Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Group 18 Noble Gases Or Inert Gases
GROUP
18 NOBLE GASES OR INERT GASES
Group 18 of the periodic table consists of helium, neon,
argon, krypton, xenon and radon. All these are gases under ordinary
conditions of temperature and pressure.
All of them (except Rn) are present in air in traces. Rn is obtained from radio active distintegration of radium.
On account of their very minute quantities in
atmosphere, they were named as rare gases. Due to their chemical inactivity
these were named as inert gases. A number of xenon compounds and two krypton fluorides
were prepared and thus they were named as
noble gases.
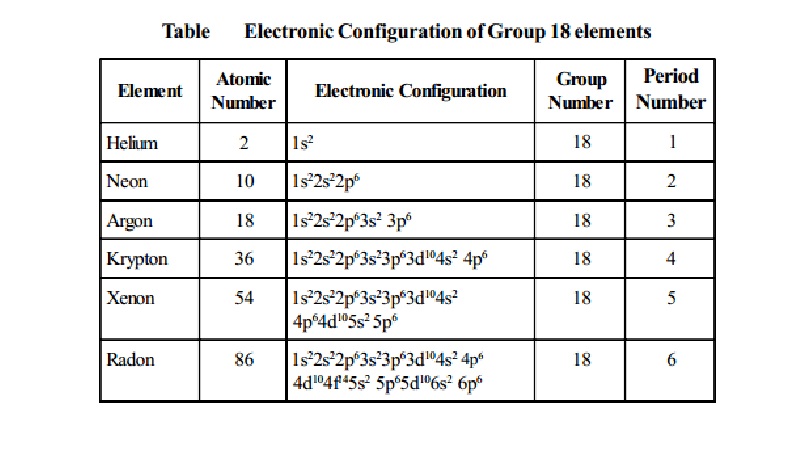
Electronic Configuration
All these elements possess ns2 np6 configuration. The differentiating electron enters
into p-sub shell and thus are included in p-block elements.
Table Electronic
Configuration of Group 18 elements
Helium -
Atomic Number : 2 Electronic
Configuration : 1s2 Group Number : 18 Periodic
Number : 1
Neon -
Atomic Number : 10 Electronic Configuration : 1s22s22p6 Group
Number : 18 Periodic Number
: 2
Argon -
Atomic Number : 18 Electronic Configuration : 1s22s22p63s2 Group Number : 18
Periodic Number : 3
Krypton -
Atomic Number : 36
Electronic Configuration : 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s2 4p6 Group Number : 18
Periodic Number : 4
Xenon -
Atomic Number : 54 Electronic Configuration : 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s2 4p64d105s2 5p6 Group Number : 18
Periodic Number : 5
Radon -
Atomic Number : 86 Electronic Configuration : 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s2 4p6 4d104f145s2 5p65d106s2 6p6 Group Number :
18 Periodic Number :
6
ISOLATION OF NOBLE GASES
The noble gases are isolated from air by removing oxygen
and nitrogen from air free from
carbon-di-oxide, water vapour, dust particles, etc., This can be accomplished by either chemical methods or physical
methods. In the chemical method, the
unwanted gases are removed by means of compound formation while in the physical method, these are removed by the
fractional evaporation of liquid air.
CHEMICAL METHOD
The first step in this method is to isolate the noble
gases mixed together, from the atmosphere
by passing repeated electric sparks in air so as to remove nitrogen and oxygen as nitrogen dioxide (N2 + 2O2 ® 2NO2 ). The second step
is to separate the various constituents from one another
taking advantage of the fact that they can
be adsorbed on activated charcoal at different temperatures.
Step 1 Removal of oxygen and nitrogen of the atmosphere
as Nitrogen
dioxide
Ramsay - Raleigh's method:- A mixture of air and oxygen is constantly admitted into a glass globe of about 50 litres capacity.
Two platinum electrodes are introduced and a discharge from a transformer of
about 6000 - 8000 volts is passed by the
action of which nitrogen and oxygen rapidly combine to form oxides of nitrogen. The oxides are dissolved out in a
solution of sodium hydroxide continuously
circulated through the flask.
N2+ O2 ® 2 NO
2 NO + O2 ® 2NO2
2NO2 + 2NaOH ® NaNO3 + NaNO2 + H2O
Oxygen if any is removed by introducing alkaline
pyrogallol in the globe.
The supply of air and electric discharge is shut after
some time and the remaining mixture of
noble gases is pumped out.
