Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
General properties of Lanthanides
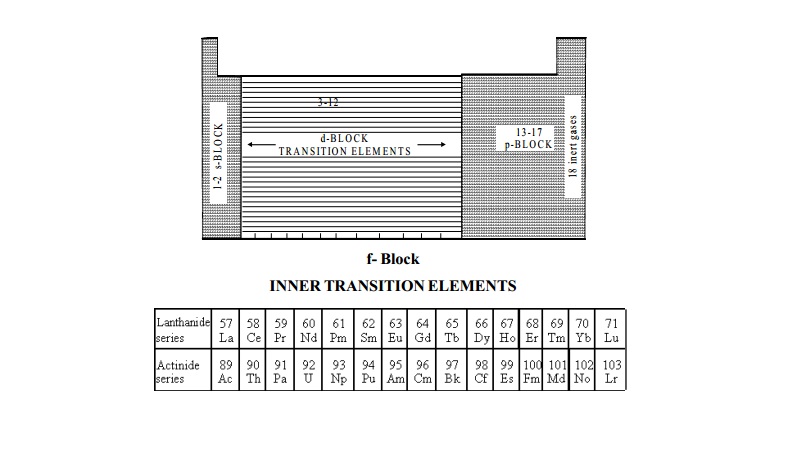
The position of f block elements in the periodic table, is explained
above.
The elements in which the extra electron enters ( n- 2 )f
orbitals are called f- block elements.
These elements are also called as inner transition elements because they form a transition series within the
transition elements. The f-block elements
are also known as rare earth elements. These are divided into two series.
i) The Lanthanide series (4f-block elements)
ii) The Actinide series (5f- block elements )
The
Lanthanide Series
The Lanthanide series include fifteen elements i.e.
lanthanum (57 La) to lutetium
(71 Lu). Lanthanum and Lutetium have no partly
filled 4f- subshell but have electrons in 5d-subshell.
Thus these elements should not be included in this series. However, all these elements closely resemble
lanthanum and hence are considered
together.
General properties of Lanthanides
1. Electronic configuration
The electronic configuration of Lanthanides are listed
in the table . The fourteen electrons
are filled in Ce to Lu with configuration [54 Xe ]4f1-14 5d1 6s2
2. Oxidation states
The common oxidation state exhibited by all the
lanthanides is +3 (Ln3+) in aqueous solutions
and in their solid compounds. Some elements exhibit +2 and +4 states as
uncommon oxidation states.
La - +3
Ce - +3, +4,
+2
Pr - +3, +4
Nd - +3, +4,
+2
3. Radii of tripositive lanthanide ions
The size of M3+ ions
decreases as we move through the lanthanides from lanthanum to lutetium. This steady decrease in ionic
radii of M3+ cations in the lanthanide series is called Lanthanide contraction.
Cause of lanthanide contraction
The lanthanide contraction is due to the imperfect
shielding of one 4f electron by another in the same sub shell. As we move along the
lanthanide series, the nuclear charge and
the number of 4f electrons increase by one unit at each step. However, due to imperfect shielding, the effective
nuclear charge increases causing a
contraction in electron cloud of 4f-subshell.
Consequences of lanthanide contraction
Basicity of ions
i) Due to lanthanide contraction, the size of Ln3+ ions decreases regularly with increase in atomic number. According to Fajan's rule,
decrease in size of Ln3+ ions increase the
covalent character and decreases the basic character between Ln3+ and OH- ion in Ln(OH)3. Since the order of size of Ln3+ ions
are
La3+> Ce3+ ............... >Lu3+
ii) There is regular decrease in their ionic radii.
iii) Regular decrease in their tendency to act as
reducing agent, with increase in atomic
number.
iv) Due to lanthanide contraction, second and third rows
of d-block transistion elements are quite close in properties.
v) Due to lanthanide contraction, these elements occur
together in natural minerals and are
difficult to separate.
Related Topics