Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Methods for the purification of liquids Distillation
Methods
for the purification of liquids Distillation
Distillation is used for separating the
constituents of a liquid mixture which differ in their boiling points.
Depending upon the difference in the boiling points of the constituents,
different types of distillation are employed. These are described below.
i) Simple
Distillation
Liquids with boiling points widely apart (about 40K and above) can be
purified by simple distillation if they do not decompose under ordinary
pressure. Simple distillation involves conversion of a liquid into its vapour
by heating in a distilling flask and then condensation of the vapour into a
liquid in the receiver.
Mixtures like the following can be separated by this simple
distillation.
a Nitro
benzene (b.p 484K) and benzene (b.p.354K)
b. Diethyl
ether (b.p.308K) and ethyl alcohol (b.p.351K)
Note : Simple distillation is also helpful in separating non-volatile
impurities from liquids.
Fractional
Distillation
This method is applicable for the separation and
purification of a mixture of two or more miscible liquids whose boiling points
lie very close to each other.
This is similar to the ordinary distillation method with the only
exception that a fractionating column is introduced in-between the distillation
flask and the condenser.
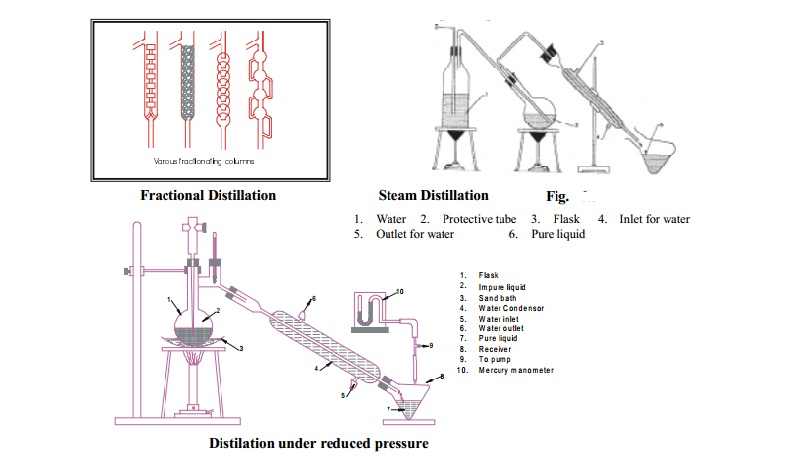
The process of separation of the components in a liquid mixture at their
respective boiling points in the form of vapours and the subsequent
condensation of those vapours is called fractional distillation.
The
fractionating columns used for the purpose are of different shapes.
Steam Distillation
In steam
distillation impure compounds are distilled in a current of steam. This method
is applicable to solids as well as liquids. For purification by steam
distillation, an impure compound must satisfy the following conditions:
1.
It should not decompose at the steam
temperature.
2. It should have a fairly high vapour pressure at 373 K.
3. It should be insoluble in water.
4. The impurities present should be non-volatile
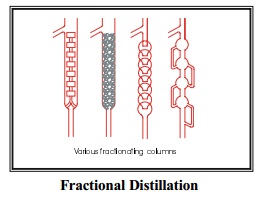
1. Water
2. Protective tube 3.
Flask4. Inlet for water
5. Outlet for water 6. Pure liquid
The apparatus used for steam distillation is shown in the figure (16.5).
The impure compound is taken in the round bottomed flask and a small quantity
of water is added. The flask is then heated gently. Now steam is bubbled
through the contents in the flask. The vapours of the compound mix up with
steam and escape into the condenser. The condensate thus obtained is a mixture
of water and the organic compound which can be separated.
Theory of
steam distillation
Let p1 represent the vapour pressure of water
and p2 the vapour pressure of the organic liquid. In steam distillation the
liquid boils at a temperature at which
p1 + p2 = Atmospheric Pressure
This temperature must be lower than the normal boiling point of water or
the organic liquid. The reason that p1 + p2 becomes equal to the atmospheric
pressure must earlier than p1 or p2 alone. Thus in steam distillation, the
impure liquid boils at a temperature which is lower than its normal boiling
point. Hence, steam distillation serves the same purpose as distillation under
reduced pressure. However, the former is cheaper but less useful than the
latter.
Distillation
under reduced pressure
This technique is used for purifying or
separating thermally unstable liquid compounds which decompose at their normal
boiling points.
Principle :
Lowering of pressure on the surface of a liquid lowers its boiling
point. As a result, a liquid can be boiled and distilled at a temperature much
below the normal boiling point without any decomposition.
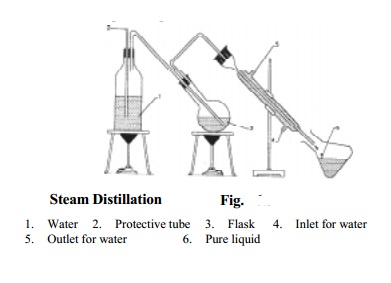
Procedure :
Distillation under reduced pressure or vacuum is carried out in a
specially designed glass apparatus as shown in (Fig.).
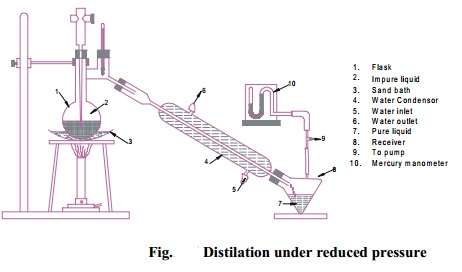
The receiver is attached to a vacuum pump to reduce pressure. The
pressure is measured with the help of a manometer.
Advantages
of distillation under reduced pressure
Distillation under reduced pressure has the following advantages:
i)
The compounds which decompose on heating to
their boiling points under normal pressure can be purified by distillation
under reduced pressure. This is because at a reduced pressure, a liquid would
boil at temperature much below its normal boiling point.
In distillation under reduced pressure, a liquid boils at temperature
well below the normal boiling point. So, the distillation under reduced
pressure is more fuel-economical.
Extraction
with solvents
This method is based on the fact that organic substances are more
soluble in organic solvents than in water.
The organic substance is extracted from its
aqueous solution adopting the following procedure.
1.
The aqueous solution containing organic
substance is shaken with a suitable organic solvent which dissolves the
substance but is immiscible with water. Two layers are formed; the organic
layer and aqueous layer.
2.
The solvent layer containing the organic substance
(organic layer) is separated using a `separating funnel'. The impurities remain
in the aqueous layer removed by distillation to obtain the organic substance.
The organic solvent is removed by distillation to obtain the organic
substance.
Related Topics