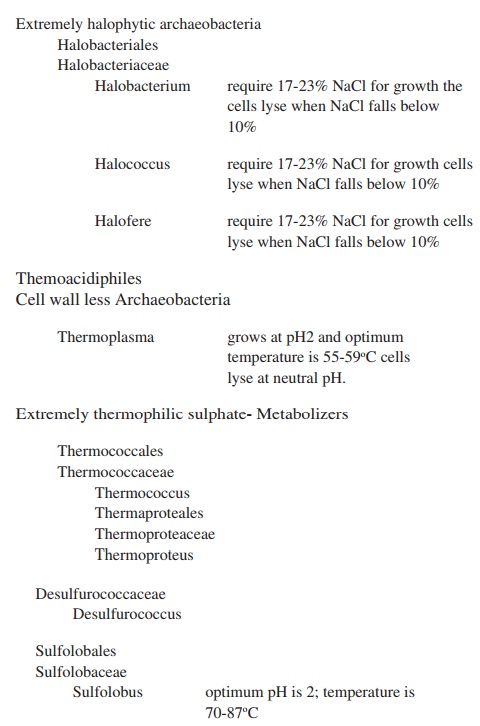

Related Topics