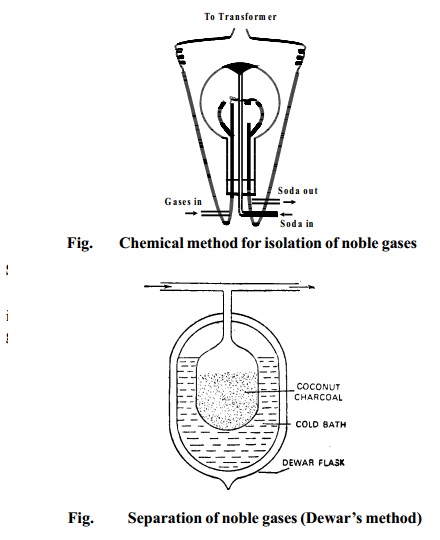
Step 2 Separation of noble gases (DEWAR'S METHOD)
The mixture of noble gases obtained by the above method
is separated into individual
constituents by the use of coconut charcoal which adsorbs different gases at different temperatures.
The mixture of noble gases is passed into a
double-walled bulb containing coconut
charcoal and placed in a low temperature bath at 173K. It is allowed to remain in contact with the charcoal for about half an
hour. At 173K, only argon,
krypton and xenon are adsorbed by the charcoal while
helium and neon remain unadsorbed. These
are pumped out and collected.
The mixture of helium and neon is kept in contact with
coconut charcoal at 93K which completely
adsorbs neon leaving free helium.
The charcoal at 173K containing argon, krypton and xenon
is placed in contact with another charcoal at the temperature of the
liquid air when argon diffuse into the other charcoal.
The temperature of the first charcoal (temp.173K) still
containing krypton and xenon is
raised to 183K when krypton is set free while xenon remain adsorbed in the charcoal. When it is heated, xenon is recovered.
XENON FLUORIDE COMPOUNDS
Xenon forms three binary Fluorides XeF2, XeF4, and XeF6 by the direct union of elements under appropriate experimental conditions.
Xe+F2 --- 673K
-- > XeF2
Xe + 2 F2 --- 673K
-- > XeF4
Xe+ 3 F2 --- 573K
-- > XeF6
PROPERTIES:
Xe F2,
Xe F4 and Xe F6 are colourless crystalline solids subliming readily
at 298K. They are powerful fluorinating agents. They are readily hydrolysed by even traces of water. For example.
2Xe F2 + 2 H2O ® 2Xe + 4HF + O2
Structure:
The structure of the three xenon fluorides can be deduced from VSEPR theory. XeF2 and XeF4 have the linear and square planar structure respectively. XeF6, has 7 electron pairs (6 bonding and
one lone pair) and thus
have a distorted octahedral structure in the gas phase.
USES OF NOBLE GAS
(A) HELIUM
1. Because of its lightness and non-inflammability
helium is used to filling balloons for
meteorological observations.
2. Because of its lightness it is used in inflating
aeroplane tyres.
3. Helium oxygen mixture is used by deep-sea divers in
preference to nitrogen oxygen mixtures. It
is much less soluble in blood than N2. This prevents "bends" which is the pain caused by formation of
nitrogen bubbles in blood veins when a
diver comes to the surface.
4. A mixture of oxygen and helium is used in the
treatment of asthma.
5. Liquid helium (b.pt 4.2K) is used as cryogenic agent
for carrying out various experiments at low
temperatures.
6. It is used to produce and sustain powerful super
conducting magnets which form essential
part of modern NMR Spectrometers and Magnetic Resonance Imaging system (MRI) for clinical diagnosis.
(B) NEON
1. Neon is used in discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs
for advertisement display purposes.
2. Mixed with helium it is used to protect electrical
instruments from high Voltages.
3. It is also used in beacon lights for safety of air
navigation as the light possesses fog
and storm-penetrating power.
4. Neon light is used in botanical gardens as it
stimulates growth and helps the formation
of chlorophyll.
(C) ARGON
1. Mixed with 26% percent nitrogen it is used in gas
filled electric lamps. 2. It is also used
in radio valves and tubes.
(D) KRYPTON AND XENON
1. Krypton and xenon are also used in filling
incandescent metal filament electric
bulbs.
2. They are also used to a small extent in discharge
tubes.
(E)
RADON
1. It is used in radioactive research and in radiotherapy
for treatment of cancer.
Related Topics