Chapter: Ophthalmology: The Eyelids
Hordeolum
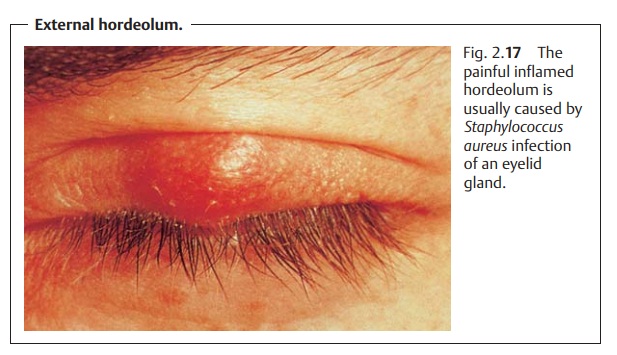
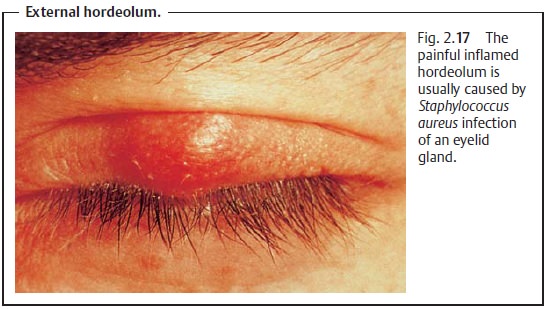
Hordeolum
Definition
A hordeolum
is the result of an acute bacterial infection of one or more eyelidglands.
Epidemiology and etiology:
Staphylococcus aureusis a common cause ofhordeolum. External hordeolum involves infection of the glands of Zeis or
Moll. Internal hordeolum arises from
infection of the meibomian glands. Hordeolum is often associated with diabetes,
gastrointestinal disorders, or acne.
Symptoms and diagnostic considerations:
Hordeolum presents aspainfulnodules with a central core of pus. External hordeolumappears on the
margin of the eyelid where the sweat glands are located (Fig. 2.17).Internal horde-olum of a sebaceous gland is usuallyonly revealed by everting the eyelidandusually
accompanied by a more severe reaction such as conjunctivitis or che-mosis of
the bulbar conjunctiva. Pseudoptosis and swelling of the preauricu-lar lymph
nodes may also occur.
Differential diagnosis:
Chalazion (tender to palpation) and
inflammation ofthe lacrimal glands (rarer and more painful).
Treatment:
Antibiotic ointments and application of dry heat (red heat lamp)will rapidly heal the lesion.
Clinical course and prognosis:
After eruption and drainage of the pus,
thesymptoms will rapidly disappear. The prognosis is good. An underlying
inter-nal disorder should be excluded in cases in which the disorder frequently
recurs.
Related Topics